方案详情文
智能文字提取功能测试中
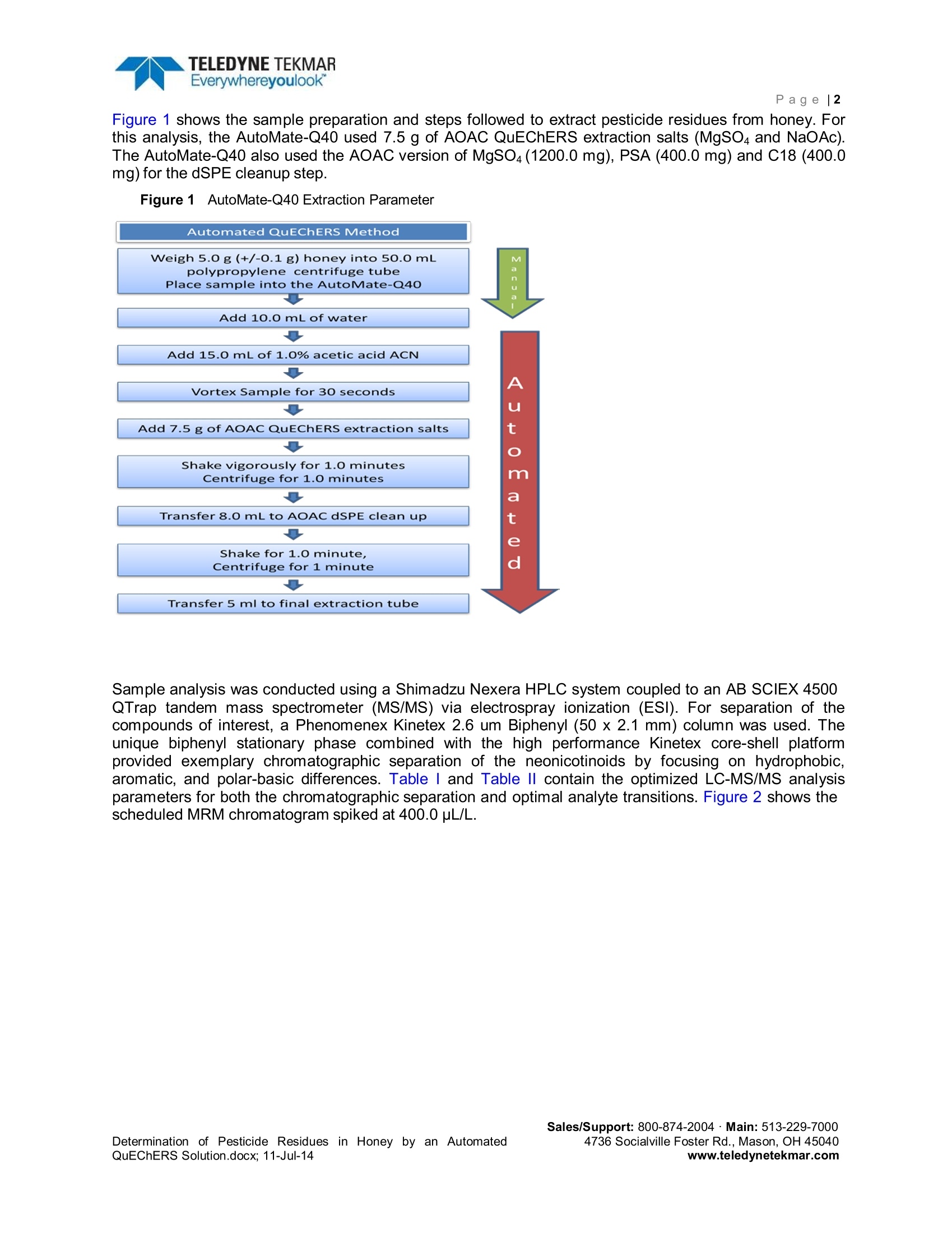
Pa ge |1 TELEDYNE TEKMAREverywhereyoulookPage |2 Determination of Pesticide Residues inHoney, by an Automated QuEChERSSolution Application Note Abstract The QuEChERS (Quick-Easy-Cheap-Effective-Rugged-Safe) sample extraction method was developedfor the determination of pesticide residues in agricultural commodities. While originally QuEChERS hadbeen developed for plant matrices, the technique has since been adapted for many additional matricessuch as honey, as well as several other applications. With the rise in popularity of this extraction technique and due to the reliability of its multiresidue methods,it has driven the need for automation of the QuEChERS extraction to increase productivity andthroughput. The AutoMate-Q40 streamlines the QuEChERS method by adding Acetonitrile (ACN) andbuffering salts, shaking, mixing, centrifugating the sample, transferring to a dispersive solid phaseextraction (d-SPE) tube, measuring and delivering the extract. The aim of this project is to validate the extraction performance of the AutoMate-Q40 by monitoringneonicotinoids and other pesticides in honey. The target residuesswere determined by liquidchromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). Colony CollapseDisorder: (CCD))is anoccurrence in which worker bees from thehoney bee colony unexpectedly disappears.During the winter of 2006-2007, beekeepersbegan to report high losses of 30-90% of theirhives. With these high losses many hivescannot sustain themselves without the workerbees. Many regulatory agencies have theoriesabout: the causeecofthe CCD, includingpesticidepoisoning through exposuretopesticides applied to crops or for in-hive insector mite control. insecticides that affect the central nervous system of insects, resulting in paralysis and death. The European Commission has restricted the use ofclothianidin, imidacloprid and thiamethoxam, but the US has not adopted any such restriction. The QuEChERS extraction method is the most applicable method, since it offers good selectivity, andsensitivity when extracting pesticide residues in honey. The aim of this project is to evaluate theperformance and versatility of the AutoMate-Q40 for the extraction of neonicotinoids and other pesticidesin honey. Liquid Chromatography coupled to triple-quadrupole mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) wasemployed for the detection of pesticides in honey. Quantification was based on matrix-matchedcalibration curves. Experimental Instrument Conditions Honey was purchased from a local market in Ohio. The samples were prepared according to theprocedure described in the “AOAC Official Method 2007.01 Pesticide Residues in Foods by AcetonitrileExtraction and Partitioning with Magnesium Sulfate".The sample was stored at room temperature untilextraction. Figure 1 shows the sample preparation and steps followed to extract pesticide residues from honey. Forthis analysis, the AutoMate-Q40 used 7.5 g of AOAC QuEChERS extraction salts (MgSO4 and NaOAc).The AutoMate-Q40 also used the AOAC version of MgSO4(1200.0 mg), PSA (400.0 mg) and C18 (400.0mg) for the dSPE cleanup step. Figure 11AutoMate-Q40 Extraction Parameter Sample analysis was conducted using a Shimadzu Nexera HPLC system coupled to an AB SCIEX 4500QTrap tandem mass spectrometer (MS/MS) via electrospray ionization (ESl). For separation of thecompounds of interest, a Phenomenex Kinetex 2.6 um Biphenyl (50 x 2.1 mm) column was used. Theunique biphenyl stationary phase combined with the high performance Kinetex core-shell platformprovided exemplary chromatographic separation of the neonicotinoids by focusing on hydrophobic,aromatic, and polar-basic differences. TableI and Table Il contain the optimized LC-MS/MS analysisparameters for both the chromatographic separation and optimal analyte transitions. Figure 2 shows thescheduled MRM chromatogram spiked at 400.0 pL/L. Tablel LC-MS/MS SRM Transitions and Parameters for AB SCIEX4500 QTrap Curtain Gas (CUR) 20 lon Spray Voltage (IS) 4000 Temperature (TEM) 450 Collision Gas (CAD) High Analyte Transitions Compounds RT(min) Precursor lon (m/z) Quantization product lon(m/z) DP(V) CE(V) CXP(V) Acetamiprid 3.03 222.93 126.00 41 29 10 Azoxystrobin 6.60 404.04 372.10 66 23 12 Chlorpyrifos 8.40 349.86 197.70 56 23 14 Clothianidin 2.20 249.91 168.80 21 17 20 Coumaphos 7.85 362.93 226.80 91 33 24 Imidacloprid 2.79 255.95 208.90 46 17 30 Nitenpyram 1.65 270.99 224.90 35 15 14 Thiamethoxam 2.15 291.94 210.90 36 15 16 Column Kinetex 2.6 um Biphenyl Dimensions 50 X 2.1 mm Mobile Phase A:0.1% Formic Acid in Water B:0.1%Formic Acid in Acetonitrile Gradient Time %B 0.10 5% 10.0 70% 12.0 70% 12.1 5% 14.1 Stop Flow Rate (mL/min) 0.5 Column Temperature (C) 40 Figure 2400.0 ng/g Spike in Honey Experimental Results Automating the QuEChERS extraction enables a fast, easy, reliable and more reproducible extraction.The AutoMate-Q40 offers significant labor savings, while improving the reproducibility and consistencybetween samples. A precision and accuracy study was performed using the AutoMate-Q40. A 2.0 ug/mL stock pesticidesolution was used to fortify the honey samples. Check standards were fortified at 10.0 and 30.0 pg/Lusing the AutoMate-Q40's ability to make standard additions. This translates to 30.0 and 90.0 ng/g forhoney. These QC samples were quantitated against their corresponding matrix matched calibrationCurve. The analysis was performed in two parts. The AutoMate-Q40, can extract the honey samples with andwithout a dSPE cleanup. Two sets of data will be presented in this precision and accuracy study. Figure 3and Figure 4 show data using the AutoMate-Q40 to extract unclean honey samples. Figure 5 and Figure6 show data that used the dSPE cleanup option on the AutoMate-Q40. Figure 3 Average Recovery for Unclean Honey Samples Figure 4 Average %RSD for Unclean Honey Samples Sales/Support: 800-874-2004· Main:513-229-7000 www.teledynetekmar.com Figure 5 Average% Recovery for Clean Honey Samples Figure 66 Average %RSD for Clean Honey Samples Figures 4-6 show that data derived from AutoMate-Q40 extracted pesticide residues in honey exhibitedrecoveries ranging from 77.55% to 107.25% for all spiked QC samples. The AutoMate-Q40 also demonstrated great precision; ranging from 1.25% to 13.11%RSD for the spiked QC samples. Thesespike recoveries fall within the recommended mean values for the Document N°Sanco/12495/2011. Thisdocument states that the mean recoveries must fall between 70% to 120% with a RSD <20%. Conclusion This study demonstrates the Automate-Q40's ability to successfully process honey samples for pesticideresidue by the QuEChERS extraction method. By automating the liquid handing, addition of salt/buffers,sample mixing, pipetting, and liquid level sensing using the patent pending VialVisionTM, the AutoMate-Q40 frees the scientist from a labor-intensive extraction method and exposure to unhealthy chemicals.The extraction process is faster, more reliable, and easier. This enables time and labor savings, whileimproving consistency and reproducibility of the extraction. As shown above in Figures 4-6 the combinedpesticide spikes recoveries of 93.74%, with an average RSD of 5.92% exceed the requirement outlined inThe Document N° Sanco/12495/2011.These numbers indicate superb precision and accuracy thusvalidating the performance of the AutoMate-Q40 to adequately perform the QuEChERS pesticideextraction method for honey. References 1p://www.epa.gov/pesti httcides/about/intheworks/honeybee.htm2 Galeano K.; Scordino M.; Sabatino L.; UHPLC/MS-MS Analysis of Six Neonicotinoids inHoney by Modified QuEChERS: Method Development, Validation, and UncertaintyMeasurement 3. AOCA Official Method 2007.07 Pesticide Residues in Food by Acetonitrile Extraction andPartitioning with Magnesium Sulfate. Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry andLiquid Chromatography/Tandem Mass Spectrometry, First Action 2007 4. Method Validation and Quality Control Procedure for Pesticide Residues Analysis in Foodand Feed (DocumentN° SANCO/12495/2011) Acknowledgements A special thanks to Phenomenex for supplying the new Phenomenex Kinetex 2.6 um Biphenyl (50x2.1mm) column along with the optimum chromatographic separation parameters. Without their help andknowledge this project wouldn't have been possible. Sales/Support: Main: Socialville Foster Rd.,Mason, OH ww.teledynetekmar.comDetermination of Pesticide Residues in Honey by an AutomatedQuEChERS Solution.docx; Jul-
关闭-
1/7

-
2/7
还剩5页未读,是否继续阅读?
继续免费阅读全文产品配置单
仪真分析仪器有限公司为您提供《使用AutoMate-Q40检测蜂蜜中的农残》,该方案主要用于蜂产品中农药残留检测,参考标准《暂无》,《使用AutoMate-Q40检测蜂蜜中的农残》用到的仪器有null。
我要纠错
相关方案


 咨询
咨询
