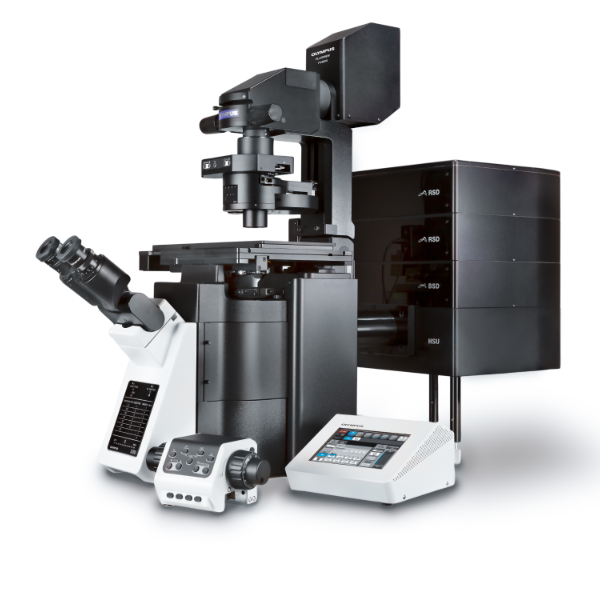
TISSUEscope™ 数字病理切片扫描成像系统
Huron Technologies是数字病理技术的全球领导者。自1994年,Huron已经为病理研究提供先进完整的显微成像解决方案。
公司旗舰产品TISSUEscope,是目前最先进的数字病理切片扫描成像系统,也是目前唯一可以提供高分辨率共聚焦荧光成像和超大样品扫描的数字病理成像系统。采用“激光扫描透镜” 专利技术,替代传统的CCD和物镜模式,因此具备更宽的视野,更快的扫描速度以及更小的光漂白毒性。
凭借最先进的共聚焦荧光扫描技术,TISSUEscope在刚刚结束的2012国际扫描仪竞赛中,无可非议的赢得20X和40X荧光扫描两项冠军。
服务高端数字病理扫描,TISSUEscope提供无与伦比的性能:
1. 唯一可提供共聚焦荧光扫描,与传统荧光技术相比,共聚焦荧光技术可提供更高质量的图像,更小的噪音和光漂白。
2. 可增配明场扫描模块,实现共聚焦和明场双成像模式
3. 最大可扫描200mm X 150mm超大样品,如:灵长类动物的脑,乳腺,肺,肝脏,前列腺等大尺寸完整样品扫描。
4. 最多可达五个激光激发光源,可同时捕获四种荧光
5. 极高的光学分辨率,可达0.25um像素大小
6. Z-stack切片三维序列扫描
目前市面上唯一一款激光共聚焦病理切片扫描仪
市面上的病理切片扫描仪均是荧光扫描仪,无法避免光漂白的现象;而且荧光扫描仪可扫描的病理切片的厚度仅限于20um以内,切片尺寸也都比较小;而TISSUEscope扫描切片厚度可以达到100-500um,切片尺寸更是可达达到惊人的20 cm×15cm,并可同时捕获4种荧光。
技术指标
具体应用请下载附件 Huron Technologies资料.rar
Huron Technologies资料.rar
参考文献:
Digital Transplantation Pathology: Combining Whole Slide Imaging, Multiplex Staining and Automated Image Analysis
2011: American Journal of Transplantation
Increasing specimen coverage using digital whole-mount breast pathology: Implementation, clinical feasibility and application in research
2011: Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics
Biomechanical Property Quantification of Prostate Cancer by Quasi-static MR Elastography at 7 Telsa of Radical Prostatectomy, and Correlation with Whole Mount Histology
2011: The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine
Megapixel Digital PCR
2011: Nature Methods
Evaluation of Microscopic Disease in Oral Tongue Cancer Using Whole-Mount Histopathologic Techniques: Implications for the Management of Head-and-Neck Cancers
2011: International Journal of Radiation Oncology*Biology*Physics
Hypoxia predicts aggressive growth and spontaneous metastasis formation from orthotopically-grown primary xenografts of human pancreatic cancer
2011: Cancer Research
Evaluating the Extent of Cell Death in 3D High Frequency Ultrasound by Registration with Whole Mount-tumor Histopathology
2010: Medical Physics
Technical Note: Fiducial Markers for Correlation of Whole-Specimen Histopathology with MR Imaging at 7 Tesla
2010: Medical Physics
Activation of Src and Src-associated Signaling Pathways in Relation to Hypoxia in Human Cancer Zenograft Models
2008: International Journal of Cancer
Developing a Methodology for Three-Dimensional Correlation of PET-CT images and Whole-Mount Histopathology in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer
2008: Current Oncology
Effect of Distributional Heterogeneity on the Analysis of Tumor Hypoxia Based Carbonic Anhydrase IX
2007: Laboratory Investigation
Imaging and Modulating Antisense Microdistribution in Solid Human Xenograft Tumor Models
2007: Clinical Cancer Research
Measurements of Aneurysm Morphology Determined by 3-D Micro-Ultrasound Imaging as Potential Quantitative Biomarkers in a Mouse Aneurysm Model
2007: Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology
Measurement of Signaling Pathway Activities in Solid Tumor Fine-needle Biopsies by Slide-based
Cytometry
2007: Diagnostic Molecular Pathology
Predictive and Pharmacodynamic Biomarker Studies in Tumor and Skin Tissue Samples of Patients With Recurrent or Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck Treated With Erlotinib
2007: Journal of Clinical Oncology
A Phase 2 Clinical and Pharmacodynamic Study of Temsirolimus in Advanced Neuroendocrine Carcinomas
2006: British Journal of Cancer
A New Wide Field-of-view Confocal Imaging System and its Applications in Drug Discovery and Pathology
2005: Optical Methods in Drug Discovery and Development
Huron Technologies是数字病理技术的全球领导者。自1994年,Huron已经为病理研究提供先进完整的显微成像解决方案。
公司旗舰产品TISSUEscope,是目前最先进的数字病理切片扫描成像系统,也是目前唯一可以提供高分辨率共聚焦荧光成像和超大样品扫描的数字病理成像系统。采用“激光扫描透镜” 专利技术,替代传统的CCD和物镜模式,因此具备更宽的视野,更快的扫描速度以及更小的光漂白毒性。
凭借最先进的共聚焦荧光扫描技术,TISSUEscope在刚刚结束的2012国际扫描仪竞赛中,无可非议的赢得20X和40X荧光扫描两项冠军。
服务高端数字病理扫描,TISSUEscope提供无与伦比的性能:
1. 唯一可提供共聚焦荧光扫描,与传统荧光技术相比,共聚焦荧光技术可提供更高质量的图像,更小的噪音和光漂白。
2. 可增配明场扫描模块,实现共聚焦和明场双成像模式
3. 最大可扫描200mm X 150mm超大样品,如:灵长类动物的脑,乳腺,肺,肝脏,前列腺等大尺寸完整样品扫描。
4. 最多可达五个激光激发光源,可同时捕获四种荧光
5. 极高的光学分辨率,可达0.25um像素大小
6. Z-stack切片三维序列扫描
目前市面上唯一一款激光共聚焦病理切片扫描仪
市面上的病理切片扫描仪均是荧光扫描仪,无法避免光漂白的现象;而且荧光扫描仪可扫描的病理切片的厚度仅限于20um以内,切片尺寸也都比较小;而TISSUEscope扫描切片厚度可以达到100-500um,切片尺寸更是可达达到惊人的20 cm×15cm,并可同时捕获4种荧光。
技术指标
| 检测模式 | 明场和共聚焦荧光:可同时检测4种荧光 |
| 荧光检测器 | 高灵敏度光电倍增管(PMT) |
| RGB检测器 | RGB传感器 |
| 图像文件格式 | Big TIFF(24-bit RGB 和 16-bit 灰度) |
| 聚焦模式 | 自动聚焦(或手动聚焦) |
| 标配激光 | 405,488,532,638 nm |
| 可选配激光 | 561,680,750nm中任一种 |
| 发射滤光片 | 匹配常用荧光标记(DAPI, FITC, Cy3, Cy5) |
| 分辨率 | 0.25,0.5,1,2,5,10,20,30,50,100 um |
| 动力学范围 | 12-bit 数据捕获 |
| 扫描速度 | 10mm × 10mm,0.5um<2 mins |
| 最大扫描区域 | 200mm × 150mm |
| 可选玻片支架 |
12片75×25mm 4片 75×50mm 2片 100×75mm 1片125×100mm 1片175×125mm 1片200×150 mm |
| 扫描仪尺寸 | 600mm(W) × 700mm(D) × 550mm(H), 130Kg |
| 认证 | CSA(CUS),满足FDA二级激光产品标准 |
具体应用请下载附件
 Huron Technologies资料.rar
Huron Technologies资料.rar参考文献:
Digital Transplantation Pathology: Combining Whole Slide Imaging, Multiplex Staining and Automated Image Analysis
2011: American Journal of Transplantation
Increasing specimen coverage using digital whole-mount breast pathology: Implementation, clinical feasibility and application in research
2011: Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics
Biomechanical Property Quantification of Prostate Cancer by Quasi-static MR Elastography at 7 Telsa of Radical Prostatectomy, and Correlation with Whole Mount Histology
2011: The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine
Megapixel Digital PCR
2011: Nature Methods
Evaluation of Microscopic Disease in Oral Tongue Cancer Using Whole-Mount Histopathologic Techniques: Implications for the Management of Head-and-Neck Cancers
2011: International Journal of Radiation Oncology*Biology*Physics
Hypoxia predicts aggressive growth and spontaneous metastasis formation from orthotopically-grown primary xenografts of human pancreatic cancer
2011: Cancer Research
Evaluating the Extent of Cell Death in 3D High Frequency Ultrasound by Registration with Whole Mount-tumor Histopathology
2010: Medical Physics
Technical Note: Fiducial Markers for Correlation of Whole-Specimen Histopathology with MR Imaging at 7 Tesla
2010: Medical Physics
Activation of Src and Src-associated Signaling Pathways in Relation to Hypoxia in Human Cancer Zenograft Models
2008: International Journal of Cancer
Developing a Methodology for Three-Dimensional Correlation of PET-CT images and Whole-Mount Histopathology in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer
2008: Current Oncology
Effect of Distributional Heterogeneity on the Analysis of Tumor Hypoxia Based Carbonic Anhydrase IX
2007: Laboratory Investigation
Imaging and Modulating Antisense Microdistribution in Solid Human Xenograft Tumor Models
2007: Clinical Cancer Research
Measurements of Aneurysm Morphology Determined by 3-D Micro-Ultrasound Imaging as Potential Quantitative Biomarkers in a Mouse Aneurysm Model
2007: Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology
Measurement of Signaling Pathway Activities in Solid Tumor Fine-needle Biopsies by Slide-based
Cytometry
2007: Diagnostic Molecular Pathology
Predictive and Pharmacodynamic Biomarker Studies in Tumor and Skin Tissue Samples of Patients With Recurrent or Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck Treated With Erlotinib
2007: Journal of Clinical Oncology
A Phase 2 Clinical and Pharmacodynamic Study of Temsirolimus in Advanced Neuroendocrine Carcinomas
2006: British Journal of Cancer
A New Wide Field-of-view Confocal Imaging System and its Applications in Drug Discovery and Pathology
2005: Optical Methods in Drug Discovery and Development
激光共聚焦数字病理扫描成像信息由倍辉科技有限公司为您提供,如您想了解更多关于激光共聚焦数字病理扫描成像报价、型号、参数等信息,欢迎来电或留言咨询。
相关产品



 仪器对比
仪器对比



 关注
关注












