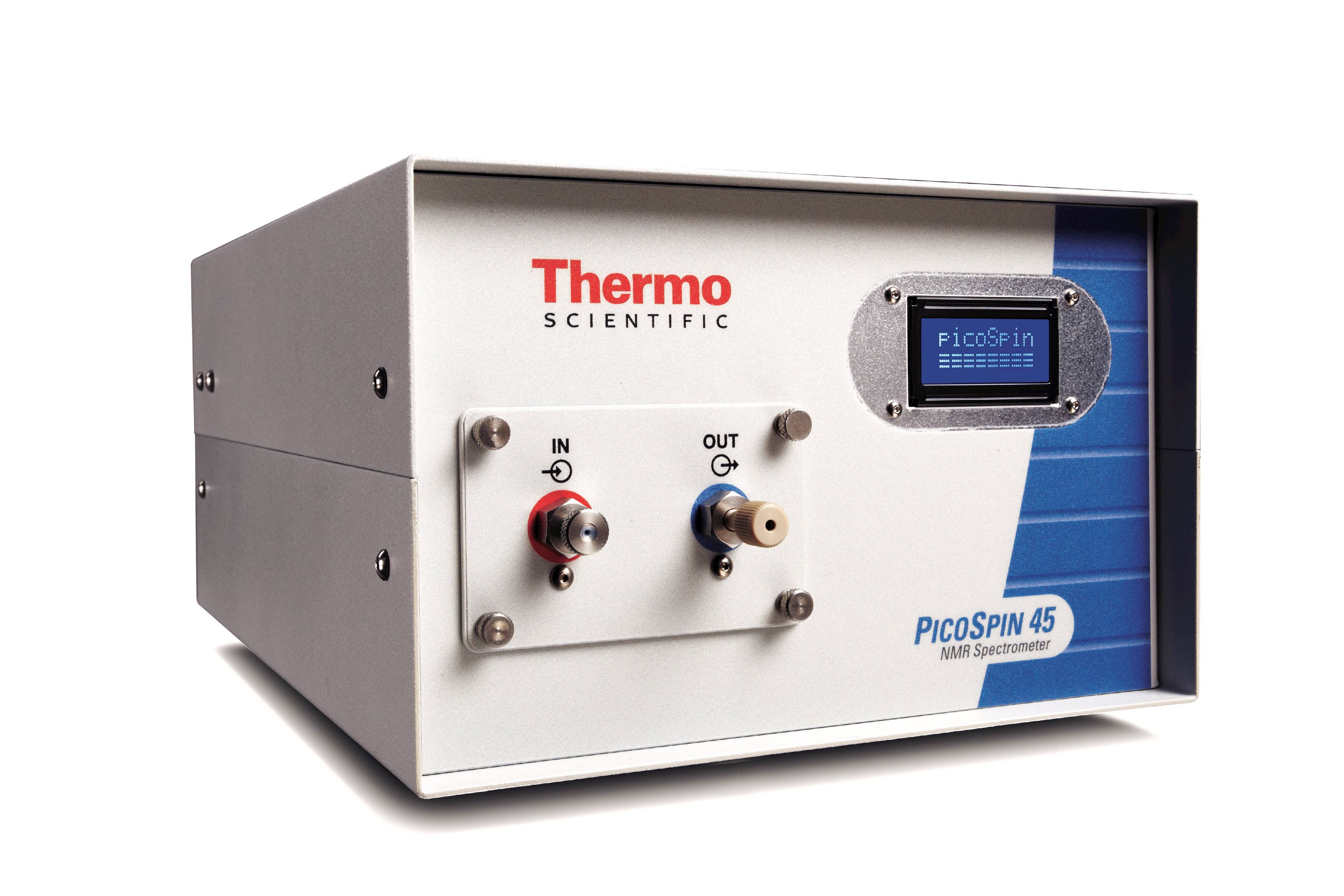

 400-858-8867
400-858-8867
 留言咨询
留言咨询
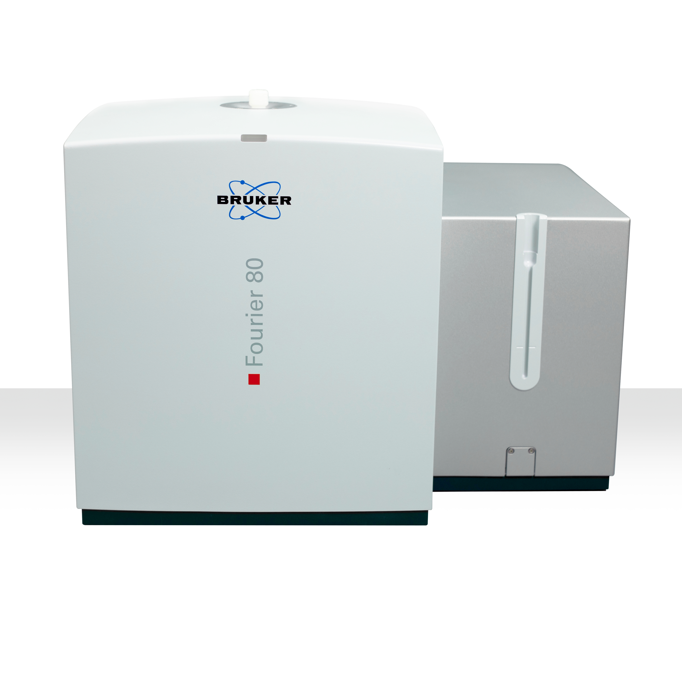

 400-889-7796
400-889-7796
 留言咨询
留言咨询
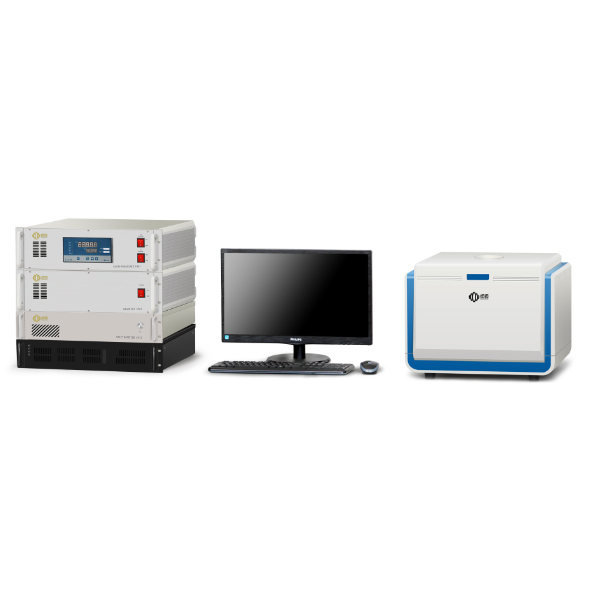

 400-858-9311
400-858-9311
 留言咨询
留言咨询
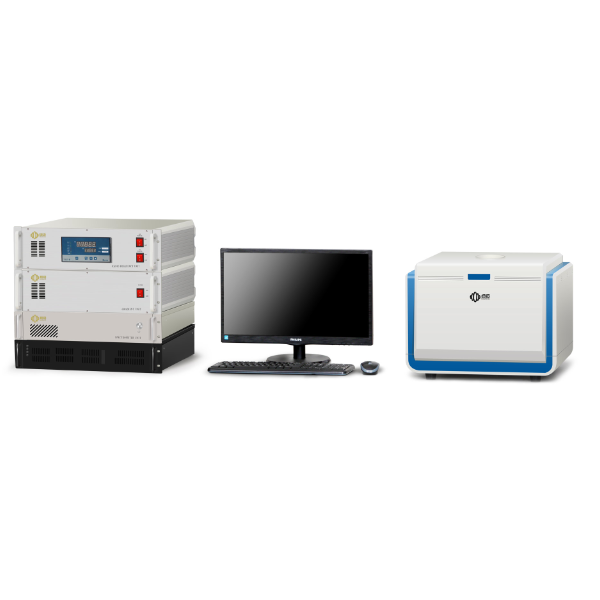

 400-858-9311
400-858-9311
 留言咨询
留言咨询

 400-860-5168转1037
400-860-5168转1037
 留言咨询
留言咨询
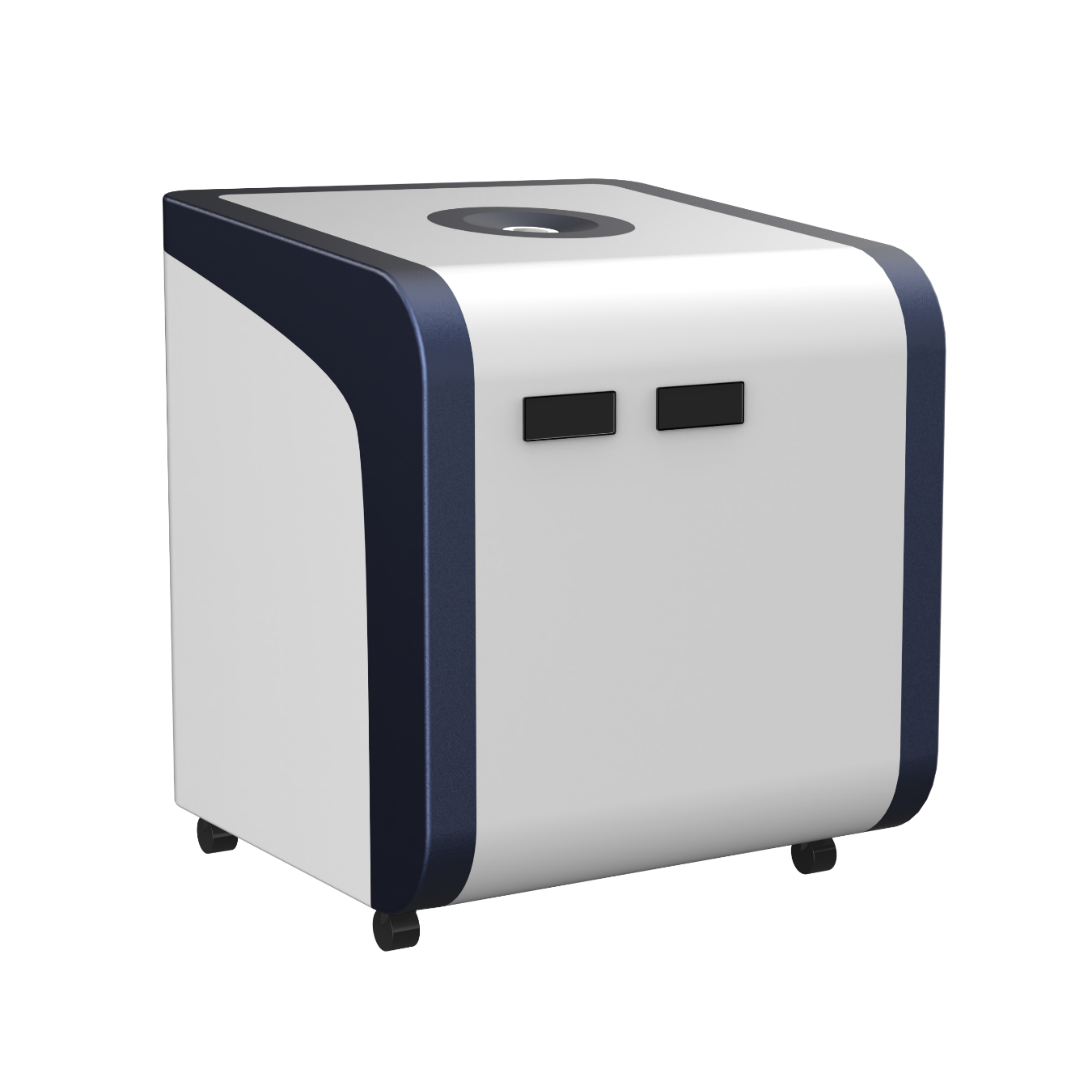

 400-860-5168转2770
400-860-5168转2770
 留言咨询
留言咨询
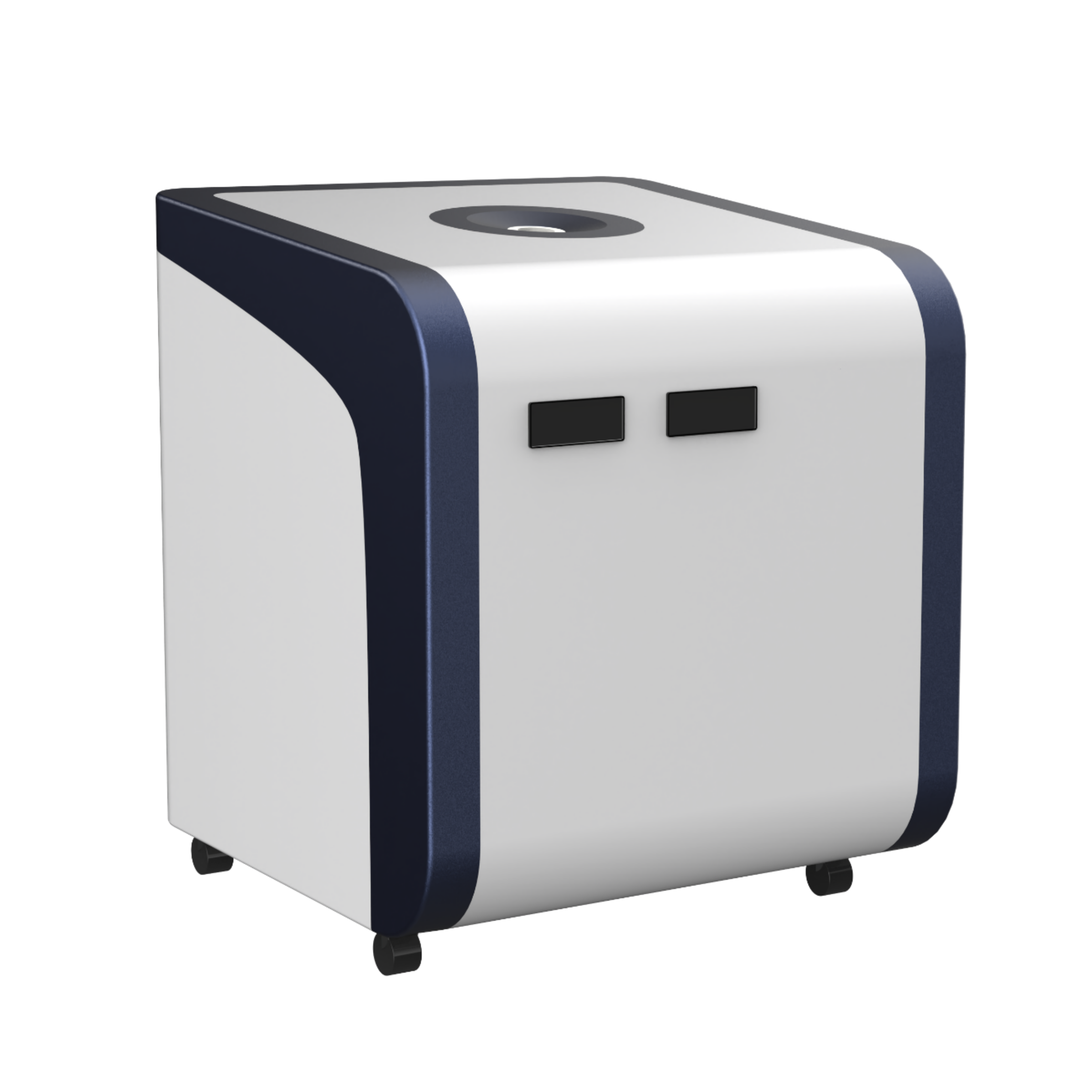

 400-860-5168转2770
400-860-5168转2770
 留言咨询
留言咨询

 400-860-5168转6220
400-860-5168转6220
 留言咨询
留言咨询

 400-860-5168转4275
400-860-5168转4275
 留言咨询
留言咨询
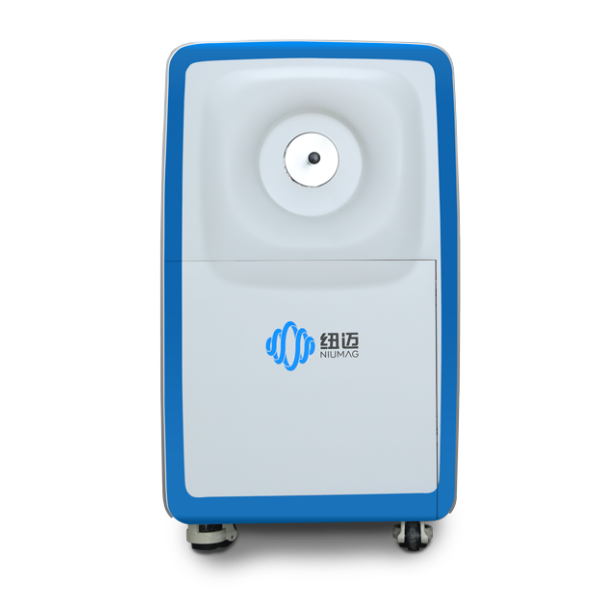

 400-858-9311
400-858-9311
 留言咨询
留言咨询
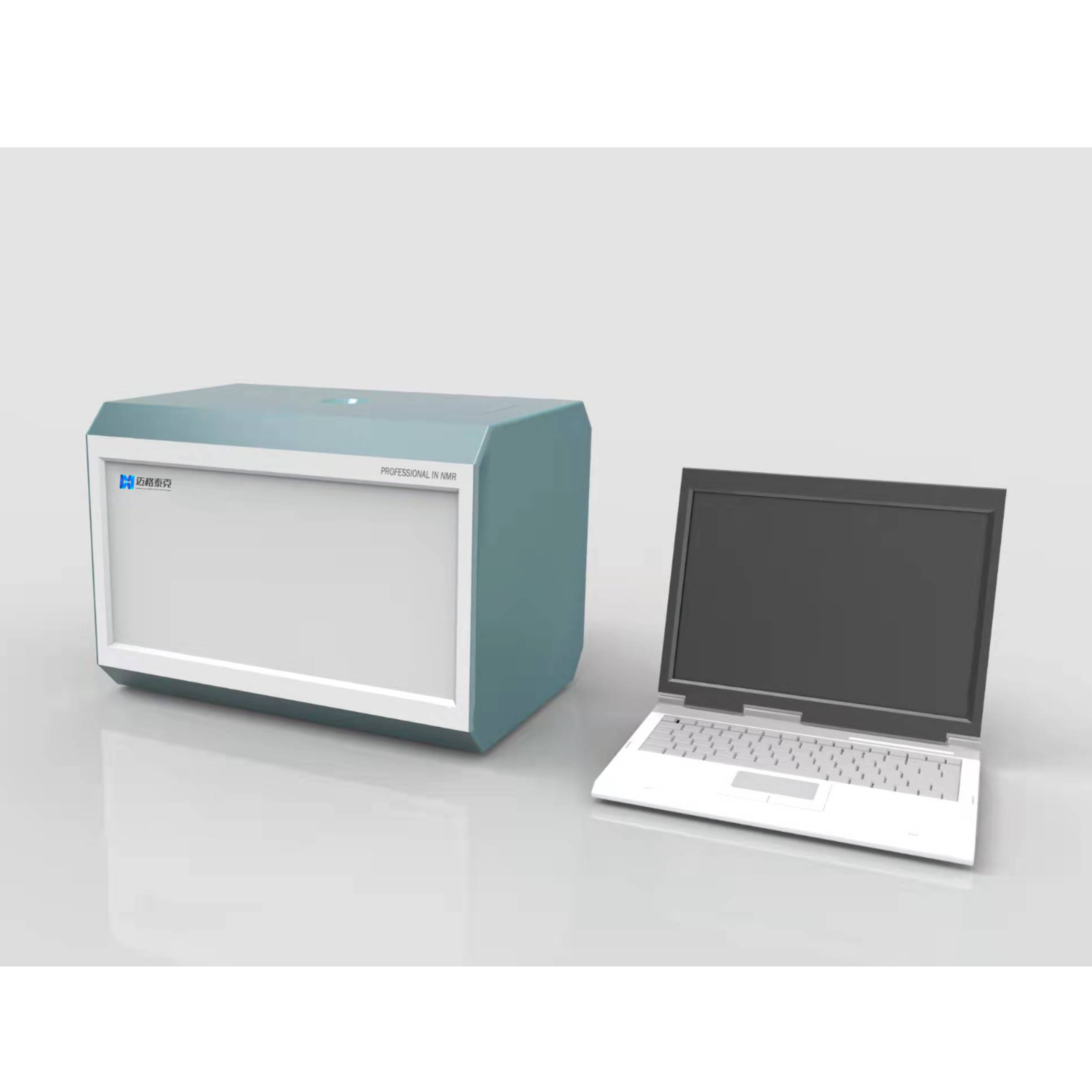

 400-860-5168转6220
400-860-5168转6220
 留言咨询
留言咨询
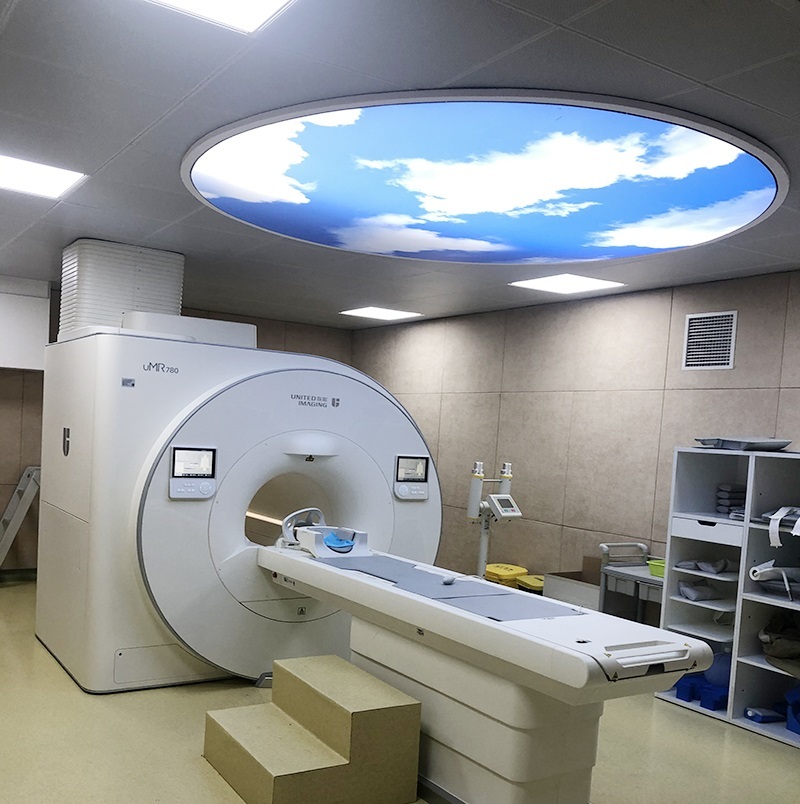
 留言咨询
留言咨询
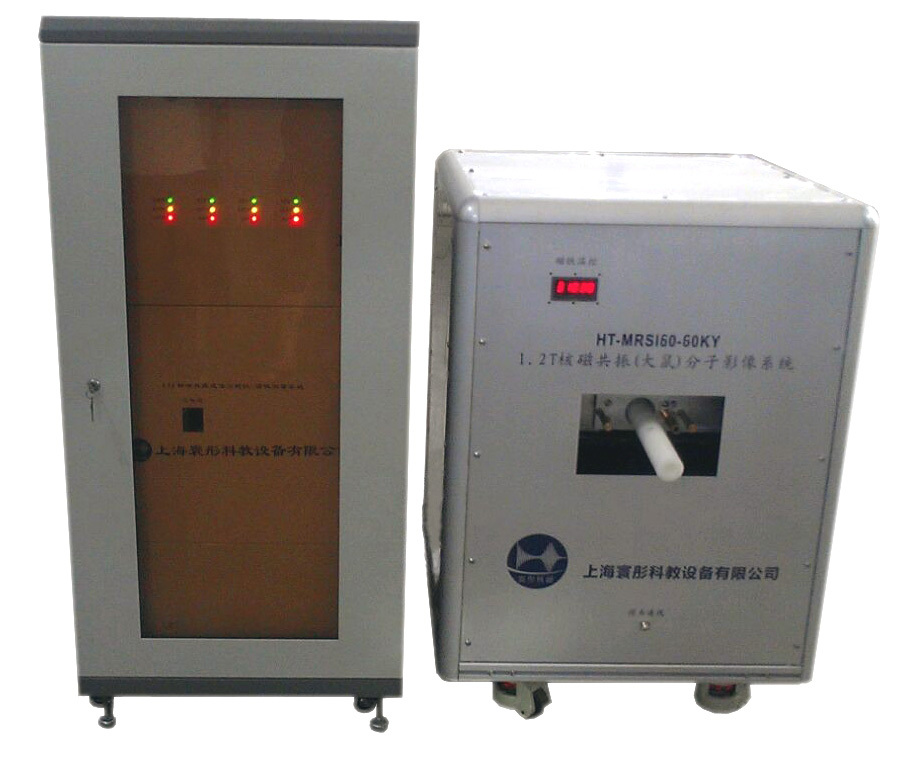

 400-860-5168转2770
400-860-5168转2770
 留言咨询
留言咨询

 400-858-9311
400-858-9311
 留言咨询
留言咨询

 400-860-5168转2770
400-860-5168转2770
 留言咨询
留言咨询

 400-860-5168转6287
400-860-5168转6287
 留言咨询
留言咨询
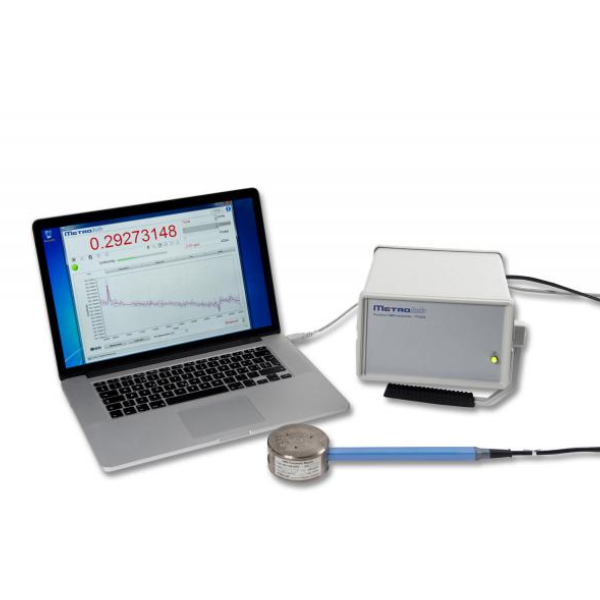
 400-860-5168转2831
400-860-5168转2831
 留言咨询
留言咨询
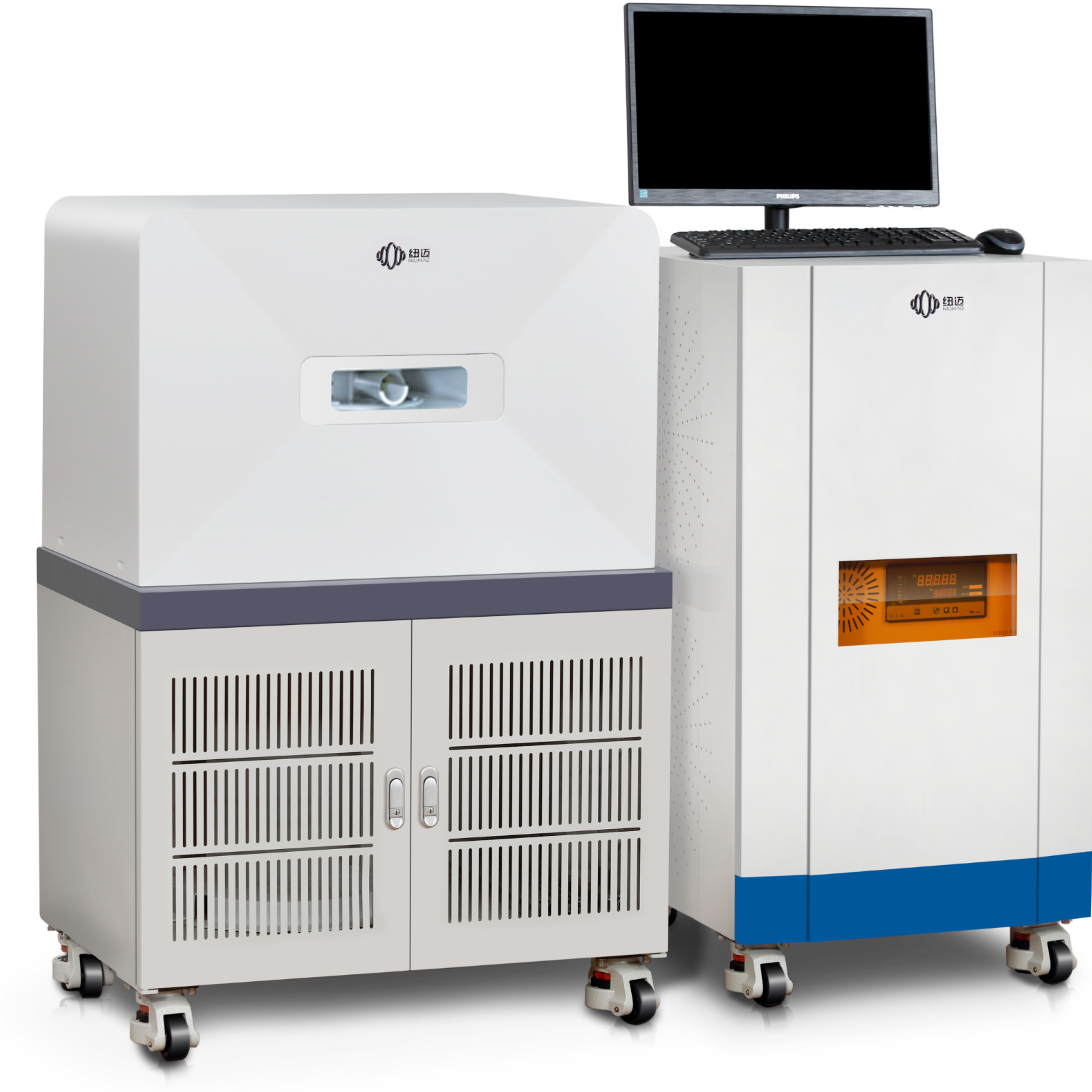

 400-858-9311
400-858-9311
 留言咨询
留言咨询
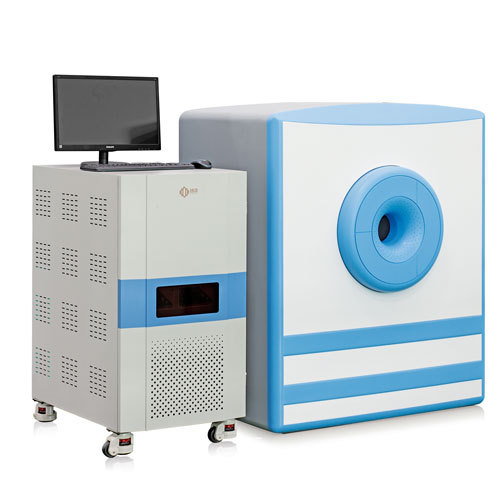

 400-858-9311
400-858-9311
 留言咨询
留言咨询
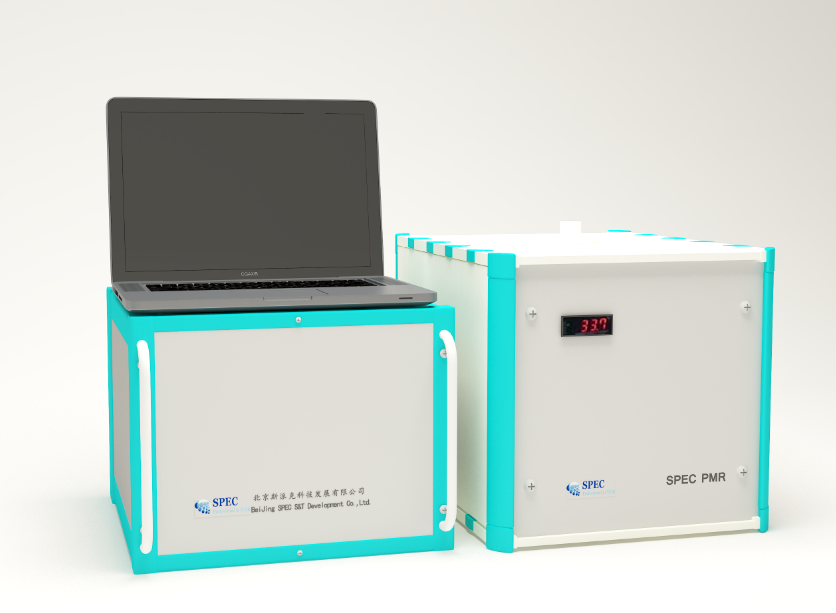

 留言咨询
留言咨询

 400-860-5168转1037
400-860-5168转1037
 留言咨询
留言咨询
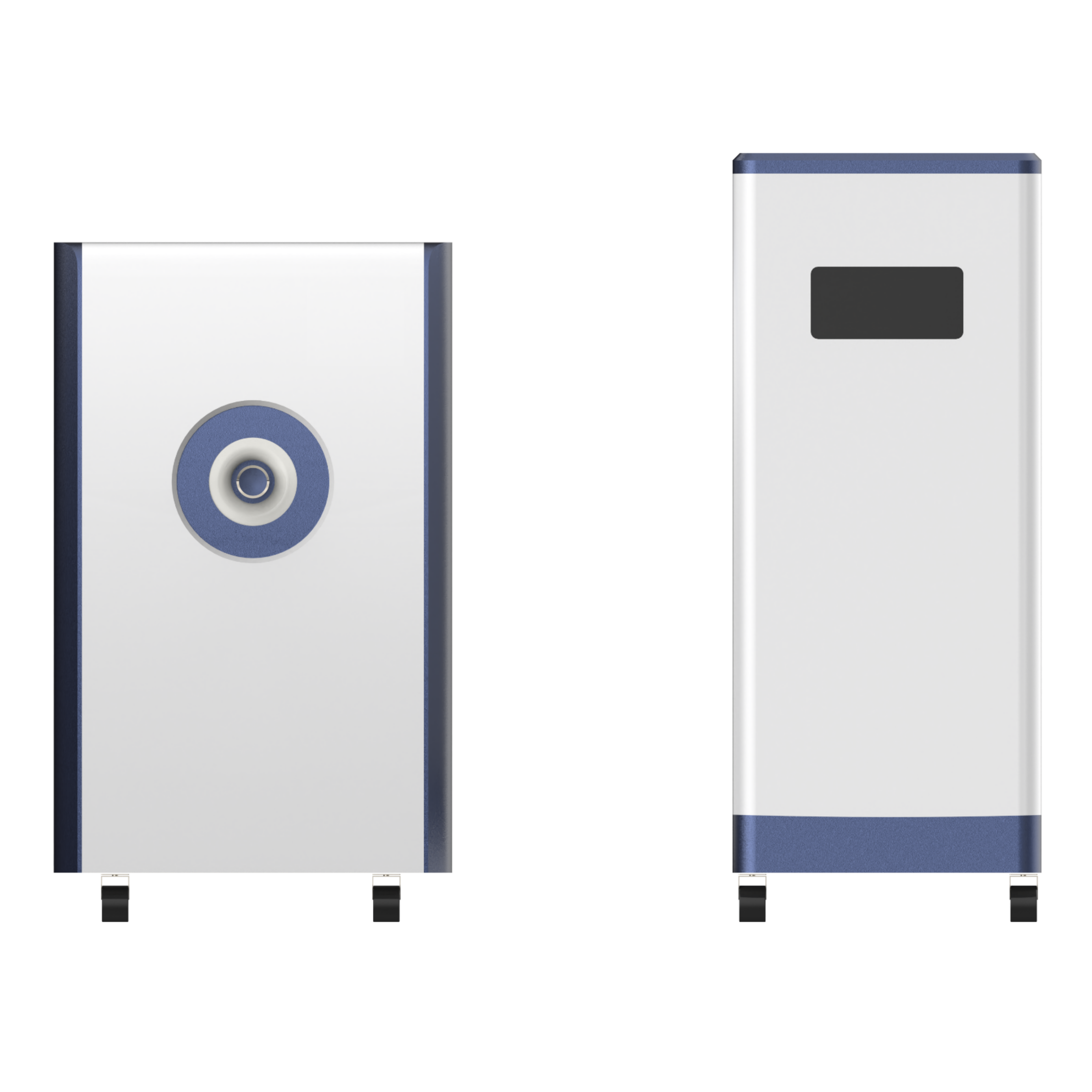

 400-860-5168转2770
400-860-5168转2770
 留言咨询
留言咨询

 400-860-5168转2623
400-860-5168转2623
 留言咨询
留言咨询
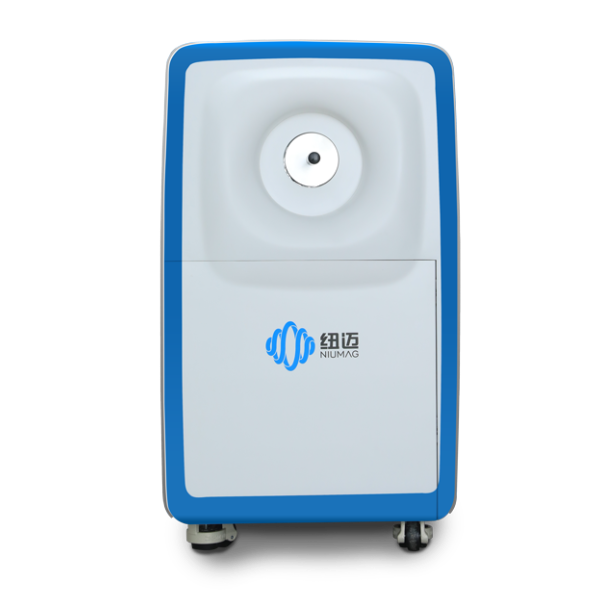

 400-858-9311
400-858-9311
 留言咨询
留言咨询

 400-858-9311
400-858-9311
 留言咨询
留言咨询

 400-860-5168转4527
400-860-5168转4527
 留言咨询
留言咨询
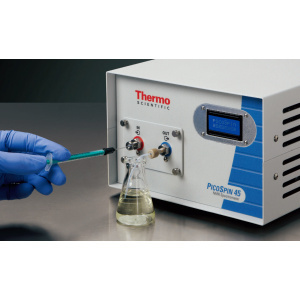
 400-860-5168转3993
400-860-5168转3993
 留言咨询
留言咨询

 400-860-5168转2714
400-860-5168转2714
 留言咨询
留言咨询

 400-860-5168转1490
400-860-5168转1490
 留言咨询
留言咨询

 400-858-9311
400-858-9311
 留言咨询
留言咨询