方案详情文
智能文字提取功能测试中
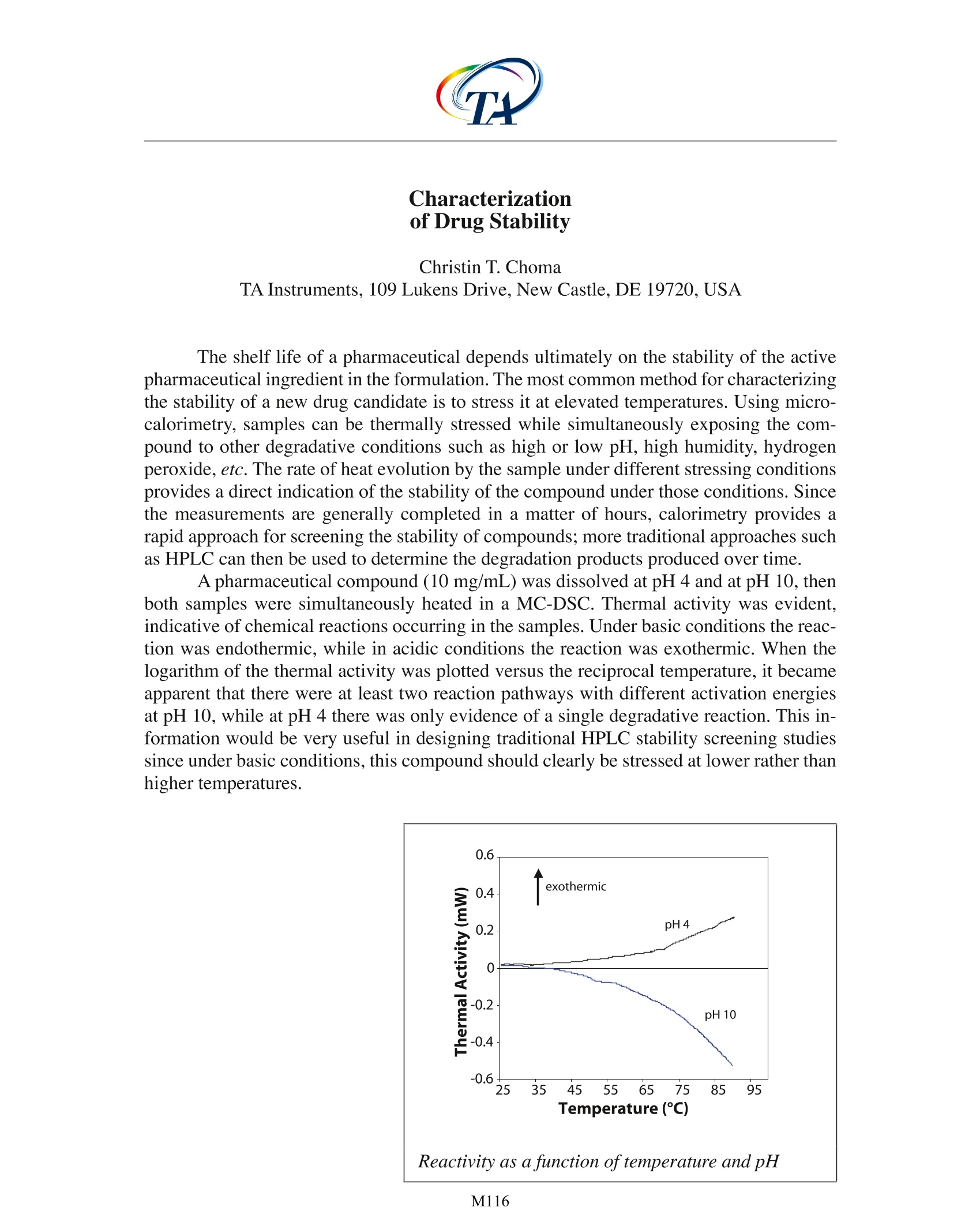
M116 Characterizationof Drug Stability Christin T. Choma TA Instruments, 109Lukens Drive, New Castle, DE 19720, USA The shelf life of a pharmaceutical depends ultimately on the stability of the activepharmaceutical ingredient in the formulation. The most common method for characterizingthe stability of a new drug candidate is to stress it at elevated temperatures. Using micro-calorimetry, samples can be thermally stressed while simultaneously exposing the com-pound to other degradative conditions such as high or low pH, high humidity, hydrogenperoxide, etc. The rate of heat evolution by the sample under different stressing conditionsprovides a direct indication of the stability of the compound under those conditions. Sincethe measurements are generally completed in a matter of hours, calorimetry provides arapid approach for screening the stability of compounds; more traditional approaches suchas HPLC can then be used to determine the degradation products produced over time. A pharmaceutical compound (10 mg/mL) was dissolved at pH 4 and at pH 10, thenboth samples were simultaneously heated in a MC-DSC. Thermal activity was evident,indicative of chemical reactions occurring in the samples. Under basic conditions the reac-tion was endothermic, while in acidic conditions the reaction was exothermic. When thelogarithm of the thermal activity was plotted versus the reciprocal temperature, it becameapparent that there were at least two reaction pathways with different activation energiesat pH 10, while at pH 4 there was only evidence of a single degradative reaction. This in-formation would be very useful in designing traditional HPLC stability screening studiessince under basic conditions, this compound should clearly be stressed at lower rather thanhigher temperatures. The shelf life of a pharmaceutical depends ultimately on the stability of the active pharmaceutical ingredient in the formulation. The most common method for characterizing the stability of a new drug candidate is to stress it at elevated temperatures. Using microcalorimetry, samples can be thermally stressed while simultaneously exposing the compound to other degradative conditions such as high or low pH, high humidity, hydrogen peroxide, etc. The rate of heat evolution by the sample under different stressing conditions provides a direct indication of the stability of the compound under those conditions. Since the measurements are generally completed in a matter of hours, calorimetry provides a rapid approach for screening the stability of compounds; more traditional approaches such as HPLC can then be used to determine the degradation products produced over time.
关闭-
1/1
产品配置单
TA仪器为您提供《药物中稳定性检测方案(差示扫描量热)》,该方案主要用于药物中稳定性检测,参考标准《暂无》,《药物中稳定性检测方案(差示扫描量热)》用到的仪器有TA仪器+差示扫描量热仪+NANO DSC。
我要纠错
推荐专场
差示扫描量热仪(DSC/DTA)
更多相关方案






 咨询
咨询


