空气水界面两侧破碎波的高速PIV测量研究
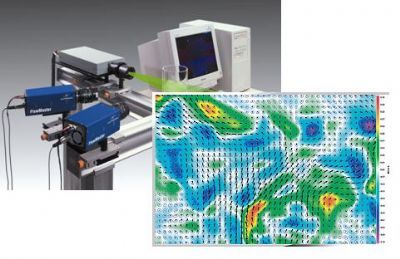
This paper presents high speed Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) experiments on small-scale, steep,breaking waves forced by shoaling the waves up an angled slope to a level plateau, in a lidded tank with an initiallyquiescent air-side. Both spilling and plunging breakers are considered. A PIV system, using a high speed digitalvideo camera at up to 500 frames per second, was used to obtain quantitative data on both the air and water side ofthe free surface interface. Waves are generated by a computer controlled, paddle-type wave maker at one end oflong, narrow acrylic tank. In order to obtain breaking waves on a small scale, surface tension was lowered bymixing isopropyl alcohol with distilled water. Surface tension characteristics of the water-IPA mixture are alsopresented herein. To perform high speed PIV measurements, a low-cost, Lasiris Magnum, near-IR, TTL diode linegenerator laser is used to form the light sheet. To seed the water, traditional silver coated hollow-glass sphereswere used. While seeding in the water was quite straight-forward, seeding in the air was quite complex. In ordernot to adversely affect the surface tension, a water-based fog was used to seed the air. Qualitative visualizations andPIV show the formation of the vortex aft of the breaking wave and reveal strong counterclockwise vorticity in the airside of the interface. Results for the plunging breaking wave case are presented herein and compared withnumerical results from Hendrickson (2004).