Correlation of Physical and Structural利多卡因/丙胺卡因外用药
Abstract
摘要
Background and Purpose:In the past few years a collective weight of evidence approach has been recommended to demonstrate bioequivalence (BE) for several topical dermatological drug products.An essential component of this approach is a comprehensive characterization of the physical and structural (Q3) properties of complex topical semisolid dosage forms. The purpose of this study is to determine if comparative Q3 characterization of topical lidocaine and prilocaine products maybe used to predict the comparative product performance, which was evaluated by comparing cutaneous pharmacokinetics (PK) of lidocaine and prilocaine in vitro and in vivo.
背景和目的:在过去的几年中,已经推荐了一种集体证据权重法来证明几种局部皮肤病药物的生物等效性。该方法的一个重要组成部分是对复杂局部半固体剂型的物理和结构(Q3)特性的全面表征。本研究的目的是通过比较利多卡因/丙胺卡因在体外和体内的皮肤药代动力学(PK),确定是否可以利用外用利多卡因和丙胺卡因产品的比较Q3特性来预测产品的比较性能。
Methodology: The products evaluated in this study were 1) the reference product, EMLA® (lidocaine; prilocaine) cream, 2.5%;2.5% 2) a generic version of EMLA® cream, and 3) Oraqix® (lidocaine; prilocaine) gel, 2.5%;2.5% as a different formulation with the same strength of lidocaine and prilocaine. The comparative Q3 properties of these three drug products were assessed. The cutaneous PK of lidocaine and prilocaine from the gel and cream products were compared by an in vitro permeation test (IVPT). The BE of the generic cream and of Oraqix® gel to EMLA® cream was evaluated based upon cutaneous PK endpoints for both lidocaine and prilocaine. The dermal bioavailability of EMLA® and Oraqix® was also compared in an in vivo pilot study using dermal open flow microperfusion (dOFM) in 6 healthy subjects.
方法学:本研究评价的产品为:1)参比产品EMLA®乳膏(2.5%利多卡因/2.5%丙胺卡因),2)EMLA®乳膏的仿制药,3)Oraqix®凝胶(2.5%利多卡因/2.5%丙胺卡因)。比较了这三种药品的Q3性质。通过体外渗透试验(IVPT)比较利多卡因/丙胺卡因凝胶和乳膏产品的皮肤PK。基于利多卡因/丙胺卡因的皮肤PK终点,评估了Oraqix®凝胶与EMLA®乳膏的生物等效性BE。EMLA®和Oraqix®的皮肤生物利用度也在6名健康受试者的皮肤开放流微灌注(dOFM)体内试点研究中进行了比较
Results: The Q3 properties of the reference and generic lidocaine/prilocaine topical creams were similar to each other, while Oraqix® gel had a lower pH, a higher evaporative rate, a lower yield stress, and an absence of globules compared to the cream products. The results of IVPT study demonstrated that the cutaneous PK of lidocaine and prilocaine was comparable between the reference and generic creams. By contrast, the maximum flux (Jmax) and area under the curve (AUC) of both lidocaine and prilocaine were lower for Oraqix® gel compared to EMLA® cream and the gel and cream products were not found to be bioequivalent. The results of an in vivo cutaneous PK study using dOFM in healthy subjects were in agreement with the in vitro (IVPT) results.
结果:参比型和仿制型利多卡因/丙胺卡因外用乳膏的Q3性质相似,而Oraqix®凝胶与乳膏产品相比具有较低的pH值、较高的蒸发速率、较低的屈服应力,与凝胶产品相比乳膏没有球状物的特点。IVPT研究结果表明,利多卡因/丙胺卡因的皮肤PK在参比乳膏和仿制乳膏之间具有相关性。相比之下,Oraqix®凝胶与EMLA®乳膏相比,利多卡因/丙胺卡因的最大通量(Jmax)和曲线下面积(AUC)都较低,凝胶和乳膏产品没有生物等效性。使用dOFM对健康受试者进行的体内皮肤PK研究结果与体外(IVPT)结果一致。
Conclusion:These results demonstrate the correlation between the Q3 similarity or difference of three lidocaine prilocaine topical products used for comparison and the similarity or difference in their product performance (cutaneous PK), both in vitro (IVPT) and in vivo (dOFM). The similarity of Q3 characteristics between the reference and generic creams accurately correlated with and was predictive of comparable bioavailability (and bioequivalence) for both lidocaine and prilocaine, whereas the difference in Q3 characteristics between the reference cream and the gel accurately correlated with and was predictive of differences in bioavailability.
结论:本研究结果表明,三种利多卡因/丙胺卡因外用产品的Q3相似性或差异性与其产品在体外(IVPT)和体内(dOFM)性能的相似性或差异性之间存在相关性。参比制剂乳膏和仿制药乳膏Q3特征的相似性与利多卡因丙胺卡因的可比生物利用度(和生物等效性)准确相关并可预测,而参比制剂乳膏和凝胶之间Q3特征的差异与生物利用度的差异准确相关并可预测。
Introduction
引言
In the past few years, a collective weight of evidence approach has been recommended to support a demonstration of bioequivalence (BE) for several topical drug products. An essential component of this approach is a comprehensive characterization of the physico-structural (Q3) properties of complex topical semisolid dosage forms.
在过去的几年中,已经推荐了一种集体证据权重方法来支持几种外用药物产品的生物等效性(BE)论证。该方法的一个重要组成部分是对复杂局部半固体剂型的物理结构(Q3)特性的全面表征。
The purpose of this study was to determine if comparative Q3 characterization of topical lidocaine and prilocaine products maybe used to predict the comparative product performance, which was evaluated by comparing the cutaneous pharmacokinetics (PK) of lidocaine and prilocaine in vitro and in vivo. The specific objectives of this study include:
本研究的目的是通过比较利多卡因和丙胺卡因在体外和体内的皮肤药代动力学(PK),确定是否可以用外用利多卡因/丙胺卡因产品的比较Q3特性来预测产品的比较性能。本研究的具体目标包括:
•Characterize and compare the Q3 properties of cream and gel products, each containing both lidocaine and prilocaine
•表征并比较含有利多卡因/丙胺卡因的乳膏和凝胶产品的Q3特性
•Compare the performance of lidocaine/prilocaine cream and gel products using in vitro and in vivo cutaneous PK studies
•通过体外和体内皮肤PK研究比较利多卡因/丙胺卡因乳膏和凝胶产品的性能
Materials and Methods
材料与方法
The products evaluate in this study were 1) the reference product, EMLA® (lidocaine; prilocaine) topical cream, 2.5%;2.5% 2) a generic version of EMLA® cream, and 3) Oraqix® (lidocaine; prilocaine) dental gel, 2.5%;2.5% as a different formulation with the same strength of lidocaine and prilocaine. The comparative Q3 assessment of these three drug products included microscopic examination, pH, evaporative rate, and rheological behavior. The cutaneous PK of lidocaine and prilocaine from the gel and cream products were compared by an in vitro permeation test (IVPT) with a replicate study design (six skin donors with six replicates per donor) using heat separated human epidermis and a flow through diffusion system. The BE of the generic cream and of Oraqix® gel to EMLA® cream was evaluated based upon cutaneous PK endpoints for both lidocaine and prilocaine, using a reference scaled average BE (SABE) analysis and evaluation of the 90% confidence interval (CI). The dermal bioavailability of EMLA® and Oraqix® was also compared in an in vivo pilot study using dermal open flow microperfusion (dOFM) in 6 healthy subjects. The dose of all products used in the IVPT and dOFM studies was 10 mg product/cm2 .
本研究评价的产品有:
1)参比产品EMLA®乳膏(利多卡因/丙胺卡因);2) EMLA®乳膏的仿制药,以及3)Oraqix®凝胶(2.5%利多卡因/2.5%丙胺卡因)。这三种药品的Q3比较评价包括显微镜检查、PH值、蒸发速率和流变行为。采用体外渗透试验(IVPT),采用重复研究设计(6个皮肤供体,每个供体6个重复),利用热分离的人体表皮和流动扩散系统,比较利多卡因和丙胺卡因凝胶和乳膏产品的皮肤PK。使用参考标度平均BE (SABE)分析和90%置信区间(CI)评估,基于利多卡因/丙胺卡因的皮肤PK终点,对Oraqix®凝胶与EMLA®乳膏进行BE评估。EMLA®和Oraqix®皮肤生物利用度也在6名健康受试者的皮肤开放流微灌注(dOFM)体内试点研究中进行了比较。在IVPT和dOFM研究中使用的所有产品的剂量为10mg/cm2。
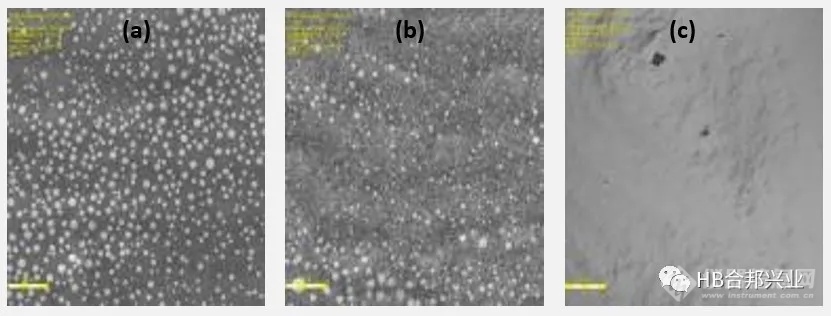
Figure 1. Light microscopy images: (a) EMLA® cream and (b) generic lidocaine and prilocaine cream showing globules, vs. a homogenous globule-free matrix in the (c) Oraqix® gel. The scale bars are 20 µm in images a and b, and 100 µm in image c.
图1所示.显微镜图像:(a) EMLA®乳膏和(b)仿制药利多卡因和丙胺卡因乳膏显示球状,(c) Oraqix®凝胶中均匀无球状基质。图a和图b的比例尺为20µm,图c的比例尺为100µm。
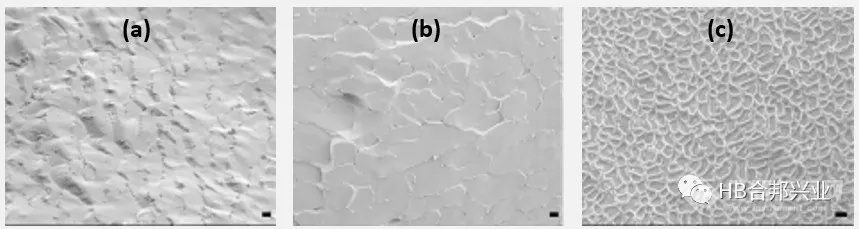
Figure2.Cryo-SEM images at 3000X magnification depicting the internal microstructures of (a) EMLA® cream (b) generic lidocaine prilocaine cream and (c) Oraqix® gel. Scale bar - 1µm
图2. 3000倍放大的冷冻扫描电镜图像描绘了(a) EMLA®乳膏(b)通用利因双卡因乳膏和(c) Oraqix®凝胶的内部微观结构。比例尺- 1µm
Results and Discussion
结果与讨论
Quality tests and Q3 propertie
质量测试和Q3属性
The Q3 properties of the reference and generic lidocaine and prilocaine topical creams were similar to each other and different from those of Oraqix® gel:
•The average pH values measured for the reference lidocaine/prilocaine cream, the generic lidocaine/prilocaine cream, and Oraqix®gel were 9.10, 8.90 (i.e., 9.0 ± 0.1) and 7.65, respectively.
•The microscopic images of the cream products showed the presence of globules with a diameter of 1-3 µm, while the Oraqix® gel appeared to be a homogenous globule-free system. The cream products also showed a different microstructure than the gel product under cryo-scanning electron microscopy (cryo-SEM) (Figure 2).
与Oraqix®凝胶相比,参比型和仿制药利多卡因/丙胺卡因外用乳膏的Q3性质相似,但与Oraqix®凝胶的Q3性质不同:
•参比型利多卡因/丙胺卡因乳膏、仿制型利多卡因/丙胺卡因乳膏和Oraqix®凝胶的平均pH值分别为9.10、8.90(即9.0±0.1)和7.65。
•凝胶产品的显微图像显示直径为1-3 μ m的小球的存在,而Oraqix®凝胶似乎是一个均匀的无小球系统。在冷冻扫描电镜(cryo-SEM)下,乳霜产品也显示出与凝胶产品不同的微观结构(图2)。
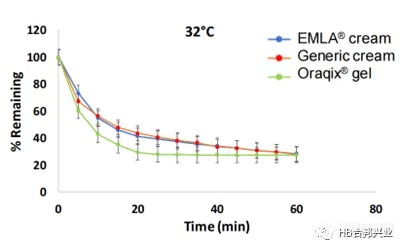
Figure 3.Rate of evaporation of volatile components from lidocaine; prilocaine topical cream and gel products measured gravimetrically at 32ºC. Data are expressed as Mean ± SD (n=3).
图3.在32℃利多卡因/丙胺卡因挥发性成分的蒸发速率;重量法测量,数据以Mean±SD (n=3)表示。
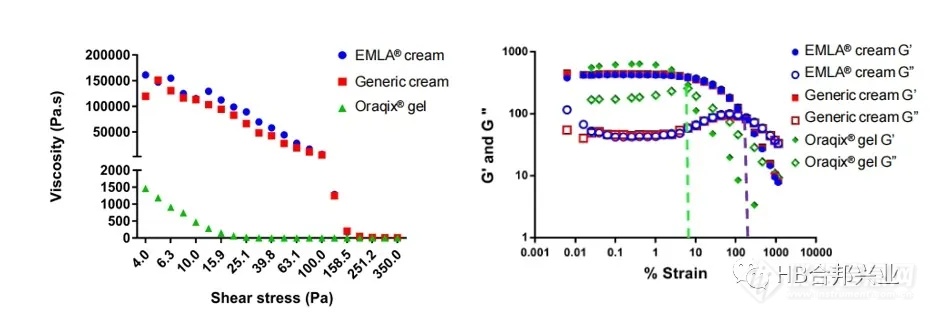
Figure 4. Left: Viscosity as a function of shear stress for lidocaine and prilocaine cream and gel products.Right: Strain sweep for all three products. Closed symbols (G’) represent the storage modulus and the open symbols represent loss modulus (G”). The yield stress was determined to be 110 for the cream products and 11 for Oraqix®gel.
图4.左图:利多卡因/丙胺卡因乳膏和凝胶产品的粘性随剪切应力的变化。右图:对所有三种产品进行应变扫描。闭合符号(G’)表示存储模量,开放符号(G”)表示损耗模量。凝胶的屈服应力为110,Oraqix®凝胶的屈服应力为11。
Performance tests性能测试
In vitro cutaneous PK study using IVPT
1.体外应用IVPT研究皮肤PK
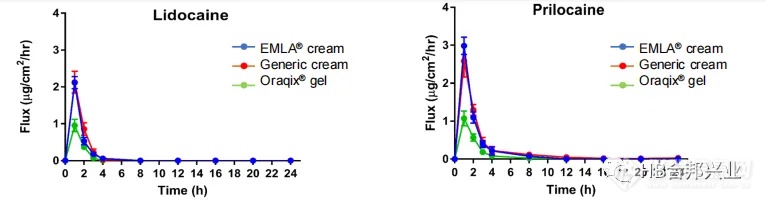
Figure 5. Cutaneous PK (flux profile) of lidocaine and prilocaine in vitro
from topical applications of the same dose of EMLA® cream, the generic
cream, and Oraqix®gel.Data are shown as Mean ± SEM from 6 donors
and 6 replicates.
图5.相同剂量的EMLA®乳膏、仿制药乳膏和Oraqix®凝胶对体外利多卡因/丙罗卡因皮肤PK(通量Jmax)的影响。数据显示为来自6个供体和6个重复的平均值±SEM
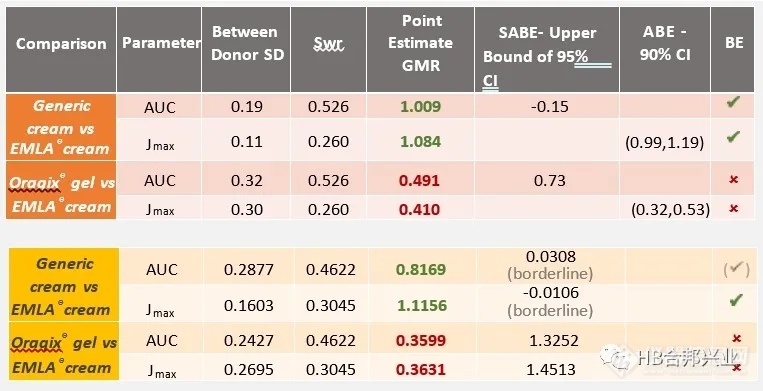
Table 1. BE analysis results for lidocaine (in orange); prilocaine (in yellow) based on PK endpoints of area under the curve (AUC ) and maximum flux (Jmax) and within donor variability associated with EMLA® cream (Swr)
表1.利多卡因BE分析结果(橙色);基于曲线下面积(AUC)和最大通量(Jmax)的PK终点以及与EMLA®乳膏(Swr)相关的供体变异性,丙胺卡因(黄色)
2.In vivo cutaneous PK study using dOFM 使用dOFM研究体内皮肤PK
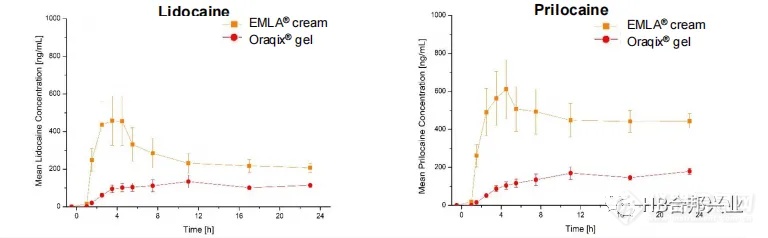
Figure6.Mean lidocaine and prilocaine concentration-time profiles (±SE) for EMLA® cream and for Oraqix® gel following application of 10 mg/cm2 of products.Data are shown as Mean±SEM from six subjects.
图6.EMLA®乳膏和Oraqix®凝胶在给药10mg /cm2产品后的平均利多卡因/丙胺卡因浓度-时间曲线(±SE)。数据以6名受试者的平均值±SEM表示。
Conclusion
结论
These results demonstrate the correlation between the Q3 similarities (or differences) of three comparator products and their corresponding cutaneous PK, both in vitro (IVPT) and in vivo (dOFM). The similarity of Q3 characteristics between the reference and generic creams accurately correlated with and was predictive of comparable bioavailability (and bioequivalence) for both lidocaine and prilocaine between the two creams, with the exception of prilocaine AUC in the (underpowered) IVPT study. The difference in Q3 characteristics between the reference cream and the gel accurately correlated with and was predictive of differences in bioavailability.
这些结果证明了三种比较产物的Q3相似性(或差异)与其相应的皮肤PK之间的相关性,无论是体外(IVPT)还是体内(dOFM)。仿制和参比制剂乳膏Q3相似性与生物利用度(和生物等效性)准确相关,并可预测两种乳膏之间的一致性,(underpowered)IVPT研究中丙胺卡因AUC除外。参比制剂乳膏和凝胶之间Q3差异与生物利用度的差异准确相关,并可预测。
Acknowledgement and Disclaimer: Funding for this work was made possible, in part, by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration through award U01FD005226 and award 1U01FD005861. The views expressed here do not reflect the official policies of the U.S . Food and Drug Administration or the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; nor does any mention of trade names, commercial practices, or organization imply endorsement by the United States Government.
确认和免责声明:本工作的资金部分由美国食品和药物管理局通过奖励U01FD005226和奖励1U01FD005861提供。这里表达的观点不反映美国食品和药物管理局或美国卫生与公众服务部的官方政策;任何提及商品名称、商业惯例或组织也不意味着得到美国政府的认可。
来源于:北京合邦兴业科学仪器有限公司
热门评论
最新资讯
厂商动态
新闻专题













