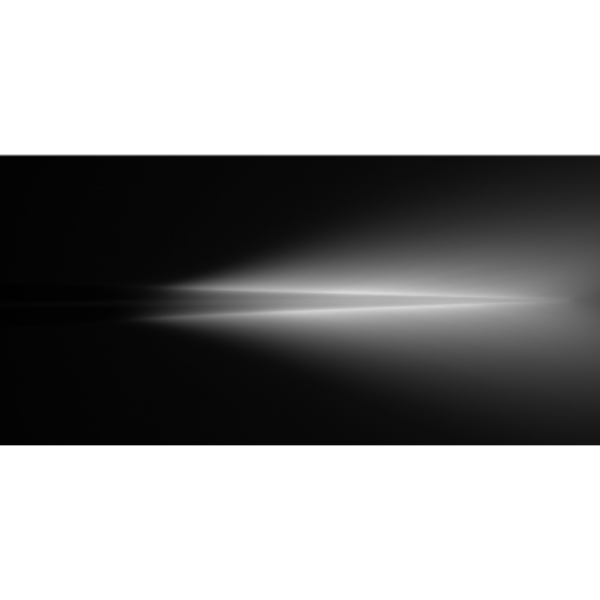
锥形光纤探针昊量光电新推出的锥形光纤探针Lambda Fibers是一种光纤探针,锥形光纤探针一端从其全宽逐渐减小到直径小于1um,长度为几毫米。锥形光纤探针新颖设计为光遗传学和光纤光度学实验提供了一种独特的方法,锥形光纤探针允许均匀的大体积照明和空间可寻址的光传输,具有极薄和锋利的光纤。锥形光纤探针Lambda Fibers独特的光学特性是光纤沿其非锥度部分引导的光模沿锥度在不同位置外耦合。这意味着通过激发光纤的所有光学模式(即通过使用与光纤具有相同或更高数值孔径的光源注入光),光将从锥形扩散发射。更有趣的是,通过非常规的光传输策略(一种方法是通过改变角度将准直光束注入光纤的近端)仅激发一部分模式,可以将光发射限制在锥度的一小部分:当使用锥形光纤探针Lambda Fibers进行光收集时,导光的模态含量与锥度的活动部分或子部分之间的关系保持不变。为了在不同光纤之间获得更高的重复性,并在扫描范围内实现均匀的发射长度,建议使用Lambda-Plus Fibers:Lambda-Plus Fibers是锥度轮廓上有严格公差的锥形纤维。锥形光纤探针Lambda Fibers为光遗传学和光纤光度测定实验提供了一种新的方法。由于光传输/收集是从锥形表面进行的,因此Lambda Fibers通常插入要控制的区域。有效发射/收集光的锥度部分由有效长度定义。\由于锥形光纤探针Lambda Fiber的光活性表面比标准光纤更大——一个锥体的表面的高度等于有效长度与光纤核心面积的关系——因此需要更大的总输入光功率来获得相同的照明功率密度。由锥形的有源表面发出的平均照明功率密度可以计算为由锥形光纤发出的总光功率除以锥形光纤的有源面积。总光功率可以通过将锥形光纤放在前面并非常靠近光功率传感器来测量,就像通常使用扁平光纤一样。以平方毫米为单位的有效面积可以计算为锥度的有效长度(以毫米为单位)与纤维类型相关系数A的乘积:Fiber type.22/105.39/200.66/200Coefficient A [mm]0.0860.1890.243联系昊量光电获得LightSpread软件来估计Lambda光纤发出的光在脑组织中的分布情况。参考文献:[1] F. Pisanello, et al., “Dynamic illumination of spatially restricted or large brain volumes via a single tapered optical fiber”, Nature Neuroscience (2017)[2] F. Pisano, et al., “Depth-resolved fiber photometry with a single tapered optical fiber implant”, Nature Methods (2019)锥形光纤探针应用:光遗传学Lambda Fibers套管可用于靶向大量组织。锥形光学特性允许将光传输到感兴趣的整个区域或部分区域,这取决于光如何发射到光纤中。光纤光度测定Lambda Fibers锥形光纤探针套管可以通过整个锥形表面收集光。当使用选择性光传递来激发功能性荧光时,可以实现单纤维的多位点光纤光度测定。锥形光纤探针更多应用参考文献,请联系昊量光电!2022den Bakker H, Van Dijck M, et al., “Sharp-wave ripple associated activity in the medial prefrontal cortex supports spatial rule switching“, BioRxivGreenstreet F, Martinez Vergara H, et al., “Action prediction error: a value-free dopaminergic teaching signal that drives stable learning“, BioRxivCruz BF, Guiomar G, et al., “Action suppression reveals opponent parallel control via striatal circuits“, Nature2021Dacre J, Colligan M, et al., “A cerebellar-thalamocortical pathway drives behavioral context-dependent movement initiation“, NeuronRobert B, Kimchi EY, et al., “A functional topography within the cholinergic basal forebrain for processing sensory cues associated with reward and punishment “, eLifeAlvarado JS, Goffinet J, et al., “Neural dynamics underliying birdsong practice and performance“, NatureLee J & Sabatini B, “Striatal indirect pathway mediates exploration via collicular competition“, NatureDrake RAR, Steel KAJ, “Loss of cortical control over the descending pain modulatory system determines the development of the neuropathic pain state in rats” , eLifeHamilos AE, Spedicato G., et al., “Slowly evolving dopaminergic activity modulates the moment-to-moment probability of reward-related self-timed movements“, eLife2020Cruz BF, Soarez S, et al., “Striatal circuits support broadly opponent aspects of action suppression and production” , BioRxivIto H, Sales A, et al., Probabilistic, spinally-gated control of bladder pressure and autonomous micturition by Barrington’s nucleus CRH neurons , eLifeLee J, Wang W, et al., “Anatomically segregated basal ganglia pathways allow parallel behavioral modulation“, Nature NeuroscienceVincis R, Chen K, et al., “Dynamic Representation of Taste-Related Decisions in the Gustatory Insular Cortex of Mice“, Current Biology2019Hayat H, Regev N, et al., “Locus-coeruleus norepinephrine activity gates sensory-evoked awakenings from sleep“, Science AdvancesFernandez-Lamo I, Gomez-Dominguez D, et al., “Proximodistal Organization of the CA2 Hippocampal Area“, Cell RepGuo J, Sauerbrei B, et al., “Disrupting cortico-cerebellar communication impairs dexterity“, eLifeJackman SL, Chen CH, et al., “In Vivo Targeted Expression of Optogenetic Proteins Using Silk/AAV Films“, J. Vis. Exp.2018Fernandez DC, Fogerson PM, et al., “Light Affects Mood and Learning through Distinct Retina-Brain Pathways“, Cell关于昊量光电:上海昊量光电设备有限公司是光电产品专业代理商,产品包括各类激光器、光电调制器、光学测量设备、光学元件等,涉及应用涵盖了材料加工、光通讯、生物医疗、科学研究、国防、量子光学、生物显微、物联传感、激光制造等;可为客户提供完整的设备安装,培训,硬件开发,软件开发,系统集成等服务。
 留言咨询
留言咨询

 留言咨询
留言咨询

 留言咨询
留言咨询

 400-860-5168转1567
400-860-5168转1567
 留言咨询
留言咨询

 400-860-5168转3205
400-860-5168转3205
 留言咨询
留言咨询
 400-860-5168转6216
400-860-5168转6216
 留言咨询
留言咨询

 400-860-5168转2555
400-860-5168转2555
 留言咨询
留言咨询

 400-860-5168转1567
400-860-5168转1567
 留言咨询
留言咨询

 400-860-5168转4727
400-860-5168转4727
 留言咨询
留言咨询

 400-860-5168转3205
400-860-5168转3205
 留言咨询
留言咨询

 400-860-5168转0314
400-860-5168转0314
 留言咨询
留言咨询

 400-860-5168转1567
400-860-5168转1567
 留言咨询
留言咨询

 400-860-5168转1567
400-860-5168转1567
 留言咨询
留言咨询

 400-601-1369
400-601-1369
 留言咨询
留言咨询

 400-860-5168转4727
400-860-5168转4727
 留言咨询
留言咨询

 400-860-5168转1567
400-860-5168转1567
 留言咨询
留言咨询

 400-860-5168转4727
400-860-5168转4727
 留言咨询
留言咨询

 400-860-5168转2831
400-860-5168转2831
 留言咨询
留言咨询

 400-860-5168转4470
400-860-5168转4470
 留言咨询
留言咨询

 400-860-5168转1567
400-860-5168转1567
 留言咨询
留言咨询

 400-860-5168转3662
400-860-5168转3662
 留言咨询
留言咨询

 400-860-5168转3429
400-860-5168转3429
 留言咨询
留言咨询

 400-860-5168转3541
400-860-5168转3541
 留言咨询
留言咨询

 400-860-5168转2831
400-860-5168转2831
 留言咨询
留言咨询

 400-860-5168转3985
400-860-5168转3985
 留言咨询
留言咨询

 400-860-5168转1082
400-860-5168转1082
 留言咨询
留言咨询

 400-860-5168转0927
400-860-5168转0927
 留言咨询
留言咨询

 400-860-5168转4727
400-860-5168转4727
 留言咨询
留言咨询

 400-860-5168转2826
400-860-5168转2826
 留言咨询
留言咨询

 400-860-5168转2765
400-860-5168转2765
 留言咨询
留言咨询

 400-860-5168转6216
400-860-5168转6216
 留言咨询
留言咨询