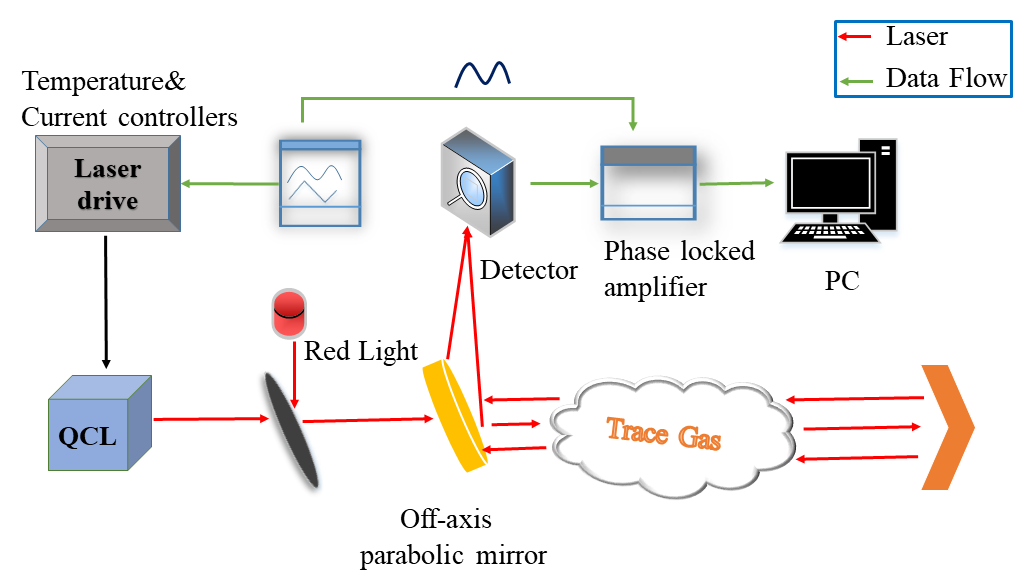
应用案例 | 使用开路传感器系统研究温度和湿度对N2O吸收谱和浓度的影响
近日,来自山东师范大学物理与电子科学学院的联合研究团队发表了一篇题为Effects of Temperature and Humidity on the Absorption Spectrum and Concentration of N2O Using an Open-Path Sensor System的研究论文。IntroductionSince China’ s proposal of the “carbon peak” and “carbon neutrality” goals, the government and society have attached great importance to the problems of air pollution and global warming. Nitrous oxide (N2O) isamong the six greenhouse gases under the Kyoto Protocol. N2O content is relatively low compared to carbon dioxide (CO2), but its global warming potential is about 310 times that of CO2. In addition, it is destructive to ozone (O3). There are many reasons for the changes in N2O concentrations in the atmosphere, which are partly due to anthropogenic activities, such as the widespread use of fertilizers in agricultural activities. The concentrations of other gases in the atmosphere, as well as the wind speed and direction, are all correlated with changes in N2O concentrations. At the macro level, temperature and humidity are also factors affecting the absorption coefficient of N2O gas. However, relatively few studies have been conducted on the specific effects of temperature and humidity on N2O gas, and analysis has also been lacking on the influence of temperature and humidity on the absorption spectrum and the concentration of N2O. Moreover, some uncertainty and variability remain in the observations of the relationship between N2O gas concentrations and temperature and humidity. The reasons for these discrepancies may be regional differences, differences in observation methods, and imperfections in data, which are all important bases for measuring the N2O concentration in atmospheric, medical, combustion, and agricultural processes. Thus, further research and exploration, combined with additional field observations and modeling experiments, can uncover the mechanism of temperature and humidity on the N2O concentration. Consequently, providing a scientific basis for this concentration is essential for reducing N2O emissions, controlling climate change, and promoting sustainable development and environmental protection. 简介自中国提出“碳峰值”和“碳中和”目标以来,政府和社会对空气污染和全球变暖问题给予了极大关注。N2O是《京都议定书》下的六种温室气体之一。与二氧化碳(CO2)相比,N2O含量相对较低,但其全球变暖潜力约为CO2的310倍。此外,它对臭氧(O3)具有破坏性。大气中N2O浓度的变化有许多原因,部分原因是人类活动造成的,例如在农业活动中广泛使用化肥。大气中其他气体的浓度以及风速和风向都与N2O浓度的变化相关。在宏观水平上,温度和湿度也是影响N2O气体吸收系数的因素。然而,对温度和湿度对N2O气体具体影响的研究相对较少,对温度和湿度对N2O吸收谱和浓度的影响分析也不足。此外,在N2O气体浓度与温度和湿度之间的关系观察中仍存在一些不确定性和变异性。导致这些差异的原因可能是地区差异、观测方法差异以及数据的不完善,这些都是测量大气、医疗、燃烧和农业过程中N2O浓度的重要基础。因此,进一步的研究和探索,结合更多的现场观测和建模实验,可以揭示温度和湿度对N2O浓度的机制。因此,为减少N2O排放、控制气候变化,促进可持续发展和环境保护提供科学依据至关重要。Experimental DetailsSensor SetupBased on WMS technology and an open optical path, an open optical-path detection system for detecting N2O gas in the atmosphere was built. The schematic diagram is shown in Figure 1. The sensor system is composed of a light-source module, photoelectric Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5390 4 of 11 detection module, and data processing module. The light-source module mainly consists of signal generation, a laser drive, QCL, and an indication light source. To effectively realize the tunable characteristics of laser emission wavelength, we designed the signal generator plate to generate a high-frequency sine wave signal with a frequency of 10 kHz to realize the modulation function and to generate a low-frequency sawtooth wave signal with a frequency of 10 Hz to realize the scanning function. The two signals are superimposed on the laser driver, controls the temperature and central emission wavelength of QCL and converts it into an injection current acting on the detection light source QCL so that the emission wavelength of QCL is in the tunable range of 2203.7–2204.1 cm&minus 1.实验细节传感器设置基于波长调制光谱学(WMS)技术和开路光学路径,建立了一种用于检测大气中N2O气体的开路光学路径检测系统。示意图如图1所示。该传感器系统由光源模块、光电检测模块和数据处理模块组成。光源模块主要包括信号生成、激光驱动、量子级联激光器(QCL)和指示光源。为了有效实现激光发射波长的可调特性,我们设计了信号生成器板,生成频率为10 kHz的高频正弦波信号以实现调制功能,并生成频率为10 Hz的低频锯齿波信号以实现扫描功能。这两个信号叠加在激光驱动器上,控制QCL的温度和中心发射波长,并将其转化为作用于检测光源QCL的注入电流,使QCL的发射波长处于2203.7–2204.1 cm-1的可调范围内。Figure 1. Schematic diagram of N2O open optical sensor system.项目使用的激光驱动器是宁波海尔欣光电科技有限公司的QC750-TouchTM量子级联激光屏显驱动器。&bull 集成电流及温控驱动,功能完备;&bull 温度控制驱动采用非PWM式的连续电流输出控制,大大延长TEC器件的使用寿命;&bull 多种输出安全保护机制,保护QCL使用安全:可调电流钳制、输出缓启动、过压欠压保护、超温保护、继电器短路输出保护;&bull 大电流软钳制功能,避免误操作大电流损坏激光管;&bull UI界面显示便于用户操作使用及数据观测;&bull 全自主研发,集成度高,性价比高。QC750-TouchTM, Ningbo HealthyPhoton Technology, Co., Ltd.Selection of N2O TransitionsTo achieve effective detection of N2O gas molecules, we need to select the absorption line intensity and the emission central wavelength of the laser. First, combined with the HITRAN-2016 database, the wave number range of 2000–2250 cm&minus 1 was selected to analyze the region of the absorption spectral line intensity of N2O, and then carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (CO2), and water (H2O) molecules were simulated and analyzed, as shown in Figure 2. Within this wave number range, the absorption spectra of CO2 were mainly distributed within the 2000–2081 cm&minus 1 range, and the absorption spectra of CO gas were distributed within the 2025–2200 cm&minus 1 wave number range. The absorption spectra of N2O gas were distributed before the 2020 cm&minus 1 wave number range. The absorption spectra of N2O gas molecules were mainly distributed in the 2200–2250 cm&minus 1 wave number range, and they were far from the absorption spectra of water vapor and other gases, reducing interference. At around 2203.7 cm&minus 1 , the absorption spectra ofN2O gas were the strongest. Therefore, we set the position of the N2O absorption line to 2203.7333 cm&minus 1, which was used as the wave number of the QCL emission center. The corresponding spectral line intensity was 7.903 × 10&minus 19 (cm&minus 1 .mol&minus 1 ). The central current and temperature of QCL were set at 330 mA and 36.0 ◦ C, respectively.N2O跃迁的选择为了有效检测N2O气体分子,我们需要选择吸收线强度和激光的发射中心波长。首先,结合HITRAN-2016数据库,选择了2000–2250 cm&minus 1的波数范围,以分析N2O吸收光谱线强度的区域,然后对一氧化碳(CO)、二氧化碳(CO2)和水(H2O)分子进行了模拟和分析,如图2所示。在这个波数范围内,CO2的吸收光谱主要分布在2000–2081 cm&minus 1范围内,CO气体的吸收光谱分布在2025–2200 cm&minus 1波数范围内。H2O气体的吸收光谱分布在2020 cm&minus 1波数范围之前。N2O气体分子的吸收光谱主要分布在2200–2250 cm&minus 1波数范围内,远离水蒸气和其他气体的吸收光谱,减少了干扰。在2203.7 cm&minus 1左右,N2O气体的吸收光谱最强。因此,我们将N2O吸收线的位置设置为2203.7333 cm&minus 1,用作QCL发射中心的波数。相应的光谱线强度为7.903 × 10&minus 19(cm&minus 1mol&minus 1)。QCL的中心电流和温度分别设置为330 mA和36.0 ℃。Figure 2. The intensity distribution of absorption lines of N2O, CO, CO2, and H2O in the range of 2000–2250 cm&minus 1.ConclusionsIn this study, we investigated the effects of temperature and humidity on the concentration of N2Oand its absorption spectra using an open-path sensor system. By combining theoretical analysis and field monitoring, we first conducted monitoring of N2O in a campus environment, analyzing the effects of temperature on its concentration and absorption spectra. We discovered that the concentration of N2O would increase correspondingly with the increase in temperature. The influence of humidity on N2O concentration was monitored under the condition that the ambient temperature of the laboratory remained unchanged. The concentration of N2O was negatively correlated with humidity. The 2f and 1f signals under different temperature and humidity levels were extracted for analysis. We found that the higher the temperature, the smaller the peak value ofthe 2f and the 1f signals, which accords with the trend of the Gaussian function changing with temperature. Under different humidity conditions, the lower thehumidity, the larger the 2f signal peak the higher the humidity, the smaller the 2f signal. This study is of great significance for analyzing the relationship between N2O and environmental parameters such as temperature and humidity. We hope that our research findings can assist environmental agencies in formulating more effective environmental policies for different environments. In the future, we can use QCL to analyze the relationship between N2Oand other environmental and gas parameters.结论在本研究中,我们利用开路传感器系统研究了温度和湿度对N2O浓度及其吸收光谱的影响。通过理论分析和现场监测相结合,我们首先在校园环境中进行了N2O监测,分析了温度对其浓度和吸收光谱的影响。我们发现随着温度升高,N2O浓度相应增加。在实验室环境中,保持环境温度不变的条件下监测了湿度对N2O浓度的影响。N2O浓度与湿度呈负相关。在不同温度和湿度水平下提取并分析了2f和1f信号。我们发现温度越高,2f和1f信号的峰值越小,这与高斯函数随温度变化的趋势相符。在不同湿度条件下,湿度越低,2f信号峰值越大;湿度越高,2f信号越小。这项研究对分析N2O与温度、湿度等环境参数之间的关系具有重要意义。我们希望我们的研究结果能够协助环境机构为不同环境制定更有效的环境政策。未来,我们可以利用QCL来分析N2O与其他环境和气体参数之间的关系。参考:Effects of Temperature and Humidity on the Absorption Spectrum and Concentration of N2O Using an Open-Path Sensor System, Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5390.