用户动态|中科院上海硅酸盐所卓尚军、钱荣等人在《Analytical Chemistry》发表关于射频GDMS的文章
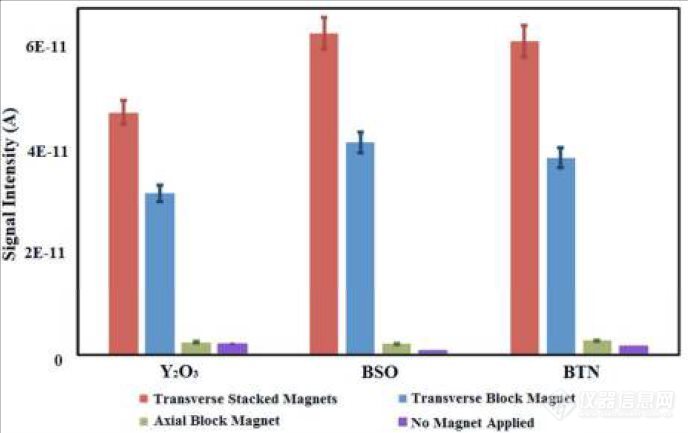
最近,中科院上海硅酸盐研究所无机材料分析测试中心卓尚军、钱荣等人的课题组与英国质谱仪器公司(MSI)合作,将堆叠磁铁系统和辉光放电质谱仪(Autoconcept GD90-RF)的射频源耦合,在非导体样品中观察到了超过50%的信号强度增益。作者借助ANSYS,对这种显著信号增强现象的机理进行了分析,发现:振荡磁场的引入,扩展了电子的运动路径,增大了电子和中性粒子间的碰撞几率,从而提高了非导体样品的电离效率。同时,该现象在多种非导体样品中得以再现,表明该方法是一种简便、有效且具备一定普适性的方法。相关工作发表在国际权威学术期刊《Analytical Chemistry》上。 横向堆叠磁铁、横向块体磁铁、轴向块体磁铁耦合和无磁铁耦合情况下,Y2O3、BSO (Bi12SiO20)、BTN (Ba5.52La0.32Ti2Nb8O30)样品中的Y、Bi、Ba的射频放电信号对比。 用典型元素的信号强度表示的放电稳定性:采用经堆叠磁铁耦合的射频源,对(a)Y2O3、(b)BSO (Bi12SiO20)、(c)BTN (Ba5.52La0.32Ti2Nb8O30)样品进行溅射得到的测量结果。文章链接如下:http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acs.analchem.6b04884 文章摘要如下:A method for signal enhancement utilizing stacked magnets was introduced into high-resolution radio frequency glow discharge-mass spectrometry (rf-GD-MS) for significantly improved analysis of inorganic materials. Compared to the block magnet, the stacked magnets method was able to achieve 50–59% signal enhancement for typical elements in Y2O3, BSO, and BTN samples. The results indicated that signal was enhanced as the increase of discharge pressure from 1.3 to 8.0 mPa, the increase of rf-power from 10 to 50 W with a frequency of 13.56 MHz, the decrease of sample thickness, and the increase of number of stacked magnets. The possible mechanism for the signal enhancement was further probed using the software “Mechanical APDL (ANSYS) 14.0”. It was found that the distinct oscillated magnetic field distribution from the stacked magnets was responsible for signal enhancement, which could extend the movement trajectories of electrons and increase the collisions between the electrons and neutral particles to increase the ionization efficiency. Two NIST samples were used for the validation of the method, and the results suggested that relative errors were within 13% and detection limit for six transverse stacked magnets could reach as low as 0.0082 μg g–1. Additionally,the stability of the method was also studied. RSD within 15% of the elements in three nonconducting samples could be obtained during the sputtering process. Together, the results showed that the signal enhancement method with stacked magnets could offer great promises in providing a sensitive, stable, and facile solution foranalyzing the nonconducting materials.