流体轨迹相关方法提高时间分辨PIV测量的速度动态范围和精度
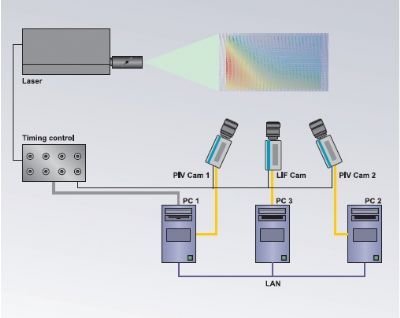
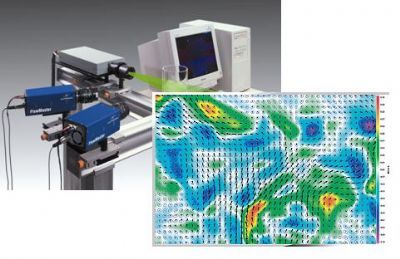
A novel method is introduced for increasing the accuracy and extending the dynamic range oftime-resolved PIV. The approach extends the well-known concept of multiframe particle trackingvelocimetry (PTV) to cross-correlation analysis employed by PIV. The working principle is based on thedetermination of fluid element trajectories by tracking their position across an image sequence. The fluidtrajectory correlation (FTC) algorithm deals with the effect of trajectory curvature and non-uniform velocityduring the considered time interval by allowing the motion within the trajectory to be nonlinear. In addition,the local image deformation accounts for the spatial velocity gradient and its change along the trajectory.The principle for reduction of the measurement error is threefold: by enlarging the temporalmeasurement interval, the relative error becomes smaller secondly, the random error is reduced with the useof a least-squares polynomial fitting approach to the individual trajectory and finally, the use of nonlinearfitting functions allows for a reduction in truncation errors. The evaluation of velocity proceeds then directlyfrom the analytical derivatives of the least-squares functions. The principal features of this algorithm arecompared with a single-pair iterative image deformation method through the use of synthetic imagesequences depicting steady flows (solid body rotation and uniform motion), and with an application to anexperimental data set of a submerged circular jet.