锤子
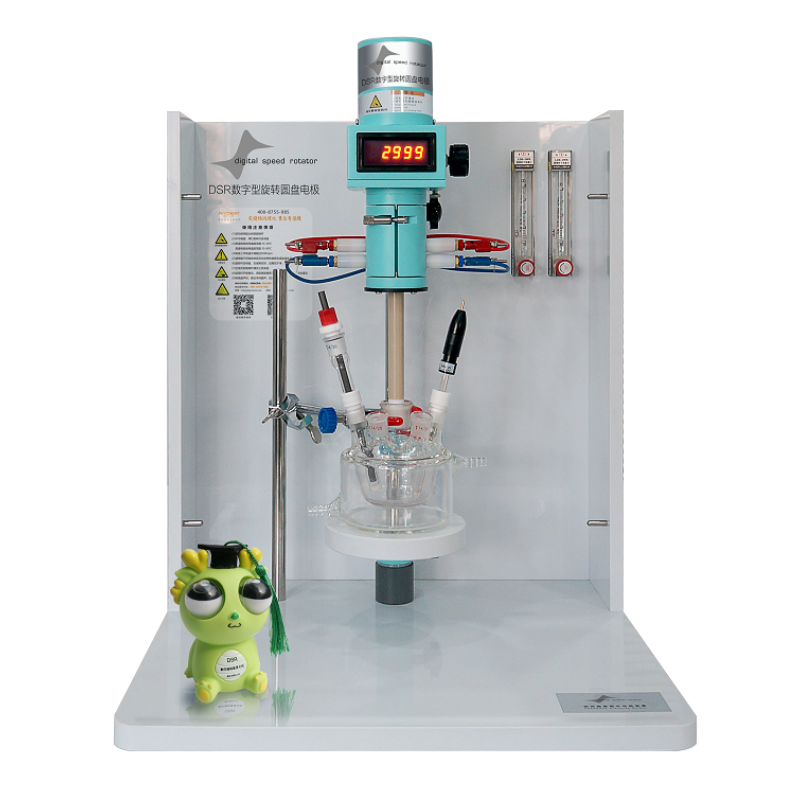
X65管道钢在油/水乳液中的电化学腐蚀
- 类别:分析方法/应用文章
- 上传人:理化香港有限公司
- 上传时间:2012/7/17 9:36:40
- 文件大小:504K
- 下载次数:8
-
消耗积分 : 免积分
简介:
The electrochemical corrosion behavior of X65 pipeline steel in the simulated oil/water emulsion was investigated under controlled hydrodynamic and electrochemical conditions by rotating disk electrode technique. Results demonstrated that mass-transfer of oxygen plays a significant role in the cathodic process of steel in both oil-free and oil-containing solutions. Electrode rotation accelerates the oxygen diffusion and thus the cathodic reduction. The higher limiting diffusive current density measured in oil-containing solution is due to the elevated solubility of oxygen in oil/water emulsion. The anodic current density decreases with the increase of electrode rotating speed, which is attributed to the accelerated oxygen diffusion and reduction, enhancing the steel oxidation. Addition of oil decreases the anodic dissolution of steel due to the formation of a layer of oily phase on steel surface, increasing the reaction activation energy. The steel electrode becomes more active at the elevated temperature, indicating that the enhanced formation of oxide scale is not sufficiently enough to offset the effect resulting from the enhanced anodic dissolution reaction kinetics. The corrosion reaction mechanism is changed upon oil addition, and the interfacial reaction is activation-controlled, rather than mass-transfer controlled. When sand particles are added in oil/water emulsion, there is a significant increase of corrosion of the steel. The presence of sands in the flowing slurry would impact and damage the oxide film and oily film formed on the steel surface, exposing the bare steel to the corrosive solution.
打开失败或需在电脑查看,请在电脑上的资料中心栏目,点击"我的下载"。建议使用手机自带浏览器。
相关产品更多>>
下载该资料的还下载了
推荐学习更多>>
- 注意:
- 1、下载文件需消耗流量,最好在wifi的环境中下载,如果使用3G、4G下载,请注意文件大小。
- 2、下载的文件一般是pdf、word文件,下载后如不能直接浏览,可到应用商店中下载相应的阅读器APP。
- 3、下载的文件如需解压缩,如果手机没有安装解压缩软件,可到应用商店中下载相应的解压缩APP。