需要购买原儿茶醛 红花苷 Crocin 红花素 羟基红花黄色素C 羟基红花黄色素K 丹酚酸B 10羟基-a-葵烯酸,请问哪里有卖?
叶黄素只能从外界摄取,这就需要我们通过吃大量的蔬菜水果补充,富含叶黄素的果蔬有:玉米、甘蓝菜、南瓜、地瓜叶、橙子、橘子、猕猴桃、芒果等。界摄取,这就需要我们通过吃大量的蔬菜水果补充,富含叶黄素的果蔬有:玉米、甘蓝菜、南瓜、地瓜叶、橙子、橘子、猕猴桃、芒果等。
叶黄素属于类胡萝卜素的一种,是视网膜黄斑的主要色素,但叶黄素在人体内不能自行合成,主要是通过进食蔬菜或水果维持体内叶黄素的需求,叶黄素含量较高的食物主要有菠菜、西兰花、芥菜、芹菜叶、胡萝卜、香菜、西红柿等蔬菜,以及柑桔、猕猴桃、鲜枣、芒果等水果。含叶黄素高的食物:1、蔬菜类。蔬菜类中含有叶黄素的食物较多,如南瓜、胡萝卜、西红柿、菠菜、甘蓝菜、绿花椰菜、韭菜、小白菜、芹菜叶、香菜等,这些绿叶蔬菜及黄橙色蔬菜中都含有较多的叶黄素,通常是人们补充叶黄素的重要蔬菜来源。2、水果类。水果类含有叶黄素较多的食物,有芒果、猕猴桃、葡萄、黄桃、橙子、橘子等。3、谷物类。谷物类中含叶黄素多的食物有玉米、小米等,同样这些谷物制品中也含有叶黄素,如玉米面、小米糕等。4、其他食物。除了上述这些食物之外,还有鸡蛋的蛋黄、红薯等中也含有大量的叶黄素,同时一些花卉中也含有较多叶黄素,如万寿菊、金盏花,这些花卉本身不可以食用,但可作为提取叶黄素的原材料,将提取的叶黄素应用到乳制品、脂肪制品、糖果、烘烤类食品等的制作中。叶黄素的作用:1、保护视力。太阳光中含有强烈的紫外线和蓝光,可以伤害视网膜和黄斑,其中蓝光对人眼的伤害甚至比紫外线还大,叶黄素能够吸收蓝光和紫外线,并协助黄斑过滤蓝光,协助视网膜抵挡紫外线,从而避免蓝光和紫外线损害视力,此外太阳光具有强氧化性,很容易损伤黄斑,眼睛若长期受到强光直射会生成大量的氧自由基,使黄斑区和视网膜退化,视力严重减退,甚至失明,叶黄素是还原剂,有强抗氧化的作用,可以抑制氧自由基生成,所以补充叶黄素,有助于保护眼睛,尤其是保护视网膜和黄斑。可以保护视力,延缓视力进展,减少视力损害。2、抗氧化作用。氧自由基可加速人体各种器官的老化,对眼睛和皮肤损害尤其严重,再加上太阳光中紫外线的照射,更会加速皮肤的老化,叶黄素具强抗氧化能力,能够抑制氧自由基生成,不仅能保护眼睛,还能保护皮肤,在一定程度上能够延缓皮肤的老化。3、其他。叶黄素对于减缓早期动脉硬化的发展也有一定作用,还可以辅助加强胰岛素降血糖的功能,减少患糖尿病的风险。
精密称取姜黄素样品约0.0015 g置50 ml容量瓶中,加流动相超声溶解,冷却至室温,用流动相稀释至刻度,摇匀,精密移取1 ml置50 ml容量瓶中。加流动相稀释至刻度,摇匀,滤过,作为供试品溶液。流动相:乙腈:5%冰醋酸=45:55流速:0.9 mL/min柱温:40 ℃检测器:UV 340 nm进样量:20 μLSpursil C18,250×4.6 mm,5 μm http://dikma.com.cn/Public/Uploads/images/898(9).JPGDiamonsil C18,250×4.6 mm,5 μmhttp://dikma.com.cn/Public/Uploads/images/898(8).JPGDiamonsil C18(2),250×4.6 mm,5 μmhttp://dikma.com.cn/Public/Uploads/images/898(10).JPG图例:1,2-杂质3-姜黄素
请问日落黄,柠檬黄,姜黄素,栀子黄,玉米黄色素,喹啉黄,羟基红花黄色素A,红曲色素,叶黄素,β-胡萝卜素的极性大小排序是怎样的?谢谢各位了!!!
样品为复方维生素,其中一项是核黄素磷酸钠,没找到核黄素磷酸钠的对照品,故用的核黄素对照品样品制备:先用水溶,然后用流动相稀释,流动相弱酸性做出的结果比标示量低了很多啊用核黄素对照品代替核黄素磷酸钠对照品,请问结果可信吗?
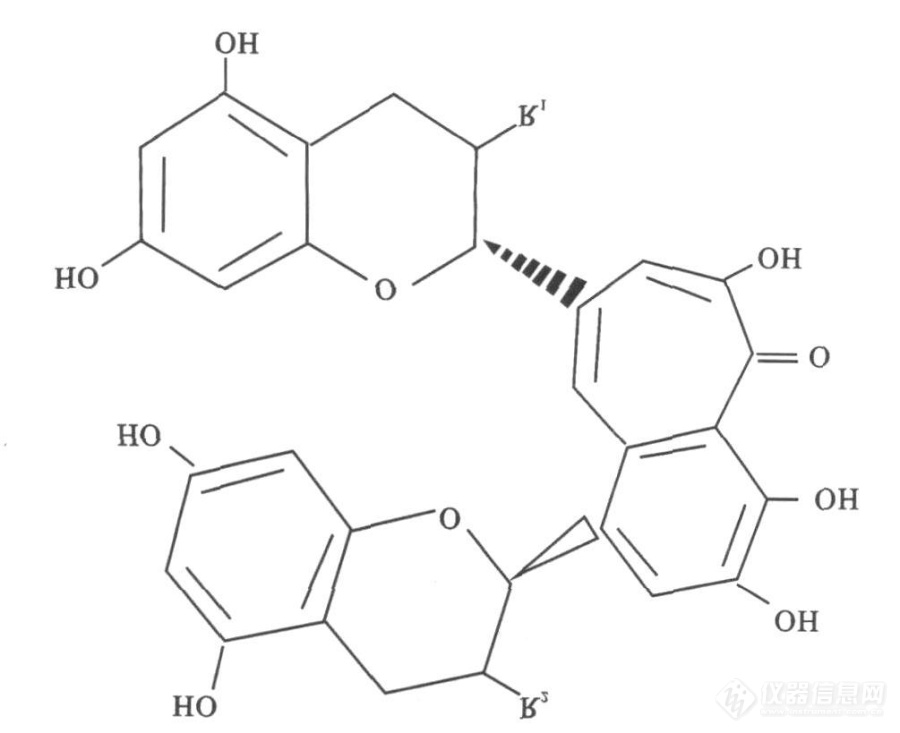
[align=center]茶黄素[/align][align=center] 邱雪[/align][align=left]摘要:[font='arial'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]茶黄素是一种金黄色色素,是茶叶发酵的产物[/back][/color][/font][font='arial'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]。其在人体的身体健康保健中有不可忽视的作用。[/back][/color][/font][font='arial'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]这篇文章将从多个方面向大家介绍茶黄素。并且介绍一些检测方法[/back][/color][/font][font='arial'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]检测其在[/back][/color][/font][font='arial'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]含量。[/back][/color][/font][/align][align=left][font='arial'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]关键词:理化性质;应用;限量;检测;标准[/back][/color][/font][/align][align=left][/align][align=left][font='arial'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]1.[/back][/color][/font][font='arial'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]前言[/back][/color][/font][/align]茶黄色素又称茶黄素,是存在于红茶中的一种金黄色色素,是茶叶[url=https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E5%8F%91%E9%85%B5/661835][color=#000000]发酵[/color][/url]的产物。在生物化学上,茶黄色素是一类多酚羟基具苯骈酚酮结构的物质,是第一个从茶叶中找到具有确切药理作用的化合物。茶黄色素占干茶重量的0.5%到2%,且取决于红茶加工的方法。茶黄色素在茶汤中鲜亮的颜色和浓烈的口感方面,起到了一定的作用,是红茶的一个重要的质量指标。茶黄色素以多酚类物质、[url=https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E5%84%BF%E8%8C%B6%E7%B4%A0][color=#000000]儿茶素[/color][/url]为主要成分,还含有[url=https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E6%B0%A8%E5%9F%BA%E9%85%B8][color=#000000]氨基酸[/color][/url]、维生索C、[url=https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E7%BB%B4%E7%94%9F%E7%B4%A0E][color=#000000]维生素[/color][/url][url=https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E7%BB%B4%E7%94%9F%E7%B4%A0E][color=#000000]E[/color][/url]、[url=https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E7%BB%B4%E7%94%9F%E7%B4%A0A%E5%8E%9F][color=#000000]维生素[/color][/url][url=https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E7%BB%B4%E7%94%9F%E7%B4%A0A%E5%8E%9F][color=#000000]A[/color][/url][url=https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E7%BB%B4%E7%94%9F%E7%B4%A0A%E5%8E%9F][color=#000000]原[/color][/url]、[url=https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E9%BB%84%E9%85%AE][color=#000000]黄酮[/color][/url]及[url=https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E9%BB%84%E9%85%AE%E9%86%87][color=#000000]黄酮醇[/color][/url]等。茶黄素是茶色素的主要成分,共有12种组分,其中茶黄素、[url=https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E8%8C%B6%E9%BB%84%E7%B4%A0-3-%E6%B2%A1%E9%A3%9F%E5%AD%90%E9%85%B8%E9%85%AF/9600430][color=#000000]茶黄素[/color][/url][url=https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E8%8C%B6%E9%BB%84%E7%B4%A0-3-%E6%B2%A1%E9%A3%9F%E5%AD%90%E9%85%B8%E9%85%AF/9600430][color=#000000]-3-[/color][/url][url=https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E8%8C%B6%E9%BB%84%E7%B4%A0-3-%E6%B2%A1%E9%A3%9F%E5%AD%90%E9%85%B8%E9%85%AF/9600430][color=#000000]没食子酸酯[/color][/url]、茶黄素-3,3’-双没食子酸酯和茶黄素-3’-没食子酸酯是4种最主要的茶黄素。在茶叶加工中主要由简单儿茶素和[url=https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E6%B2%A1%E9%A3%9F%E5%AD%90%E5%84%BF%E8%8C%B6%E7%B4%A0/9802086][color=#000000]没食子儿茶素[/color][/url]配对氧化缩合而成。茶黄素类的发现与红茶发酵过程的研究密切相关。[font='calibri'][size=13px][1][/size][/font]2.[font='b5+华光楷体_cnki'][size=18px] [/size][/font]分子结构和理化性质[font='calibri'][size=13px][1][/size][/font]茶黄素是一类具有苯并卓酚酮结构化合物的总称[font='calibri']?[/font]其中茶黄素(theaflavin[font='calibri']?[/font]TF1)、茶黄素-3-没食子酸酯(theaflavin-3-gallate[font='calibri']?[/font]TF2A)、茶黄素-3′-没食子酸酯(theaflavin-3′-gallate[font='calibri']?[/font]TF2B)和茶黄素双没食子酸酯(theaflavin-3[font='calibri']?[/font]3[font='calibri']′[/font]-digallate[font='calibri']?[/font]TF3)是4种主要的茶黄素[font='calibri']?[/font]其化学结构如图1。茶黄素的红外光谱表明[font='calibri']?[/font]所有茶黄素的最大吸收都出现在380nm和460nm。茶黄素纯物呈橙黄色针状结晶[font='calibri']?[/font]熔点237~240[font='宋体']℃[/font][font='calibri']?[/font]易溶于水、甲醇、乙醇、丙酮、正丁醇和乙酸乙酯难溶于乙醚不溶于三氯甲烷和苯。茶黄素溶液呈鲜明的橙黄色水溶液呈弱酸性pH 约5.7[font='calibri']?[/font]颜色不受茶提取液 pH 影响[font='calibri']?[/font]但在碱性溶液中有自动氧化的倾向且随pH的增加而加强。[img]https://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2021/07/202107161930268731_216_1608728_3.png[/img]图13. 茶黄素的药理功效[font='calibri'][size=13px][2][/size][/font]3.1 抗氧化自由基学说认为,正常人体内的自由基与抗氧化物质处于平衡状态。 当人体器官和组织的细胞膜在自由基过量时便可能遭受其进攻,引起脂质过氧化、蛋白质变性、DNA 链断裂、细胞解体、机体衰老,并可能诱发肿瘤等恶性疾病。 体内过量的超氧阴离子及双氧水等,是产生毒副作用的重要因素。 细胞中的主要抗氧化酶超氧化物歧化酶(Superoxide Dismutase,SOD)能够将 超 氧 阴 离 子 催 化 分 解 为 双 氧 水 (Hydrogen Oxygen,H2O2),H2O2 在过氧化氢酶(Catalase,CAT)或硒谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶 (Selenium-glutathione Peroxidase,Se-GSH-Px)催化作用下迅速转化为无毒的 O2 和 H2O。 TFs 具有良好的抗氧化性,如 TFs可以清除自由基,防止脂质过氧化,提高 SOD、谷光 甘 肽 硫 转 移 酶 (Glutathione S -Transferase,GST)、醌还原酶(Quinone Reductase,QR)的活性,增强人体免疫力。在低密度脂蛋白 (Low Density Lipid,LDL)模型中,TFs 能够抑制二价铜离子介导的脂质过氧化。 研究表明,巨噬细胞中 LDL 氧化程度与金属离子浓度有关,金属离子浓度升高,LDL 氧化程度也升高,而 TFs 能抑制 LDL 的氧化,这与它能螯合金属离子有关。 YOSHIDA 等和 HAN 等用 TFs 类化合物分别处理鼠巨噬细胞和人内表皮细胞,以考察细胞 LDL 氧化能力,结果显示 TFs能与脂质氧合酶的活性中心铁结合,从而降低脂质氧合酶的活性,并抑制细胞 LDL 氧化。另外,TFs对外源性因子引起的生物膜脂质过氧化反应有较好的效果。如持续高强度的有氧运动会使肌肉酸痛肿胀,每天给予高强度有氧运动的男大学生1760 mg 富含茶黄素的红茶提取物,持续 9 天,发现其能够缓解酸痛肿胀,即茶黄素能够提高肌肉损伤恢复能力并降低氧化应激程度。茶黄素作为天然植物多酚类成分,可形成氢自由基,淬灭体内产生的自由基,从而保护组织,起到延缓衰老、抗突变、抗癌、杀菌消炎、防治心血管疾病和动脉粥样硬化等功能, 故在医药领域得到人们广泛关注。因此,加强茶黄素类成分抗氧化机理研究与临床用药的应用显得尤为迫切。3.2 抗心脑血管疾病 心血管疾病是心脏和血管疾患的总称,包括高血压、冠心病、脑血管疾病(中风)、周围血管疾病、血栓性疾病、动脉粥样硬化、心力衰竭、心脏病等。经济转型、城市化、工业化及全球化带来生活方式的改变,包括吸烟、缺乏活动、不健康饮食是导致心血管疾病增加的重要因素。每年死于心血管疾病的人数多于其它任何病因,成为全球头号死因。 MARON 等设计了一种含有75 mg TFs、150 mg儿茶素和150 mg其他多酚的胶囊, 给予240 名 18 岁以上高胆固醇成年人群低脂饮食 12周,且每日服用该胶囊。结果表明试验组能够使总胆固醇及低密度脂蛋白分别降低 11.3%和 16.4%,高密度脂蛋白与甘油三酯增长2%左右,降脂效果优于不含 TFs 的绿茶多酚胶囊。茶黄素不仅通过抑制脂肪酸合成、 激活脂肪酸的氧化消耗来降低脂肪积累,也通过肝激酶 B(Liver Kinase B1,LKB1)与活性氧途径激活 5'—磷酸腺苷 (Adenosine 5'-Monophosphate,AMP)依赖的蛋白激酶(Activated Protein Kinase,AMPK)达到抑制乙酰辅酶 A 羧化酶,降低肝脏脂质累积的作用。在试验组与对照组在粪便量上没有显著差异的情况下,茶黄素能够抑制高脂饮食肥胖鼠体重增加及内脏脂肪累积。茶黄素可以明显抑制由胶原、ADP、前列腺素 H2(PGH2)/血栓素 A2(TxA2)(TP)受体激动剂 U46619 等多种刺激剂引起的人体血小板聚集,且呈现出剂量依赖效应。茶 黄 素 还是血小板非受体酪氨酸激酶(NonReceptor Cytoplasmic Tyrosine Kinases,SYK)胶原引起的血小板活性的一个重要的靶点抑制剂,茶黄素组和对照组相比,小鼠肠系膜动脉血管形成血栓性堵塞的时间明显延长,充分证明了茶黄素对血小板功能的抑制,且优于目前临床使用的抗血小板药物,如存在着出血、引起胃肠道不适等副作用的药物阿司匹林。3.3 抗炎症作用炎症(Inflammation)是机体对于刺激的一种防御反应,表现为红、肿、热、痛和功能障碍,包括感染引感染性炎症及非感染性炎症。任何能够引起组织损伤的因素,如致炎因子 (Inflammatory Agent)都可成为炎症的原因。每日口服 5 mg/kg 剂量的TF-3,3’-G 能够显 著改善三硝基苯磺酸(Trinitro Benzene Sulfonic Acid,TNBS)诱导的结肠炎,降低结肠上皮粘膜肿瘤坏死因子(Tumor Necrosis Factor,TNF -α)、 白细胞介素 -12(Interleukin 12,IL-12)、人干扰素-g(Interferon-g, IFN-g) 及诱导型一氧化氮合酶 (Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase,iNOS)基因与蛋白表达水平。同时茶黄素能抑制佛波酯促使的 TNF-α、白细胞介素 1β(Interleukin -1 beta,IL-1β)及白细胞介素6(Interleukin 6,IL-6)的活性。 TFs 能够有效阻止脂多糖 (Lipopolysaccharide,LPS) 诱导的巨噬细胞促炎反应,包括抑制IL-6、单核细胞趋化蛋白(Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1,MCP-1)、细胞间粘附分子-1(Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1,ICAM-1)的表达,并有效阻止 LPS 诱导的核因子抑制蛋白(Inhibitor of Nuclear Factor kappa B alpha,IκBα)与核易位蛋白(Nuclear Translocation of REL-Associated Protein,RelA),胞外信号调控激酶(Extracellular Signal Regulated Kinase,ERK1/2)、c-Jun 氨基末端激酶(c-Jun-N-Terminal Kinase,JNK)及 p38 丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase,p38 MAPK)的表达[14];在急性肺损伤小鼠模型中,TF-3,3’-G 通过减少促炎因子降低急性肺损伤(Acute Lung Injury,ALI),抑制 LPS 诱导的NK及 p38 MAPK 丝裂原活化蛋白激酶的表达。风湿性关节炎(Rheumatoid Arthritis,RA)或骨关节炎(Osteoarthritis,OA)最明显的特征是关节软骨的损伤。引起关节损伤和疼痛的 IL-1β 和IL-18 在 RA 和 OA 中促炎症因子发挥重要作用。在 IL-1β 诱导建立的 OA 细胞模型中,TF-3,3’-G 能够明显改善 OA 软骨细胞形态,上调软骨细胞分子标志物 II 型胶原(Type II Collagen,Col II)mRNA 的表达, 还可以下调炎症因子 IL-1β 与IL-6 mRNA 的表达,降低炎症诱导酶环氧化酶(Cyclooxygenase-2,COX-2)蛋白表达量;并可增强软骨细胞合成因子活性、 减弱分解因子活性并抑制细胞炎症反应, 有效延缓大鼠软骨细胞炎性退变进程。 同时,茶黄素还可显著下调由血管紧张素 II(Angiotensin II,AngII) 诱导的促炎因子 IL -6mRNA 的表达,降低由 AngII 刺激产生的大鼠血管平滑肌细胞(Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell,VSMC)中ROS水平,达到抵抗 AngII 引起的大鼠VSMC 细胞炎症作用。慢性阻塞性肺疾病(Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease,COPD)的突出特征是慢性炎症致气道阻塞,引起不完全可逆的气流受限,从而引发一系列临床症状。以往的研究表明,气道黏液高分泌是导致气流受限的危险因素。在刺激气道的各种炎性因子中,中性粒细胞弹力蛋白酶(Neutrophil Elastase,NE)被认为是肺炎性级联反应的终效应分子,以及炎症气道微生态平衡的重要恶化性推动因素,茶黄素被证明能够起到抑制气道黏液高分泌的作用。此外以高频雾化的方式使大鼠吸入茶黄素乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物(Poly Lactic Co Glycolic Acid,PLGA)纳米粒,能够抑制香烟引起的炎性气道黏蛋白(Mucoprotein 5AC,MUC5AC)高分泌作用。3.4 抗病毒与抗菌作用严重急性呼吸系统综合症(Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome,SARS)由 SARS 冠状病毒引起,该病毒属于包膜病毒,包含正极性单链 RNA,其所含有的一个开放的阅读框用于编辑两个重叠的多聚蛋白,PP1a(Polyprotein-1a,450 kDa)与PP1ab(Poplyprotein-1ab,750 kDa)负责病毒的复制。同时冠状病毒都编辑生成 Papline 类似蛋白及胰凝乳蛋白酶(Chymotrypsin,3CLPro)类似蛋白,用于病毒成熟过程中蛋白水解加工。 Papline 类似蛋白水解酶在 PP1a 蛋白上只含不超过 2 个的剪切位点,而 3CLPro 蛋白酶在PP1a 与 PP1ab 内在区域含有至少 11 个剪切位点。在720个筛选的天然化合物中仅发现 TF-3,3’-G 能够有效抑制3CLPro。并且 SARS 冠状病毒在胃肠道中的复制非常活跃, 红茶中的茶黄素类化合物具有预防该病毒对人体的侵染的应用潜力。1%的乳酸(pH4.0)能显著抑制对于单纯性 1型与 2 型疱疹病毒所引起的生殖器溃疡,但当pH4.5 时,则失去抑制活性状态。 茶黄素特别是TF-3,3’-G 能够在 5.7pH4.5 区间独立发挥作用,并在非洲绿猴肾细胞及人非小细胞肺癌细胞 A549 中得到验证。同时茶黄素还能够抗流感病毒,通过与血凝素 HA2 亚基结合,抑制病毒的神经氨酸酶活性从而抵抗高致病性禽流感(H5N1)病毒的感染。并且,TFs 可作为第二代杀微生物剂用于预防人类免疫缺陷毒(HumanImmunodeficiency Virus,HIV)的性传播,在高浓度时,还能抑制逆转录酶的活性。 白念珠菌(C.Albicans)是一种腐物寄生菌,作为机会性条件致病菌,平时生存于人体的皮肤、粘膜、 消化道及其他脏器中。当机体抵抗力降低时,白色念珠菌就会繁殖,达到一定量时,人体就会发病,通过微感染而引起的粘膜念珠菌病,对癌症、HIV 及重症病人还会造成致命性打击。茶黄素对白念珠菌 NCTC 3255 和 NCTC 3179 能够起到很强的抑制作用,其最低抑制浓度为1024 μg/mL,联合儿茶素时其最低抑菌浓度降为128 μg/mL。3.5 抗肿瘤在肝癌细胞体外处理中, 茶黄素类化合物能够通过抑制 STAT3 信号转导与转录激活因子磷酸化,并进一步阻止其下游抗凋亡蛋白 BCL-2 与生存素(Survivin)及入侵相关蛋白 MMP-2、MMP-9 来达到显著抑制肝癌细胞的迁移、入侵的作用,诱使其凋亡。此外,茶黄素类化合物对人类白血病细胞系 HL-60 与 K-562 呈剂量依赖性抑制,阻止细胞G1 期,活化 Caspase 3 和 Caspase 8,下调 BCL-2,同时上调 BAX 蛋白。4.检测[font='calibri'][size=13px][1][/size][/font]4.1 Roberts 法Roberts 法是根据茶黄素和一部分茶红素(TRsⅠ型)溶解于乙酸乙酯或4-甲基-戊酮(IBMK)这部分可利用其能溶于碳酸氢钠溶液而分离茶红素(TRsⅡ型)留在水层。该方法存在重复性差、测定含量值偏低的缺点[font='calibri']?[/font]但其方法简单、试剂价格便宜且同时测定茶红素的含量[font='calibri']?[/font]因此被广泛采用。4.2 a-氨基乙基二苯酸酯(Flavognost)试剂分析法Hiton 提出的一种快速测定方法。根据茶黄素分子中的苯并卓酚酮核可以与 Flavognost 试剂产生特异性反应产生绿色络合物测定其吸光值换算成茶黄素含量。与 Roberts 法相比[font='calibri']?[/font]该方法具有较好的重现性已被Ellis推荐为国际红茶最低质量标准的检测方法。但该法受到提取液、提取温度、水的pH值等因素的影响[font='calibri']?[/font]Flavognost 试剂仅与茶黄素顺式上的两个羟基结合[font='calibri']?[/font]使测定结果偏低[font='calibri']。[/font]同时Flavognost试剂不易购得。4.3 氯化铝比色法Likoleche-Nkhoma J W 等用 AlCl3 代 替Flavognost 试剂[font='calibri']?[/font]铝盐与茶黄素复合产生红色[font='calibri']?[/font]于波长525nm 具有最大吸收根据吸光值折算成茶黄素含量。该方法的测定值与 Flavognost 方法测定结构没有显著差异且铝盐的价格较便宜[font='calibri']?[/font]但样品中加入过量的铝盐会产生浑浊。4.4 Sephadex LH-20柱层析(Column Chromatography[font='calibri']?[/font]CC)法此方法是竹尾忠一提出的。该方法能有效地分离茶黄素而且对茶黄素的主要组分能定量[font='calibri']?[/font]但操作复杂。4.5 Whitehead 法Whitehead D L 等利用色素极性大小差异[font='calibri']?[/font]提出的一种快速测定茶黄素总量的方法[font='calibri']?[/font]该方法适于实验室和工厂的常规检测[font='calibri']?[/font]但测量值偏高。4.6 高效液相色谱法(High performance LiquidChromatography[font='calibri']?[/font]HPLC)Bailey R G 等使用光电二级管列检测器的反相 HPLC 研究红茶溶出物的性质[font='calibri']?[/font]4种茶黄素能够得到分离纯化[font='calibri']?[/font]提出了 HPLC 法测定茶黄素主要组分及其它物质的方法。HPLC 法更精确[font='calibri']?[/font]并能使各茶黄素单体得到较理想的分离。但该法需要高纯度的茶黄素标样。4.7 毛细管电泳法(Capillary Electrophoresis[font='calibri']?[/font]CE) Bee B L 等首次采用毛细管电泳测定儿茶素类化合物和茶黄素类化合物。Wright L P 等用非水相毛细管电泳测定红茶中的4种主要茶黄素[font='calibri']?[/font]并对有机溶剂的组成和电解质浓度对分离效果的影响进行了研究[font='calibri']?[/font]确定了最佳的分离溶剂组成为 V(乙腈)[font='宋体']∶[/font]V (甲醇)[font='宋体']∶[/font]V (乙酸)=71[font='宋体']∶[/font]25[font='宋体']∶[/font]4和90mmol/L 的醋酸铵[font='calibri']?[/font]10min 内实现了茶黄素的基线分离[font='calibri']?[/font]与常规毛细管电泳相比具有显著的优势。4.8 高速逆流色谱法(High Speed CountercurrentChromatography[font='calibri']?[/font]HSCCC) 高速逆流色谱法可避免样品与固体载体的化学反应和死吸附等缺点[font='calibri']?[/font]每次分离样品结束后[font='calibri']?[/font]管道中的残留溶剂均可以冲出[font='calibri']?[/font]不会对后续分离产生任何影响[font='calibri']?[/font]因此高速逆流色谱法分离样品具有高的回收率。 总之茶黄素的分析测定方法各有利弊[font='calibri']?[/font]可以根据具体情况选择一种切实可行的分析方法。5.结语 茶黄素总的来说是对人身体有益,但是要适量食用,身体保健从平时做起。参考文献:[1][font='b5+华光楷体_cnki'][size=18px][color=#000000] [/color][/size][/font]王洪新 孙军涛 [J]食品与生物技术学报 茶黄素的制备、分析、分离及功能活性研究进展[2] 涂云飞 茶黄素药理功效及分离纯化研究进展 [j] 健康与文化[3] MARON D J, LU G P, CAI N S, et al. Cholesterol-loweringeffect of a theaflavin-enriched green tea extract [J]. Archives of Internal Medicine, 2003, 163(12): 1448-1453[4] KUNDU T, DEY S, ROY M, et al. Induction of apoptosis in human leukemia cells by black tea and its polyphenol the aflavin [J]. Cancer Letter, 2005, 230(1): 111-121
姜黄素是从姜科、天南星科中的一些植物的根茎中提取的一种化学成分,其中,姜黄约含3%~6%,是植物界很稀少的具有二酮的色素,为二酮类化合物。姜黄素为橙黄色结晶粉末,味稍苦。不溶于水。在食品生产中主要用于肠类制品、罐头、酱卤制品等产品的着色。医学研究表明,姜黄素具有降血脂、抗肿瘤、抗炎、利胆、抗氧化等作用。 姜黄素 Curcumin Turmeric yellow, Diferuloylmethane 1,6-Heptadiene-3,5-dione,1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)- C21H20O6; 368.37 橙黄色结晶性粉末, 熔点183°。不溶于水及乙醚, 溶于乙醇及冰醋酸。 有机酸及酚类。
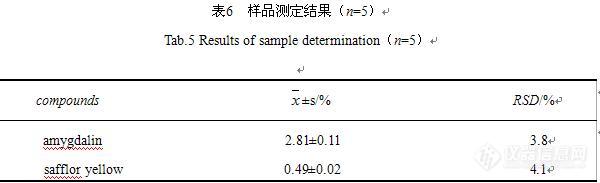
HPLC法测定桃红四物汤中苦杏仁苷和红花黄色素的含量摘 要 目的:测定桃红四物汤水提液中苦杏仁苷和红花黄色素含量。方法:采用高效液相色谱法(HPLC)测定桃红四物汤中苦杏仁苷和红花黄色素含量。苦杏仁苷色谱条件:流动相:甲醇-水(27∶73) ;色谱柱Hypersil BDS C18(4.6mm×200mm, 5µm),柱温25 ℃,检测波长218 nm;红花黄色素色谱条件:流动相:甲醇-0.1%磷酸水溶液(20∶80),色谱柱Hypersil BDS C18(4.6mm×200mm, 5µm),柱温25℃,检测波长:403nm。流速均为1.0mL·min-1,进样量均为:20μL。结果:苦杏仁苷在0.0822~1.315mg·mL-1范围内线性关系很好( r = 0.9998 ),平均回收率为98. 87 %,RSD为1.2%;红花黄色素在2.34×10-2~7.50×10-1 mg·mL-1范围内线性关系良好(r=0.9805),平均回收率为99.20%,RSD为0.88%。结论:本法简单快捷,重现性好,可作为桃红四物汤中苦杏仁苷和红花黄色素的质控方法。关键词:桃红四物汤;苦杏仁苷;红花黄色素;高效液相色谱法ABSTRACT Objective:To determine amygdalin and safflor yellow(SY)in Taohong Siwu Decoction.Methods:amygdalin was analyzed by HPLC on a Hypersil BDS C18 column (4.6mm×200mm, 5µm),[/color
请问在食品和工业上常用的黄色素有哪些?工业上指的主要是通常可能非法添加于食品中的黄色素。还想请问下面这些都是常用的黄色素吗??日落黄,柠檬黄,姜黄素,栀子黄,玉米黄色素,辣椒橙,喹啉黄,羟基红花黄色素A,红曲色素,叶黄素,β-胡萝卜素小女子初来贵地,谢谢各位了!![em31]
类胡萝卜素是一类广泛存在于自然界中的脂溶性色素,它为许多食品提供红色或黄色色泽。存在于植物的叶、茎、花、根或果实中,自然界中的类胡萝卜素以岩藻黄素(存在于藻类)最多,其次是存在于绿叶中的叶黄素、紫黄素和新黄素,其他的类胡萝卜素如β一胡萝卜素广泛存在于胡萝卜、南瓜、辣椒等蔬菜中:水果、蛋黄、奶油中的含量也较丰富。类胡萝卜素按其组成可以分为两大类,即胡萝卜素类和叶黄素类。1.番茄红素从结构上来看番茄红素是直链开环结构,无维生素A的功能,具有防癌抗癌作用,主要存在于番茄中。(1)“α-胡萝卜素“α-胡萝卜素分子断裂后可形成一分子维生素A,主要存在于胡萝卜中,其次是番茄。(2)β-胡萝卜素β-胡萝卜素则形成2分子维生素A,并且自然界中三种胡萝卜素以它占多,分布最广。1μg的β-胡萝卜素相当于1.6IU的维生素A。主要存在于胡萝卜中,其次是番茄中。(3)r-胡萝卜素 r-胡萝卜素分子断裂后可形成一分子维生素。2.叶黄素类(Xanthophylls)叶黄素类是共轭多烯烃的加氧衍生物,即在分子中含有羟基、甲氧基、羧基、酮基或环氧基,多呈浅黄、橙、黄等色泽;在绿叶中它们的含量一般比叶绿素多一倍,常见的叶黄素类色素有以下的十几种,它们可以简单地被认为是胡萝卜素类的衍生物。性质:①低浓度呈橙黄色至黄色,高浓度为橙红色;②不溶于水、甘油、丙酮、酸、碱,微溶乙醇和食用油,易溶苯、石油醚;③酸性不稳定,弱碱较稳定,不受还原物影响;④光、热、空气使其色泽变淡;⑤重金属(铁)使其褪色。
心脑血管疾病是全球发病率、死亡率最高的疾病,近年来以动脉粥样硬化为代表的心脑血管疾病的发病率持续升高,严重威胁人们的身体健康,给家庭和社会带来沉重的负担,已成为一个重要的公共卫生问题[1]。心血管疾病已成为威胁人类健康的最主要疾病,其中动脉粥样硬化是心血管疾病的主要原因和病理基础。动脉粥样硬化常累及大动脉、中动脉,临床主要特征为慢性管腔狭窄,是冠心病、脑梗死、外周血管疾病等心脑血管疾病的主要病理基础,可影响心脏、大脑、肾脏、眼睛、外周血管的动脉系统[2]。大黄素从大黄、虎杖的根和树皮中获得的蒽醌衍生物,是橙色长针状晶体,易溶于醇和碱性溶液,几乎不溶于水[3]。大黄素具有抗肿瘤、抗炎、免疫抑制、镇痛、器官保护等多种药理作用,临床可用于痢疾、肺炎、脑炎、中耳炎、小儿麻痹、肝炎、肿瘤、心脑血管疾病等多种疾病的治疗[4]。大黄素可通过降低炎症反应、降低氧化应激反应、调节脂质代谢、阻止血管平滑肌增殖、保护血管内皮功能、稳定动脉粥样硬化斑块等多种途径对动脉粥样硬化发挥防治作用。本文综述了大黄素防治动脉粥样硬化的作用机制研究进展,为大黄素防治动脉粥样硬化的临床应用提供参考。 1 降低炎症反应 1.1 阻止核因子-κB(NF-κB)激活 NF-κB是动脉粥样硬化的重要信号通路,可介导主动脉平滑肌细胞中促炎细胞因子和生长/迁移因子表达,促进主动脉平滑肌细胞的增殖和迁移,促进动脉粥样硬化的形成[5]。Meng等[6]使用大黄素干预大鼠主动脉平滑肌细胞,结果0.1~10 μmol/L大黄素可呈浓度相关性抑制肿瘤坏死因子-α(TNF-α)对主动脉平滑肌细胞的促增殖作用,阻止主动脉平滑肌细胞迁移和基质金属蛋白酶(MMP)-2、MMP-9的表达,降低白细胞介素(IL)-6、IL-1β、血管细胞黏附分子-1、细胞间黏附分子-1、单核细胞趋化蛋白1(MCP-1)等炎症因子的表达,抑制TNF-α引起的主动脉平滑肌细胞中NF-κB的活化,结果证实大黄素可通过阻止NF-κB激活以发挥抗炎作用,降低动脉粥样硬化的病情。赵剑锋等[7]使用高脂饲料饲养大鼠建立动脉粥样硬化模型,结果600、900、1 200 mg/kg大黄素能呈浓度相关性抑制大鼠体质量增加,继而降低低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(LDL-C)、总胆固醇(TC)的水平,显著降低超敏C反应蛋白(hs-CRP)、纤维蛋白原(FIB)的水平,表明大黄素可通过抗炎发挥抗动脉粥样硬化的作用。吴迪等[8]使用大黄素干预大鼠血管平滑肌细胞,结果50 μmol/L大黄素能抑制血管平滑肌细胞重叠和变性,抑制CRP、一氧化氮合酶(iNOS)、TNF-α基因和蛋白的表达,表明大黄素能通过抑制多种炎症因子的表达发挥抗动脉粥样硬化的作用。 1.2 调节γ-干扰素(IFN-γ)、MCP-1的分泌 IFN-γ属于II型干扰素,能抑制LDL-C的表达,阻止泡沫细胞的形成,在动脉粥样硬化进程中发挥双向调节作用[9]。MCP-1能促使单核细胞聚集,促进泡沫细胞形成,加速动脉粥样硬化的形成,介导多种促炎因子的分泌和血管内皮的增殖[10]。夏丽等[11]使用大黄素干预高脂饲料诱导的载脂蛋白E缺陷动脉粥样硬化小鼠,结果显示,10、20、40 mg/kg大黄素能降低小鼠LDL-C、TC、三酰甘油(TG)的水平,提高高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(HDL-C)的水平,上调IFN-γ基因的表达,下调MCP-1基因的表达,降低血清IFN-γ、MCP-1水平,表明大黄素可通过调节IFN-γ、MCP-1的分泌减轻炎症反应,发挥抗动脉粥样硬化的作用。 1.3 抑制同型半胱氨酸(Hcy)的表达 血浆Hcy水平升高是动脉粥样硬化的独立危险因素,能够通过活性氧(ROS)和丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(MAPK)信号通路刺激血管平滑肌细胞中CRP的表达,加剧血管壁的炎症过程,从而促进动脉粥样硬化进程[12]。Pang等[13]使用大黄素干预大鼠血管平滑肌细胞,发现0.1、1、10、100 μmol/L大黄素能呈浓度相关性降低血管平滑肌细胞的活力,有效降低Hcy引起血管平滑肌细胞的CRP的表达,抑制细胞外信号调节激酶(ERK)1/2和p38磷酸化进程,以浓度相关性方式拮抗Hcy对过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ(PPARγ)表达的抑制作用,还有助于降低大鼠血清Hcy和CRP水平,表明大黄素通过抑制Hcy表达以阻止ERK1/2/p38信号通路激活和促进PPARγ表达,发挥抗动脉粥样硬化作用。 2 降低氧化应激反应 缺氧、氧化应激可通过磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶途径激活磷脂酶C,导致神经酰胺的形成,神经酰胺可调节细胞凋亡和炎症,有助于动脉粥样硬化或血栓性疾病的发展[14]。Hei等[15]使用1%胆固醇和5%脂肪的饮食喂食家兔建立动脉粥样硬化模型,结果10 mg/kg大黄素能显著降低兔血清丙二醛(MDA)、氧化低密度脂蛋白(OX-LOL)的水平,提高血清超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)的水平,显著减轻家兔动脉粥样硬化程度,降低主动脉的神经酰胺浓度、鞘磷脂酶活性和凋亡泡沫细胞指数,结果证实大黄素可通过抗氧化应激反应发挥抗动脉粥样硬化的作用。张翔等[16]使用大黄素治疗高脂饲料喂养的动脉粥样硬化大鼠,结果发现20、40、80 mg/kg大黄素有助于提高大鼠的体质量,呈剂量相关性降低MDA的水平,升高SOD、总抗氧化能力(T-AOC)的水平,减轻平滑肌细胞增生和向内膜迁移,提示大黄素通过抗氧化应激反应发挥抗动脉粥样硬化的作用。张翔等[17]使用大黄素治疗高脂饲料建立的动脉粥样硬化大鼠,结果20、40、80 mg/kg大黄素能浓度相关性降低LDL、TG、TC的水平,提高HDL的水平,上调SOD、T-AOC的水平,降低MDA的水平,减轻平滑肌增生、内膜迁移、内膜水肿等动脉粥样硬化改变,提示大黄素可通过抗氧化应激反应发挥抗动脉粥样硬化的作用。 3 调节脂质代谢 3.1 消耗胆固醇以破坏脂筏 脂筏位于细胞膜和内膜中,是含有高浓度胆固醇和鞘糖脂的微结构域,参与多种信号通路的活化,可加剧炎症反应,促进动脉粥样硬化的发展,GM1-神经节苷脂是脂筏的标志物,脂质筏的破坏将导致GM1-神经节苷脂从脂筏重新分布到细胞膜非脂质筏结构域[18]。胆固醇是脂筏中主要成分,胆固醇富集使脂筏比细胞膜周围富含磷脂的非筏相更紧密,消耗脂筏中的胆固醇可破坏脂筏[19]。Meng等[20]使用大黄素干预原代人脐静脉内皮细胞,结果1~50 μmol/L大黄素能显著降低脂多糖引起的IL-1β、IL-6、IL-8、趋化因子配体2、MCP-1等多种炎症因子的分泌,阻断核因子κB抑制因子α(IκBα)的降解和NF-κB活化,大黄素将脂筏中的GM1-神经节苷脂分散到膜或内膜的非脂质筏结构域,证实大黄素通过消耗胆固醇来破坏脂筏,阻止脂多糖诱导的人脐静脉内皮细胞中NF-κB活化,发挥抗炎作用,以减轻动脉粥样硬化进程。 3.2 激活PPARγ信号通路 PPARγ在巨噬细胞中大量表达,尤其是动脉粥样硬化内的脂质泡沫细胞,PPARγ通过转录诱导ox-LDL参与动脉粥样硬化进程,还能促进ATP结合盒转运体(ABC)A1、ABCG1的表达,通过肝X受体α(LXRα)介导巨噬细胞中胆固醇的外排,在动脉粥样硬化的炎症反应、胆固醇稳态中发挥关键作用[21]。Fu等[22]使用大黄素干预THP-1单核巨噬细胞,结果1、5、10 μmol/L大黄素能促进细胞中PPAR-γ蛋白和基因的表达,以浓度相关性促进载脂蛋白A1诱导的巨噬细胞内胆固醇外排,还能促进THP-1细胞中LXR-α(PPARγ靶点)的蛋白和基因的表达,促进ABCA1、ABCG1的表达,证实大黄素可通过激活PPARγ信号通路以促进胆固醇排除,发挥抗动脉粥样硬化的作用。Zhou等[23]使用脂肪喂养载脂蛋白E建立小鼠动脉粥样硬化斑块模型,结果发现10 mg/kg大黄素能显著减轻斑块中脂质核心面积和胶原蛋白数量,抑制斑块MMP-9、粒细胞巨噬细胞集落刺激因子(GM-GSF)的表达,促进PPARγ的表达,提示大黄素可通过激活PPARγ信号通路以促使动脉粥样硬化斑块稳定有关。 4 阻止血管平滑肌增殖 动脉内膜血管平滑肌细胞的增殖是动脉粥样硬化斑块形成的关键步骤,诱导动脉内膜血管平滑肌细胞凋亡或细胞周期停滞,还会损害血管内皮细胞生理机能,导致内膜增生[24]。Xu等[25]使用大黄素干预动脉内膜血管平滑肌细胞,发现0.05~5 μmol/L大黄素可呈浓度相关性抑制动脉内膜血管平滑肌细胞的增殖,显著降低了细胞周期蛋白依赖性激酶1(CDK1)、Ki67、E2F-1基因表达,显著降低线粒体活性,还能显著减轻大鼠损伤动脉的内皮化进程,证实大黄素可通过阻止血管平滑肌增殖以抗动脉粥样硬化。 活化的半胱天冬酶(Caspase)能促使Bid断裂,诱导细胞色素C从线粒体释放,激活线粒体途径,继而激活下游Caspase-3、Caspase-8、Caspase-9,导致多种DNA链断裂,导致细胞凋亡,以阻止血管平滑肌增殖[26]。Heo等[27]使用大黄素干预大鼠主动脉平滑肌细胞,发现0.1、1、10 mmol/L大黄素能浓度相关性抑制血小板源生长因子诱导的主动脉平滑肌细胞增殖,抑制IκBα的磷酸化,促进主动脉平滑肌细胞凋亡,促进Caspase-3、Caspase-8、Caspase-9的表达,还能调节B淋巴细胞瘤-2(Bcl-2)的表达,促使MMP紊乱,证实大黄素通过Caspase途径促进线粒体依赖性细胞凋亡,进而阻止血管平滑肌细胞增殖,降低动脉粥样硬化发生。 5 保护血管内皮功能 内皮型一氧化氮合酶(eNOS)/一氧化氮(NO)系统与动脉粥样硬化密切相关,前者活性降低可促进内皮细胞增生,抑制NO的合成,后者能强效促使血管舒张,阻止血管平滑肌增殖和血栓形成[28]。吴健虹等[29]使用大黄素治疗膳食诱导的高脂血症大鼠,10 mg/kg大黄素能显著降低LDL-C、TG、TC的水平,降低肝脏脂肪变性程度,显著提高胸主动脉的总NO的水平和eNOS基因和蛋白的水平,证实大黄素能上调eNOS/NO系统以保护血管内皮细胞,减轻动脉粥样硬化的风险。 6 稳定动脉粥样硬化斑块 MMP能特异性降解细胞外基质中多种胶原蛋白的表达,破坏动脉粥样硬化斑块纤维帽结构,导致血栓形成和斑块破裂[30]。白文武等[31]使用大黄素治疗高脂饮食建立的载脂蛋白E缺陷小鼠模型,结果60 mg/kg大黄素能显著抑制血管内膜增厚和平滑肌增生,抑制粥样斑块的形成,下调MMP-2、MMP-9的表达,提高组织抑制剂1(TIMP-1)的表达,证实大黄素可通过调节MMP的分泌以稳定动脉粥样硬化斑块,发挥抗动脉粥样硬化的作用。 7 结语 大黄素可通过降低炎症反应、降低氧化应激反应、调节脂质代谢、阻止血管平滑肌增殖、保护血管内皮功能、稳定动脉粥样硬化斑块等多种途径对动脉粥样硬化发挥防治作用。由于大黄素用于人体的机制尚不明确,目前大黄素多用于动物研究,尚未用于临床试验,因此,需要进一步的研究和更多的试验来验证大黄素对人动脉粥样硬化的益处。大黄素的肝毒性、肾毒性和口服生物利用度差的问题应该在未来的研究中得到解决。总之,大黄素防治动脉粥样硬化具有良好的应用前景,可能在未来用于临床实践。
实验配置10μg/ml和15μg/ml的硼酸加入4ml 0.002g/ml的姜黄素-冰醋酸溶液,再加入4ml浓硫酸1:1冰醋酸溶液,再用酸性甲醇定容的显色30min[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/5p][color=#3333ff]液相[/color][/url]进样实验结果两个峰面积非常接近,4271和4273于是再次稀释配置成0.2和0.3μg/ml的硼酸,按上述加入显色两个峰面积只相差100请问是否操作有问题呢[img]https://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2023/12/202312201554075586_9939_6199563_3.png[/img]
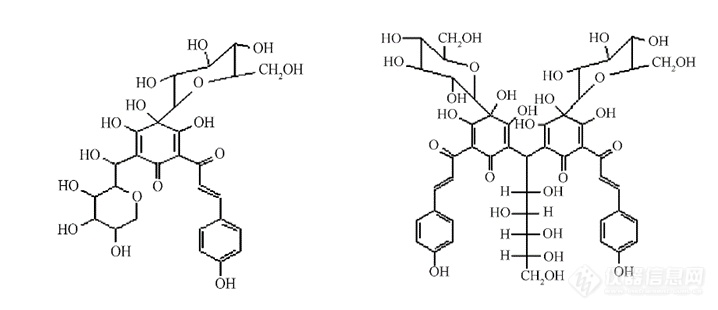
[font='黑体'][size=48px]食品添加剂——红花黄[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=24px]肖淑玲[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=24px]2021.7[/size][/font][align=center][/align][font='calibri']摘要:[/font][font='calibri']红花是[/font][font='times new roman']菊科植物的干燥花[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='calibri']是具有多种疗效的名贵中草药。从红花中提取的红花黄色素不仅是重要的天然食用色素,也具有保护心脑血管、免疫抑制等多种药理功能,一直以来都是色素界的研究热点。本文从理化性质、稳定性、制备方法、应用研究及检测方法等多方面综述了红花黄色素,帮助读者全面了解红花黄色素,尤其是了解如何运用国标检测方法测定红花黄食品添加剂含量。[/font][font='宋体']关键词:[/font][font='宋体'][size=16px]食品添加剂[/size][/font][font='宋体'][size=16px],[/size][/font][font='宋体'][size=16px]红花黄[/size][/font][font='宋体'][size=16px],[/size][/font][font='宋体'][size=16px]色素[/size][/font]1、 [font='calibri'][size=18px]引言[/size][/font][font='times new roman']红花是中国重要的中草药,为菊科植物的干燥花,内含红花红色素和红花黄色素两种色素,其性温、味辛,具有活血通经、祛瘀止痛、降低胆固醇、降血压等功效,主要用于月经不调、痛经、经闭、跌打损伤,对冠心病、传染性肝炎等疾病亦有一定的疗效。红花黄色素是从红花的花瓣中提取出的天然黄色素,为查耳酮类化合物。[/font][font='times new roman']红花黄色素是[/font][font='times new roman']我国[/font][font='times new roman']食用天然色素[/font][font='times new roman']的一种[/font][font='times new roman'],主要[/font][font='times new roman']成分[/font][font='times new roman']为红花黄色素[/font][font='times new roman']A[/font][font='times new roman']。研究发现红花黄色素[/font][font='times new roman']不仅[/font][font='times new roman']具有色泽艳丽[/font][font='times new roman']、[/font][font='times new roman']耐高压、耐低温、耐光、耐酸、耐还原和抗微生物等优点,而且还有扩张冠状动脉、抗氧化、保护心肌、降血压、免疫抑制和脑保护等多种药理功能[/font][font='times new roman'],已经被归为国家级新药[/font][font='times new roman']。[/font][font='times new roman']红花黄色素因其优良的着色性能和独特的药理功能,一直在我国色素界大放异彩,饱受关注。[/font]2、 [font='宋体'][size=18px]理化性质[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]红花黄色素为黄色或棕黄色粉末,熔点[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]230℃[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]。它具有亲水性,[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]易溶于水、稀乙醇、稀丙二醇,[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]其水溶液呈鲜艳黄色,不产生沉淀,[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]几乎不溶于无水乙醇,不溶于乙醚、石油醚、油脂、氯仿等有机溶剂[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]。[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]红花黄色素的[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]颜色随[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]pH [/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]的不同而改变。在[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]pH [/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]值[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]2[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]-[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]7[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]范围的酸性溶液中[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]颜色稳定性强[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff],呈黄色[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff];[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]在[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]碱性溶液中呈黄橙色,耐光性好,耐热性稍差。[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]红花黄色素[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]毒性极低、着色力强、色调稳定[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff];[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]在红花中含量为[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]20% ~ 30%[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][size=13px][1][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]。[/back][/color][/font][font='宋体']红花黄色素结构如下图[/font][font='宋体']一[/font][font='宋体'],为[/font][font='times new roman']查耳酮类化合物。[/font][font='times new roman']红花黄色素[/font][font='times new roman']A[/font][font='times new roman']分子式为[/font][font='times new roman']C[/font][font='times new roman'][size=13px]27[/size][/font][font='times new roman']H[/font][font='times new roman'][size=13px]32[/size][/font][font='times new roman']O[/font][font='times new roman'][size=13px]16[/size][/font][font='times new roman'],相对分子质量为[/font][font='times new roman']612.5[/font][font='times new roman']。红花黄色素[/font][font='times new roman']B[/font][font='times new roman']分子式为[/font][font='times new roman']C[/font][font='times new roman'][size=13px]48[/size][/font][font='times new roman']H[/font][font='times new roman'][size=13px]54[/size][/font][font='times new roman']O[/font][font='times new roman'][size=13px]27[/size][/font][font='times new roman'],相对分子质量为[/font][font='times new roman']1062[/font][font='times new roman'][size=13px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=13px]2][/size][/font][font='times new roman']。[/font][font='times new roman']商品化的红花黄产品应以符合国家标准的红花黄为原料,可添加食用糊精等食品辅料而制成。[/font][img]https://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2021/08/202108042202375558_3661_1608728_3.png[/img][align=center][font='宋体']图[/font][font='宋体']1[/font][font='宋体'].[/font]红花黄色素结构式:图左为红花黄色素A,图右为红花黄色素B[font='times new roman'][size=16px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2][/size][/font][/align]3、 [font='宋体'][size=18px]稳定性[/size][/font][font='times new roman']红花黄色素的稳定性,主要表现在其水溶性好、热稳定性好、金属离子对其影响小等[/font][font='times new roman']多个[/font][font='times new roman']方面。[/font][font='times new roman']研究表明,红花黄色素易溶于水、稀乙醇等强极性溶剂,难溶于无水乙醇、丙酮等弱极性有机溶剂。[/font][font='times new roman']光照或日晒对红花黄色素有一定的影响,[/font][font='times new roman']应该避光保存。[/font][font='times new roman']但[/font][font='times new roman']它[/font][font='times new roman']不受紫外光的影响,其耐光性较好。[/font][font='times new roman']p[/font][font='times new roman']H[/font][font='times new roman']3. 4[/font][font='times new roman']时,[/font][font='times new roman']10[/font][font='times new roman']0°C[/font][font='times new roman']加热[/font][font='times new roman']1 h[/font][font='times new roman']保存率在[/font][font='times new roman']80%[/font][font='times new roman']以上,说明其耐热性好[/font][font='times new roman'][size=13px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=13px]1][/size][/font][font='times new roman']。[/font][font='times new roman']但[/font][font='times new roman']红花黄色素[/font][font='times new roman']热稳定性不好[/font][font='times new roman'],当温度高于[/font][font='times new roman']60[/font][font='times new roman'] °C[/font][font='times new roman'], [/font][font='times new roman']加热一定时间后[/font][font='times new roman'], [/font][font='times new roman']羟基红花黄色素[/font][font='times new roman']A[/font][font='times new roman']就会发生水解[/font][font='times new roman'][size=13px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=13px]3[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=13px]][/size][/font][font='times new roman']。[/font][font='times new roman']经[/font][font='times new roman']Ca[/font][font='times new roman']、[/font][font='times new roman']Mg[/font][font='times new roman']等金属离子对其影响[/font][font='times new roman']的实验[/font][font='times new roman']结果表明,[/font][font='times new roman']Na[/font][font='times new roman'][size=13px]+[/size][/font][font='times new roman']、[/font][font='times new roman']Zn[/font][font='times new roman'][size=13px]2+[/size][/font][font='times new roman']、[/font][font='times new roman']Ca[/font][font='times new roman'][size=13px]2+[/size][/font][font='times new roman']、[/font][font='times new roman']Sn[/font][font='times new roman'][size=13px]2+[/size][/font][font='times new roman']对色素有增色作用,色素对[/font][font='times new roman']Fe[/font][font='times new roman'][size=13px]3+[/size][/font][font='times new roman']、[/font][font='times new roman']Cu[/font][font='times new roman'][size=13px]2+[/size][/font][font='times new roman']、[/font][font='times new roman']Vc[/font][font='times new roman']较敏感。[/font][font='times new roman']F[/font][font='times new roman']e[/font][font='times new roman'][size=13px]2+[/size][/font][font='times new roman']对色素影响较大[/font][font='times new roman'], [/font][font='times new roman']使其颜色变暗[/font][font='times new roman'], [/font][font='times new roman']且吸光度峰值随[/font][font='times new roman']F[/font][font='times new roman']e[/font][font='times new roman'][size=13px]2[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=13px]+[/size][/font][font='times new roman']浓度增高而向紫外光移动[/font][font='times new roman'], [/font][font='times new roman']还会产生乳浊液。蔗糖、淀粉、柠檬酸在短时间内能与色素共存,食盐、蔗糖、[/font][font='times new roman']H[/font][font='times new roman'][size=13px]2[/size][/font][font='times new roman']O[/font][font='times new roman'][size=13px]2[/size][/font][font='times new roman']、抗坏血酸、亚硫酸钠等一定浓度的溶液除亚硫酸钠有轻微的减色作用,糖、盐等均有不同的增色作用。色素对氧化剂较稳定[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']但还原剂对色素影响较大[/font][font='times new roman']。[/font][font='times new roman']因此[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']建议在使用色素时应避免与还原剂一起使用[/font][font='times new roman']。[/font][font='times new roman'][size=13px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=13px]1][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=13px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=13px]4][/size][/font][font='times new roman']提取方法对红花黄色素稳定性也有很大影响,红花黄色素不易在高温下提取或保存。黄宇玫等[/font][font='times new roman']人[/font][font='times new roman'][size=13px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=13px]5][/size][/font][font='times new roman']通过单因素和正交实验方法,对提取温度、浸取时间、溶剂用量进行考察,得出实验条件为:分别加[/font][font='times new roman']20[/font][font='times new roman']倍量的水提取[/font][font='times new roman']2[/font][font='times new roman']次[/font][font='times new roman'], [/font][font='times new roman']在[/font][font='times new roman']40[/font][font='times new roman'] °C[/font][font='times new roman']下[/font][font='times new roman'], 2[/font][font='times new roman']次浸取时间分别为[/font][font='times new roman']12 h[/font][font='times new roman']和[/font][font='times new roman']4 h[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']过滤[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']合并滤液。在此实验条件下,红花黄色素具有较好的稳定性。文章也指出,目前除了采用上述的提取方法对色素进行提取以提高色素稳定性外[/font][font='times new roman'], [/font][font='times new roman']主要的措施还有:加入稳定剂、抗氧化剂、金属离子封锁剂或天然色素的改性。[/font][font='times new roman']开发新的提取方法对提高所得色素的稳定性也具有重要意义,[/font][font='times new roman']如酶工程法得到的有效成分较其他方法就会更加稳定。[/font]4、 [font='宋体'][size=18px]制备方法[/size][/font]1. [font='宋体'][size=16px]传统方法[/size][/font][font='times new roman']传统的提取方法为[/font][font='times new roman']:[/font][font='times new roman']水提取法、有机溶剂沉淀精制法。主要操作方法就是把红花弄碎后用蒸馏水将其浸泡[/font][font='times new roman'], [/font][font='times new roman']然后经过过滤[/font][font='times new roman'], [/font][font='times new roman']得到浓缩液[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']将浓缩液中的沉淀与纯液体进行离心分离、干燥、粉碎。但是过去的实验[/font][font='times new roman']已经[/font][font='times new roman']发现应用传统的方式提取得到的成品的浓度不是很高[/font][font='times new roman'], [/font][font='times new roman']含有很多的杂质[/font][font='times new roman'], [/font][font='times new roman']不利于保存。[/font][font='times new roman']经过不断的改进[/font][font='times new roman'], [/font][font='times new roman']研究人员[/font][font='times new roman']不断完善了传统的溶剂提取方法[/font][font='times new roman'], [/font][font='times new roman']目前最理想的提取方法为[/font][font='times new roman']:[/font][font='times new roman']选择溶剂为[/font][font='times new roman']pH 8.9[/font][font='times new roman']的水溶液[/font][font='times new roman'], [/font][font='times new roman']液料比[/font][font='times new roman']25 mL/g[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']将红花放于[/font][font='times new roman']73 °C[/font][font='times new roman']下进行提取,一共要提取[/font][font='times new roman']3[/font][font='times new roman']次[/font][font='times new roman'], [/font][font='times new roman']每次浸泡的时间一定要充足[/font][font='times new roman'], [/font][font='times new roman']掌握在[/font][font='times new roman']98min[/font][font='times new roman']左右[/font][font='times new roman'], [/font][font='times new roman']满足了这些提取条件[/font][font='times new roman'], [/font][font='times new roman']得到的黄色素的成品质量很好[/font][font='times new roman'][size=13px][6][/size][/font][font='times new roman']。[/font]2. [font='宋体'][size=16px]大孔吸附树脂法[/size][/font][font='calibri']大[/font][font='times new roman']孔吸附树脂是[/font][font='times new roman']一类新型的非离子型有机高聚物吸附剂[/font][font='times new roman'],它[/font][font='times new roman']具有吸附容量大、选择性好、吸附速度快、解析容易、可反复使用等优点,[/font][font='times new roman']目前作为理想的黄色素提取法在广泛应用中。[/font][font='times new roman']彭永芳等人[/font][font='times new roman'][size=13px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=13px]7][/size][/font][font='times new roman']研究发现[/font][font='times new roman']将[/font][font='times new roman']AB-8[/font][font='times new roman']树脂作吸附剂[/font][font='times new roman'], [/font][font='times new roman']洗脱剂用[/font][font='times new roman']80 %[/font][font='times new roman']的乙醇[/font][font='times new roman'], [/font][font='times new roman']这样提取的成品质量较传统法好,产品杂质少,色价高,成本较低,工艺简单,收率高达干花重的[/font][font='times new roman']23. 3 %[/font][font='times new roman']。同时表明,[/font][font='times new roman']AB-8[/font][font='times new roman']树脂稳定性好,使用[/font][font='times new roman']17[/font][font='times new roman']次后其吸附率仅降低[/font][font='times new roman']2. 32 % [/font][font='times new roman']。因此,该方法适合红花黄色素的分离纯化。[/font]3. [font='宋体'][size=16px]超声波辅助提取[/size][/font][font='宋体'][size=16px][[/size][/font][font='宋体'][size=16px]8[/size][/font][font='宋体'][size=16px]][/size][/font][font='times new roman']红花黄色素[/font][font='times new roman']在高温下不够稳定,[/font][font='times new roman']超声辅助提取可以避免常规溶剂提取由于提取温度高对[/font][font='times new roman']热不稳定性[/font][font='times new roman']物质的破坏[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']且具有节能、省时、溶剂用量少、提取效率高等优点[/font][font='times new roman'], [/font][font='times new roman']目前已[/font][font='times new roman']被较多的应用于红花中黄色素的提取。[/font][font='times new roman']肖艳华[/font][font='times new roman']等人[/font][font='times new roman']研究了红花中黄色素[/font][font='times new roman']A[/font][font='times new roman']的超声提取工艺[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']结果表明[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']影响红花黄色素[/font][font='times new roman']A[/font][font='times new roman']超声辅助提取[/font][font='times new roman']因素[/font][font='times new roman']的主次顺序为[/font][font='times new roman']:[/font][font='times new roman']超声时间[/font][font='times new roman'][/font][font='times new roman']乙醇浓度[/font][font='times new roman'][/font][font='times new roman']提取温度[/font][font='times new roman'][/font][font='times new roman']溶剂用[/font][font='times new roman']量,[/font][font='times new roman']最佳提取工艺条件为[/font][font='times new roman']:[/font][font='times new roman']质量分数[/font][font='times new roman']70 %[/font][font='times new roman']乙醇为溶剂[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']提取温度[/font][font='times new roman']50 [/font][font='times new roman']°C[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']料液比[/font][font='times new roman']1[/font][font='times new roman']:[/font][font='times new roman']10[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']超声时间[/font][font='times new roman']20 min[/font][font='times new roman']。[/font][font='times new roman']此工艺条件下[/font][font='times new roman'], [/font][font='times new roman']红花黄色素[/font][font='times new roman']A[/font][font='times new roman']的提取率为[/font][font='times new roman']11.23 %[/font][font='times new roman']。[/font][font='times new roman']虽然超声辅助提取采用全物理过程[/font][font='times new roman'], [/font][font='times new roman']无任何污染[/font][font='times new roman'], [/font][font='times new roman']是一条理想的提取红花黄色素的途径[/font][font='times new roman'], [/font][font='times new roman']但由于超声提取设备的研发相对滞后[/font][font='times new roman'], [/font][font='times new roman']离实现[/font][font='times new roman']大规模[/font][font='times new roman']工业化生产还有较大距离。[/font]4. [font='宋体'][size=16px]微波辅助提取[/size][/font][font='宋体'][size=16px][[/size][/font][font='宋体'][size=16px]8[/size][/font][font='宋体'][size=16px]][/size][/font][font='times new roman']微波辅助提取是基于微波具有[/font][font='times new roman']良好的[/font][font='times new roman']吸收性、穿透性[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']可对原料和提取溶剂均匀加热[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']从而加速活性成分的溶出。微波辅助提取红花黄色素不仅无污染、成本低、且提取率高、提取时间短、节约能源[/font][font='times new roman'], [/font][font='times new roman']值得深入研究。[/font][font='times new roman']但是加热时温度对活性成分或许有影响,仍需探索。[/font]5. [font='宋体'][size=16px]酶辅助提取[/size][/font][font='宋体'][size=16px][[/size][/font][font='宋体'][size=16px]8][/size][/font][font='times new roman']酶辅助提取利用各种酶[/font][font='times new roman']有效[/font][font='times new roman']分解原料的细胞壁及细胞间质中的纤维素、半纤维素和果胶等物质[/font][font='times new roman'], [/font][font='times new roman']减少传质阻力[/font][font='times new roman'], [/font][font='times new roman']促进活性成分的溶出。[/font][font='times new roman']杜辉等采用[/font][font='times new roman']1[/font][font='times new roman']:[/font][font='times new roman']1[/font][font='times new roman']纤维素酶与果胶酶复合酶辅助提取红花中黄色素[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']通过响应面法分析得到[/font][font='times new roman']:[/font][font='times new roman']酶用量对红花黄色素提取率有极显著影响[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']pH[/font][font='times new roman']、酶用量与酶解温度交互作用、[/font][font='times new roman']p[/font][font='times new roman']H[/font][font='times new roman']与酶解温度交互作用对提取率有显著影响。其研究得出的优化提取工艺为:酶解温度[/font][font='times new roman']47[/font][font='times new roman'] °[/font][font='times new roman']C, pH[/font][font='times new roman']值[/font][font='times new roman']4.7[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']酶解时间[/font][font='times new roman']2.0 h[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']酶用量[/font][font='times new roman']0.64%[/font][font='times new roman'][size=13px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=13px]9[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=13px]][/size][/font][font='times new roman']。[/font][font='times new roman']酶辅助提取方法具有提取率高、提取条件温和及有效成分理化性质稳定的特点。但是该方法相对成本较高,应用规模尚小。[/font]6. [font='calibri'][size=16px]闪式提取[/size][/font][font='calibri'][size=16px][[/size][/font][font='calibri'][size=16px]8[/size][/font][font='calibri'][size=16px]][/size][/font][font='times new roman']闪式提取[/font][font='times new roman']可[/font][font='times new roman']在室温下[/font][font='times new roman'], [/font][font='times new roman']依靠闪式提取器的高速机械剪切力和超动分子渗透技术[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']使活性成分快速达到在提取剂与原料组织中平衡[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']再通过过滤达到提取分离[/font][font='times new roman']。[/font][font='times new roman']具有溶剂用量少[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']快速、安全、节能、高效等优点[/font][font='times new roman'], [/font][font='times new roman']极具开发应用前景。[/font]7. [font='宋体'][size=16px]减压提取[/size][/font][font='宋体'][size=16px][[/size][/font][font='宋体'][size=16px]8[/size][/font][font='宋体'][size=16px]][/size][/font][font='times new roman']减压提取是[/font][font='times new roman']一种新型提取方法,[/font][font='times new roman']采用在常规提取器上加装真空系统[/font][font='times new roman']的方法[/font][font='times new roman'], [/font][font='times new roman']使提取操作[/font][font='times new roman']在[/font][font='times new roman']负压状态下进行[/font][font='times new roman'],从而[/font][font='times new roman']降低提取剂沸点[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']使提取剂在低温下沸腾[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']实现活性成分有效提取[/font][font='times new roman'],并[/font][font='times new roman']避免活性成分被破坏。减压提取可有效降低提取温度[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']缩短提取时间[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']成本低廉[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']有[/font][font='times new roman']广阔的前景,有[/font][font='times new roman']必要深入研究。[/font]5、 [font='宋体'][size=18px]应用研究[/size][/font]1. [font='宋体'][size=16px]食品着色[/size][/font][font='宋体']红花黄色素作为一种天然、安全的食用色素[/font][font='宋体'],[/font][font='宋体']已成功应用于各种饮料、酒类及保健食品的着色。由于人工合成的柠檬黄为有毒色素,现已被许多国家禁止使用,红花黄色素可作为其首选色素[/font][font='宋体'],尤其是用于婴幼儿和老年保健食品。[/font]2. [font='宋体'][size=16px]纺织染色[/size][/font][font='宋体']红花黄色素具有[/font][font='宋体']色泽[/font][font='宋体']艳丽[/font][font='宋体']和低毒等优点,在纺织业的染色中亦有出色应用。但红花黄色素提取、精制方法繁琐,生理功能机理研究不完善,因此离推广应用仍有很大距离。[/font][font='宋体']要想大规模应用,[/font][font='宋体']未来的研究重点应是简化工艺,提高产量,深入其功能机理研究。[/font]3. [font='宋体'][size=16px]医[/size][/font][font='宋体'][size=16px]药疗效[/size][/font][font='宋体']研究表明,红花黄色素具有抗炎、镇痛、抗氧化等多种疗效,在治疗心脑血管疾病、糖尿病、肿瘤等疾病方面也展现出了令人惊喜的药理潜力。红花黄色素目前已被归类为国家级新药,相信在未来会有更多与红花黄有关的药物面世。[/font]6、 [font='calibri'][size=18px]用量要求[/size][/font][font='times new roman']《食品添加剂使用卫生标准》[/font][font='times new roman'](GB2760-2011)[/font][font='times new roman']规定[/font][font='times new roman']:[/font][font='times new roman']红花黄[/font][font='times new roman']色素[/font][font='times new roman']主要用于果味型饮料[/font][font='times new roman'] ([/font][font='times new roman']固体、液体[/font][font='times new roman'])[/font][font='times new roman']、果汁型饮料、汽水、各类果酒、配制酒、糖果、糕点上彩妆、红绿丝、果酱、水果罐头、冰制品、浓缩果汁、青梅、冰淇淋、冰棍、蜜饯和果冻,最大使用量为[/font][font='times new roman']0.2 g/kg[/font][font='times new roman']。[/font]7、 [font='宋体'][size=18px]检测方法[/size][/font]1. [font='times new roman'][size=16px]高效液相色谱法([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]HPLC[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px])[/size][/font][font='times new roman']已报道的红花黄色素含量测定方法主要为光度法、毛细管电泳法和[/font][font='times new roman']HPLC[/font][font='times new roman']法。[/font][font='times new roman']光度法仅能测定黄色素总量,[/font][font='times new roman']已报道的[/font][font='times new roman']毛细管电泳法可测定[/font][font='times new roman']Safflomin A[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']Safflomin C[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']Safflower yellow B[/font][font='times new roman']三种黄色素。而[/font][font='times new roman']王慧琴、谢明勇等人[/font][font='times new roman'][size=13px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=13px]10][/size][/font][font='times new roman']用反相高效液相色谱法,梯度洗脱,同时测定了不同产地红花中[/font][font='times new roman']Safflomin A[/font][font='times new roman']、[/font][font='times new roman']Safflower yellow A[/font][font='times new roman']、[/font][font='times new roman']Safflower yellow B[/font][font='times new roman']和[/font][font='times new roman']Safflomin C[/font][font='times new roman']四种红花黄色素的含量。该方法准确度高[/font][font='times new roman'], [/font][font='times new roman']重现性好。四种红花黄色素检出限分别[/font][font='times new roman']4.0[/font][font='times new roman']、[/font][font='times new roman']8.1[/font][font='times new roman']、[/font][font='times new roman']2.8[/font][font='times new roman']和[/font][font='times new roman']5.0 mg/L[/font][font='times new roman']。[/font][font='times new roman']唐刚等人[/font][font='times new roman'][size=13px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=13px]11][/size][/font][font='times new roman']用反相高效液相色谱法测定了红花[/font][font='times new roman']W/O[/font][font='times new roman']型乳膏剂中羟基红花黄色素[/font][font='times new roman']A[/font][font='times new roman']含量。检测结果显示,乳膏剂中辅料不影响有效成分羟基红花黄色素[/font][font='times new roman']A[/font][font='times new roman']的含量测定[/font][font='times new roman'],该方法检测限为[/font][font='times new roman']23.6 ng/mL,[/font][font='times new roman']定量限为[/font][font='times new roman']118 ng/mL[/font][font='times new roman']。较之王慧琴等人的研究,其对于羟基红花黄素的测定更加精密准确。[/font][font='times new roman']H[/font][font='times new roman']PLC[/font][font='times new roman']方法主要用于各品种红花[/font][font='times new roman']、[/font][font='times new roman']以红花[/font][font='times new roman']黄[/font][font='times new roman']为主要成分的乳膏、药丸、针剂等产品中红花黄色素含量的测定,[/font][font='times new roman']食品中红花黄含量测定也[/font][font='times new roman']可[/font][font='times new roman']运用[/font][font='times new roman']H[/font][font='times new roman']PLC[/font][font='times new roman']方法。此法[/font][font='times new roman']具有高效、准确、重现性好等优点。但是[/font][font='times new roman']H[/font][font='times new roman']PLC[/font][font='times new roman']方法也存在仪器贵重、操作复杂等局限。[/font]2. [font='times new roman'][size=16px]国家标准[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]GB 1886.61-2015[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][2][/size][/font][font='times new roman']食品中[/font][font='times new roman']所用[/font][font='times new roman']红花黄色素添加剂主要采用国家标准[/font][font='times new roman']GB 1886.61[/font][font='times new roman']-[/font][font='times new roman']2015[/font][font='times new roman']中规定的方法进行鉴别和测定,测定对象为[/font][font='times new roman']从红花中提取的[/font][font='times new roman']红花黄色素[/font][font='times new roman']A[/font][font='times new roman']和红花黄色素[/font][font='times new roman']B[/font][font='times new roman']样品[/font][font='times new roman']。[/font][font='times new roman']检测鉴定[/font][font='times new roman']时应先测定并计算色价,计算方法见下文[/font][font='times new roman']2[/font][font='times new roman'].3[/font][font='times new roman']。[/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2.1[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]技术要求[/size][/font][font='宋体']红花黄色素感官要求应符合下表1:[/font][img]https://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2021/08/202108042202377271_2806_1608728_3.png[/img][align=center][font='times new roman']表[/font][font='times new roman']1.[/font][font='times new roman']红花黄感官要求[/font][font='times new roman'][size=13px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=13px]2][/size][/font][/align][font='times new roman']红花黄理化指标应符合下表[/font][font='times new roman']2[/font][font='times new roman']:[/font][img]https://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2021/08/202108042202378882_9077_1608728_3.png[/img][align=center][font='times new roman']表[/font][font='times new roman']2.[/font][font='times new roman']红花黄理化指标[/font][font='times new roman'][size=13px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=13px]2][/size][/font][/align]2.2 [font='times new roman'][size=16px]鉴别试验[/size][/font][font='times new roman']2.2.1[/font][font='times new roman']溶解性试验[/font][font='times new roman']红花黄[/font][font='times new roman']易溶于水,微溶于[/font][font='times new roman']乙醇,几乎不溶于乙醚,可通过溶解性试验鉴别。[/font][font='times new roman']2.2.2[/font][font='times new roman']吸光度[/font][font='times new roman']([/font][font='times new roman']1[/font][font='times new roman'])[/font][font='times new roman']试剂与材料:柠檬酸[/font][font='times new roman']-[/font][font='times new roman']磷酸氢二钠缓冲溶液[/font][font='times new roman']([/font][font='times new roman']pH 5.0[/font][font='times new roman']):称取[/font][font='times new roman']21 g[/font][font='times new roman']一水合柠檬酸,溶于[/font][font='times new roman']1000 mL[/font][font='times new roman']水中,此为溶液[/font][font='times new roman']A[/font][font='times new roman'];称取[/font][font='times new roman']71.6 g[/font][font='times new roman']十二水合磷酸氢二钠,溶于[/font][font='times new roman']1000 mL[/font][font='times new roman']水中,此为溶液[/font][font='times new roman']B[/font][font='times new roman'];将溶液[/font][font='times new roman']A[/font][font='times new roman']与溶液[/font][font='times new roman']B[/font][font='times new roman']混合([/font][font='times new roman']97+103[/font][font='times new roman'])。若混合液[/font][font='times new roman']pH[/font][font='times new roman']不为[/font][font='times new roman']5.0[/font][font='times new roman'],则用溶液[/font][font='times new roman']A[/font][font='times new roman']或溶液[/font][font='times new roman']B[/font][font='times new roman']调整至[/font][font='times new roman']pH 5.0[/font][font='times new roman']。[/font][font='times new roman']([/font][font='times new roman']2[/font][font='times new roman'])测定:称取质量相当于[/font][font='times new roman']0.1 g[/font][font='times new roman']、色价为[/font][font='times new roman']10[/font][font='times new roman']的试样,用柠檬酸[/font][font='times new roman']-[/font][font='times new roman']磷酸氢二钠缓冲溶液([/font][font='times new roman']pH 5.0[/font][font='times new roman'])溶解并稀释至[/font][font='times new roman']100 mL[/font][font='times new roman'],此试样液在[/font][font='times new roman']400-408 nm[/font][font='times new roman']有最大吸收峰。[/font][font='times new roman']2.2.3[/font][font='times new roman']颜色反应[/font][font='times new roman']在[/font][font='times new roman']2.2.2[/font][font='times new roman']的测定试样液中加入[/font][font='times new roman']NaOH[/font][font='times new roman']溶液([/font][font='times new roman']40 g/L[/font][font='times new roman']),使溶液变为碱性,试样液色泽变为橙色。[/font][font='times new roman']2.2.4[/font][font='times new roman']薄层色谱[/font][font='times new roman']称取质量相当于[/font][font='times new roman']0.1 g[/font][font='times new roman']、色价为[/font][font='times new roman']10 [/font][font='times new roman']的试样,用[/font][font='times new roman']1 mL[/font][font='times new roman']水溶解,加入[/font][font='times new roman']10 mL[/font][font='times new roman']甲醇混匀,[/font][font='times new roman']3000 r/min[/font][font='times new roman']离心[/font][font='times new roman']10 min[/font][font='times new roman'],取上清液[/font][font='times new roman']20 μL[/font][font='times new roman'],点样于微晶纤维素薄层色谱板(预先在[/font][font='times new roman']60-80°C[/font][font='times new roman']下活化[/font][font='times new roman']20 min[/font][font='times new roman'])上[/font][font='times new roman'],干燥,置于展开剂(正丁醇:乙酸:水[/font][font='times new roman']=4:1:2[/font][font='times new roman'])中展开。当溶剂前沿上升至距原点约[/font][font='times new roman']10 cm[/font][font='times new roman']时,取出薄板,在空气中干燥。薄板上至少有两个黄色斑点,[/font][font='times new roman']R[/font][font='times new roman'][size=13px]f[/size][/font][font='times new roman']值应在[/font][font='times new roman']0.2-0.5[/font][font='times new roman']之间。[/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2.3[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]色价[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]400-408 nm[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px])的测定[/size][/font][font='times new roman']2.3.1[/font][font='times new roman']仪器与材料[/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]([/size][/font][font='times new roman']1[/font][font='times new roman'])仪器与设备:分光光度计[/font][font='times new roman']([/font][font='times new roman']2[/font][font='times new roman'])试剂与材料:柠檬酸[/font][font='times new roman']-[/font][font='times new roman']磷酸氢二钠缓冲溶液([/font][font='times new roman']pH 5.0[/font][font='times new roman']):称取[/font][font='times new roman']21 g[/font][font='times new roman']一水合柠檬酸,溶于[/font][font='times new roman']1000 mL[/font][font='times new roman']水中,此为溶液[/font][font='times new roman']A[/font][font='times new roman'];称取[/font][font='times new roman']71.6 g[/font][font='times new roman']十二水合磷酸氢二钠,溶于[/font][font='times new roman']1000 mL[/font][font='times new roman']水中,此为溶液[/font][font='times new roman']B[/font][font='times new roman'];将溶液[/font][font='times new roman']A[/font][font='times new roman']与溶液[/font][font='times new roman']B[/font][font='times new roman']混合([/font][font='times new roman']97+103[/font][font='times new roman'])。若混合液[/font][font='times new roman']pH[/font][font='times new roman']不为[/font][font='times new roman']5.0[/font][font='times new roman'],则用溶液[/font][font='times new roman']A[/font][font='times new roman']或溶液[/font][font='times new roman']B[/font][font='times new roman']调整至[/font][font='times new roman']pH 5.0[/font][font='times new roman']。[/font][font='times new roman']2.3.2[/font][font='times new roman']分析步骤[/font][font='times new roman']称取试样约[/font][font='times new roman']0.1 g[/font][font='times new roman'],精确到[/font][font='times new roman']0.0002 g[/font][font='times new roman'],用柠檬酸[/font][font='times new roman']-[/font][font='times new roman']磷酸氢二钠缓冲溶液([/font][font='times new roman']pH 5.0[/font][font='times new roman'])溶解,定容至[/font][font='times new roman']1000 mL[/font][font='times new roman'],摇匀,必要时过滤。取此试样置于[/font][font='times new roman']1 cm[/font][font='times new roman']比色皿中,以柠檬酸[/font][font='times new roman']-[/font][font='times new roman']磷酸氢二钠缓冲溶液([/font][font='times new roman']pH 5.0[/font][font='times new roman'])为空白对照,用分光光度计在[/font][font='times new roman']400-408 nm[/font][font='times new roman']内的最大吸收波长处测定其吸光度(吸光度应控制在[/font][font='times new roman']0.2-0.8[/font][font='times new roman']之间,否则应调整试样液浓度后重新测定)。[/font][font='times new roman']2.3.3[/font][font='times new roman']结果计算[/font][font='times new roman']色价[/font][font='times new roman']([/font][font='times new roman']400-408 nm[/font][font='times new roman'])[/font][font='times new roman']计算式如下:[/font][font='times new roman']([/font][font='times new roman']400-408 nm[/font][font='times new roman'])[/font][font='黑体']=[/font][font='times new roman']式中:[/font][font='times new roman']A[/font][font='times new roman']——实测试样液吸光度;[/font][font='times new roman']c[/font][font='times new roman']——被测试样液浓度,单位为[/font][font='times new roman']g[/font][font='times new roman']/mL[/font][font='times new roman'];[/font][font='times new roman']1[/font][font='times new roman']00[/font][font='times new roman']——浓度换算系数。[/font][font='times new roman']试验结果以平行测定结果的算术平均值为准。在重复性条件下获得的两次独立测定结果的绝对差值不大于算术平均值的[/font][font='times new roman']5%[/font][font='times new roman']。[/font]8、 [font='宋体'][size=18px]结语[/size][/font][font='times new roman']随着柠檬黄等合成色素对人体和环境的危害日益引起人们的重视,[/font][font='times new roman']合成色素退出色素市场已成趋势,人们的目光重新转向安全可靠的天然色素。开发可大规模应用的安全的天然色素对保护人体健康和推进食品工业发展都具有重大意义。红花广泛分布于我国境内,主产河南、湖南、四川、新疆、西藏等地,自古以来就是重要的中草药,也是古代胭脂的主要着色剂。红花黄色素着色能力强,色泽鲜艳,低毒且稳定,又具有独特的药用价值,市场前景极为广阔。[/font][font='times new roman']近年来,对红花黄色素的研究不断深入,科研工作者们研究了其稳定性的影响因素与控制方法,开发了多种高效、快速、安全[/font][font='times new roman']、稳定[/font][font='times new roman']的提取方法,[/font][font='times new roman']酶工程法等方法都具有广阔的前景,[/font][font='times new roman']发展了光度法、[/font][font='times new roman']HPLC[/font][font='times new roman']等多种含量测定方法[/font][font='times new roman']。针对[/font][font='times new roman']红花黄色素的[/font]生理活性和药理功能的研究也不断深入,红花黄色素在治疗心脑血管疾病和抗癌方面的疗效令人惊喜。但是,红花黄色素的许多提取方法都尚未能大规模投入工业生产,传统方法繁琐复杂产率低,大大限制了红花黄色素的进一步发展。红花黄色素的生理功能机理研究也并不完善。但是随着研究的不断推进,相信在不久的将来,红花黄色素会突破这些界限,为天然色素领域做出更大的贡献。[font='calibri'][size=16px]参考文献:[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff][[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]1[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]][/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]许[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]钢[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff].[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]天然红花黄色素稳定性研究[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff][J].[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]食品工业科技[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff],2000(01):16-18.[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff][2][/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]中华人民共和国国家标准[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]GB 1886.61-2015[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff].[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][[/font][font='times new roman']3[/font][font='times new roman']][/font][font='times new roman']王慧[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']张立伟[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']晋民杰[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']苏尚宏[/font][font='times new roman'].[/font][font='times new roman']羟基红花黄色素[/font][font='times new roman']A[/font][font='times new roman']稳定性研究[/font][font='times new roman'][J].[/font][font='times new roman']太原科技大学学报[/font][font='times new roman'],2010,31(01):81-84.[/font][font='times new roman'][[/font][font='times new roman']4[/font][font='times new roman']][/font][font='times new roman']吴冬青[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']林敏[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']王学文[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']许莹堂[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']张爱平[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']史茂才[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']陈桂花[/font][font='times new roman'].[/font][font='times new roman']红花黄色素稳定性研究[/font][font='times new roman'][J].[/font][font='times new roman']河西学院学报[/font][font='times new roman'],2003(05):32-36.[/font][font='times new roman'][[/font][font='times new roman']5[/font][font='times new roman']][/font][font='times new roman']罗晶[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']黄宇玫[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']曾文雪[/font][font='times new roman'].[/font][font='times new roman']红花中羟基红花黄色素[/font][font='times new roman']A[/font][font='times new roman']的提取工艺及其热稳定性研究[/font][font='times new roman'][J].[/font][font='times new roman']江西中医学院学报[/font][font='times new roman'],2009,21(05):39-42.[/font][font='times new roman'][[/font][font='times new roman']6[/font][font='times new roman']][/font][font='times new roman']魏安池[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']代红丽[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']谷文英[/font][font='times new roman']. [/font][font='times new roman']响应面分析法优化红花黄色素提取工艺条件[/font][font='times new roman'][ J] . [/font][font='times new roman']食品与机械,[/font][font='times new roman']2006[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']22( 2) [/font][font='times new roman']:[/font][font='times new roman']11- 14.[/font][font='times new roman'][[/font][font='times new roman']7[/font][font='times new roman']][/font][font='times new roman']彭永芳[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']马银海[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']阎孝金,等[/font][font='times new roman']. AB-[/font][font='times new roman']8[/font][font='times new roman']树脂吸附和分离红花黄色素[/font][font='times new roman'][ J] . [/font][font='times new roman']食品科学,[/font][font='times new roman']2001[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']22( 5)[/font][font='times new roman']:[/font][font='times new roman']39- 41.[/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff][[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]8[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]][/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]展俊岭[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff],[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]高子怡[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff],[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]皇甫阳鑫[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff],[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]赵三虎[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff],[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]赵二劳[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff].[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]红花黄色素提取工艺研究进展[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff][J].[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff]山东化工[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][color=#333333][back=#ffffff],2017,46(18):67+75.[/back][/color][/font][font='times new roman'][[/font][font='times new roman']9[/font][font='times new roman']][/font][font='times new roman']杜辉[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']马永强[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']李春阳[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']李波[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']刘晓林[/font][font='times new roman'].[/font][font='times new roman']响应面法优化复合酶提取红花黄色素工艺[/font][font='times new roman'][J].[/font][font='times new roman']南方农业学报[/font][font='times new roman'],2015,46(04):657-663.[/font][font='times new roman'][1[/font][font='times new roman']0[/font][font='times new roman']][/font][font='times new roman']王慧琴[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']谢明勇[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']傅博强[/font][font='times new roman'].[/font][font='times new roman']红花中红花黄色素含量的反相高效液相色谱测定[/font][font='times new roman'][J].[/font][font='times new roman']分析科学学报[/font][font='times new roman'],2005(04):408-410.[/font][font='times new roman'][1[/font][font='times new roman']1[/font][font='times new roman']][/font][font='times new roman']唐刚[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']金坚[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']杨子毅[/font][font='times new roman'].RP-HPLC[/font][font='times new roman']测定红花[/font][font='times new roman']W/O[/font][font='times new roman']型乳膏剂中羟基红花黄色素[/font][font='times new roman']A[/font][font='times new roman']的含量[/font][font='times new roman'][J].[/font][font='times new roman']中国药科大学学报[/font][font='times new roman'],2020,51(02):161-167.[/font]
你好!我这学期在做姜黄素分光光度法测定食品中硼酸的相关论文。实验过程中碰到了该问题:不知道这个实验为何须在55摄氏度水浴箱中水浴蒸干。请有相关经验的大侠帮忙解答。同时有做过相关实验的朋友可以一起探讨。我的QQ是369583862(力)。
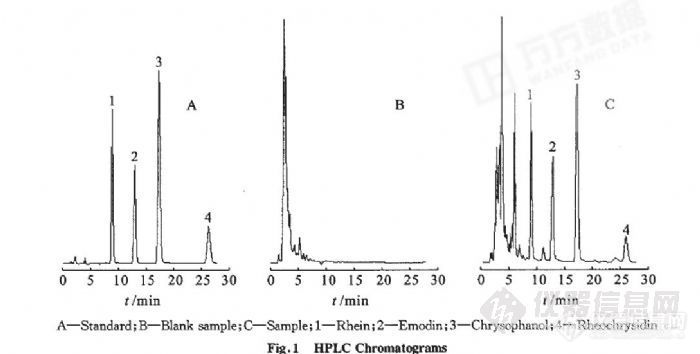
HPLC法测定胃力片中大黄酸、大黄素、大黄酚和大黄素甲醚的含量张红霞,金艺,许海燕,赵怀清(沈阳药科大学药学院,辽宁沈阳110016)摘要:目的建立胃力片中大黄酸、大黄素、大黄酚、大黄素甲醚的含量测定方法。方法采用HPLC法,色谱柱:Diamonsil c18(4.6 mm×200 mm,5弘m),以甲醇一体积分数为0.1%的磷酸水溶液(体积比为82:18)为流动相,流速:1.0 mL·min~,柱温:35℃,检测波长:254 nm。结果大黄酸、大黄素、大黄酚、大黄素甲醚分别在1.42~12.79、2.02~18.14、1.28~11.52、0.76~8.36 mg·Lo内呈良好的线性关系,相关系数分别为O.999 1、O.999 4、O.999 0和0.999 6,平均回收率分别为102。7%(RSD=l。0%,魁=9)、10l。2%(RSD=2.7%,露=9)、99.4%(RSD=1。6%,n=9)和97.9%(RSD=2.8%,咒=9)。结论本方法可作为胃力片质量控制方法之一。关键词:胃力片;大黄酸;大黄素;大黄酚;大黄素甲醚;高效液相色谱法http://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2012/07/201207241901_379466_2355529_3.jpg
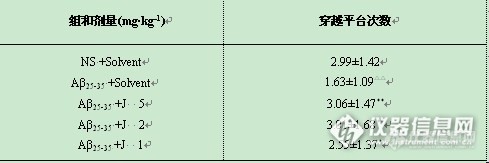
姜黄素对β-淀粉样蛋白致小鼠空间学习记忆障碍的改善作用阿尔茨海默病(Alzheimer’s disease,AD)是一种常见的慢性进行性精神功能衰退性疾病。近年来,研究发现AD患者大脑中的主要成分β-淀粉样蛋白(Aβ)明显增多,Aβ可能是该病发病机制的起始因素和关键环节。 姜黄素为二苯庚烷类化合物具有较明显的抗炎、抗菌、降血脂、抗老年痴呆,但其是否可以对抗Aβ引起的神经毒性未见报道。本文通过研究其对Aβ引起的记忆障碍模型小鼠的保护作用],为临床可能应用姜黄素治疗老年性痴呆症提供依据。 本题为探讨姜黄素对β[font=Times New Roman]-[font=宋体]淀粉样蛋白[font=Times New Roman]25-35[font=宋体]致小鼠空间学习记忆障碍的改善作用。方法采用侧脑室一次性注射[font=Times New Roman]β-[font=宋体]淀粉样蛋白4μl[font=宋体]导致小鼠空间学习记忆障碍模型,采用隐藏平台获得实验和空间搜索实验,观察姜黄素[font=Times New Roman]J(5、2、1 mg·kg-1[font=宋体])对空间学习记忆障碍模型小鼠的保护作用。结果显示姜黄素各个剂量组均能明显改善β-淀粉样蛋白致小鼠空间学习记忆障碍,能明显缩短寻找站台潜伏期和游泳路径。材料与方法1 材料与仪器1.1 [font=楷体_GB2312]动物 雄性昆明种小鼠,上海实验动物中心提供。1.2 药品和试剂[font='Times
因为刚接触药品检验,在做核黄素磷酸钠的游离磷酸的测定的时候,做了几次都不合格。 按照标准要求进行对照及样品配制,对照品为蓝色的澄清液体,但是样品很浑浊,土黄色。在730nm处进行测定,结果不符合规定。 因为样品很浑浊,所以吸收值很大(2.0),大过了对照品; 我们把样品用0.45的滤膜过滤,吸收值(0.35)低于对照,但是我们怀疑过滤的影响太大,我们就再次过滤样品,吸收值又降低了一半(0.13). 请各位大侠帮帮忙啊!!!
请问一下用姜黄素法做水质硼的时候,水浴锅55度是要蒸多久才能干,我已经蒸了一天了还是没有蒸干。
水质硼的测定姜黄素法,水浴锅55度蒸不干呀,求赐教??
水质 硼的测定 姜黄素的方法中曲线绘制好像没有空白,但是标准里面有空白试验的方法,那做曲线和样品的时候要做空白吗
般而言,人们都希望饮料澄清透明。比如茶,清亮的总比浑浊的更有吸引力一些。所以,人们发现有的红茶茶汤在放凉之后出现浅褐色或橙色乳状的浑浊之后,在相当长的时间里并不待见它。直到后来有农艺师指出这其实是优质红茶的标志,这种被称为“冷后浑”的现象才受到人们的欢迎。冷后浑是如何产生的?为什么它又被认为是好茶的标志呢?茶叶中有许多种成分,其中有一类在化学结构上有共同之处,统称为茶多酚,现在已经识别出了有几十种。在未经加工的茶叶中,茶多酚大多数以儿茶素的形态存在。红茶制作中要进行充分的氧化,许多儿茶素会转化成茶黄素,还有的会进一步转化成茶红素。茶黄素和茶红素,就是为红茶带来红亮颜色的功臣。茶黄素的溶解度受温度影响比较大。在高温下,它还能好好地呆在茶汤中。当温度降低,它们就开始扎堆。温度越低,扎的堆就越大。大到一定程度——大致相当于牛奶中的乳滴大小,看起来就是茶汤变浑浊了。再进一步扎堆,就会形成乳酪那样的东西,与茶汤分层。茶中还有一种成分是咖啡因。其实它跟茶黄素一样,随着温度的降低也会喜欢扎堆,溶解度也会降低。不过在茶汤中的咖啡因含量低于它的溶解度,所以它们自己并不足以导致茶汤浑浊。但咖啡因非常喜欢茶黄素——相对于自己扎堆,它们更喜欢跟茶黄素混在一起。一个茶黄素分子上有两个位置能够结合咖啡因,当第一个咖啡因分子傍上茶黄素之后,就会使茶黄素露出第二个结合位点,再容纳另一个咖啡因分子。咖啡因到了人的嘴里,会与舌头上的苦味受体结合,让我们尝到苦味。而多酚类物质到了嘴里,则可能与舌头上的蛋白质结合,生成不溶于唾液的沉淀物,然后我们就感觉到了涩。相对来说,绿茶中的儿茶素和咖啡因比较多,所以绿茶比较容易出现苦涩。在红茶里,儿茶素经过氧化和聚合变成茶黄素,能与蛋白质结合的位点变少了,涩味也就降低了。茶黄素与咖啡因的结合在茶黄素自己扎堆之前就会进行。这种结合不仅进一步消耗了茶黄素的结合位点,同时也限制了咖啡因与舌头上苦味受体的结合。于是,与同样固体含量的绿茶茶汤相比,红茶茶汤的苦涩味就往往要低。茶黄素与咖啡因的络合产物溶解度更低,更容易扎堆变大,从而导致冷后浑的出现。因此,许多人认为冷后浑是茶黄素和咖啡因发生反应的结果。在实际的红茶中,咖啡因和茶黄素都存在,所以这样的解释也说得过去。“无事生非”的科学家,会把红茶中的咖啡因去掉,非要看看茶黄素自己能否出现冷后浑——结果是能,只是需要的茶黄素浓度会高一些。冷后浑还有一个名字叫做“茶乳酪”。跟牛奶形成奶酪一样,茶中的茶黄素等成分含量越高,就越容易出现冷后浑。茶黄素是红茶最关键的标志成分——冷后浑意味着它的含量高,“冷后浑是好茶的标志”之说,也就主要是这个原因。在红茶饮料生产中,冷后浑的出现导致产品不均一、外观不合格,风味口感也受到影响。在生产过程中,有一些阶段是以红茶提取物浓缩液的状态存在。因为固体含量高,“茶乳酪”就更容易出现——这会导致有效成分的损失,也为下一步的生产流程带来困难。因此,这个产业需要避免冷后浑的出现——这种需要,也就导致了许多关于冷后浑的研究。科学家们发现,除了咖啡因,茶汤中的钙离子对冷后浑的出现也有显著的作用。他们把茶乳酪拿去分析,发现其中的钙占固体总量的比例,大大高于茶汤中的钙占其固体含量的比例。这是因为,茶汤中的茶黄素带着负电,而钙离子带着正电——类似于卤水点豆腐,钙离子会把本来不想扎堆的茶黄素们拉到一起,让它们沉淀析出。茶中本来就具有不少钙,要避免它导致冷后浑,就需要压制住它的活动。在食品饮料工业中,这可以通过加入“螯合剂”来实现——螯合剂是一些结构特殊的分子,对于钙离子有超级强大的吸引力。只要螯合剂一出现,钙离子们就纷纷投奔而去,茶黄素也就“无钙问津”,不会被它们拉到一起扎堆了。科学家们还发现,如果把糖分子通过“糖苷化”加到茶黄素上,可以增加茶黄素的溶解度、避免冷后浑的出现。红茶制作中的氧化那一步加入一些糖,它们就会在后续的加工过程中结合到茶黄素上去。最后得到的红茶,就不容易出现冷后浑。“冷后浑是优质红茶的标志”是对的,但只是针对正常的红茶。当科学研究让我们对冷后浑有了更深入的认识,就会发现:如果我们不喜欢它,可以通过技术手段避免它的出现;如果我们喜欢它,也可以“捣鬼”促使它的出现。转自:科学松鼠会
[color=#444444]请问有没有什么叶黄素的质谱方法?我怎么没找到啊[/color]
求助土壤有效硼 姜黄素NY/T 149的曲线,第一次做,求助!!!
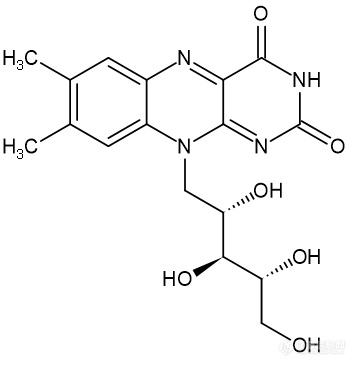
何莉萍CNS_08.148_核黄素[align=center][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]目录[/color][/size][/font][/align][font='等线'][size=14px]3[/size][/font][url=#][font='等线'][size=14px].[/size][/font][/url][url=#][font='等线'][size=14px]核黄素的物理性质[/size][/font][/url][url=#][font='等线'][size=14px]1[/size][/font][/url][url=#][font='等线'][size=14px]2[/size][/font][/url][font='等线'][size=14px]3[/size][/font][url=#][font='等线'][size=14px].[/size][/font][/url][url=#][font='等线'][size=14px]核黄素的光物理和光化学性质[/size][/font][/url][url=#][font='等线'][size=14px]第二章核黄素的生理功能[/size][/font][/url][url=#][font='等线'][size=14px]2[/size][/font][/url][url=#][font='等线'][size=14px]1[/size][/font][/url][font='等线'][size=14px]4[/size][/font][url=#][font='等线'][size=14px].[/size][/font][/url][url=#][font='等线'][size=14px]核黄素与铁代谢[/size][/font][/url][url=#][font='等线'][size=14px]2[/size][/font][/url][url=#][font='等线'][size=14px]3[/size][/font][/url][font='等线'][size=14px]5[/size][/font][url=#][font='等线'][size=14px].[/size][/font][/url][url=#][font='等线'][size=14px]核黄素与心血管疾病[/size][/font][/url][url=#][font='等线'][size=14px]第三章 核黄素的应用[/size][/font][/url][url=#][font='等线'][size=14px]3[/size][/font][/url][url=#][font='等线'][size=14px]1[/size][/font][/url][font='等线'][size=14px]5[/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px]6[/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px]6[/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px]6[/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px]6[/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px]6[/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px]7[/size][/font][url=#][font='等线'][size=14px].[/size][/font][/url][url=#][font='等线'][size=14px]微生物法[/size][/font][/url][url=#][font='等线'][size=14px]参考文献[/size][/font][/url] [font='等线'][size=14px]9[/size][/font][align=center][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]第一章 核黄素的理化性质[/color][/size][/font][/align][size=16px]核黄素是一种水溶性[/size][font='times new roman'][size=16px]B[/size][/font][size=16px]族维生素[/size][size=16px]。[/size][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]920[/size][/font][size=16px]年第[/size][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][size=16px]次发现[/size][size=16px],[/size][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]933[/size][/font][size=16px]年第[/size][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][size=16px]次从卵蛋白中分离出来[/size][size=16px],[/size][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]935[/size][/font][size=16px]年核黄素的化学结构被鉴定[/size][size=16px]。[/size][size=16px]核黄素是人体新陈代谢酶系统的一个组成部分[/size][size=16px],[/size][size=16px]也是生物生命活动中不可缺少的维生素之一[/size][size=16px],[/size][size=16px]与人体内碳水化合物[/size][size=16px]、[/size][size=16px]脂肪及氨基酸代谢有着密切的关系[/size][size=16px],[/size][size=16px]核黄素缺乏可以引起体内多种代谢障碍。[/size][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]1[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6].[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]1[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]核黄素的物理性质[/color][/size][/font][size=16px]水溶性维生素,但微溶于水,在[/size][font='times new roman'][size=16px]27.5℃[/size][/font][size=16px]下,溶解度为[/size][font='times new roman'][size=16px]12mg/100mL[/size][/font][size=16px]。可溶于氯化钠溶液,易溶于稀的氢氧化钠溶液,在碱性溶液中容易[/size][size=16px]分[/size][size=16px]解,在强酸溶液中稳定。耐热、耐氧化。光照及紫外照射引起不可逆的分解。[/size][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]1[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6].[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]2[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]核黄素的化学性质[/color][/size][/font][size=16px]分子式为[/size][font='times new roman'][size=16px]C[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]17[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]H[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]20[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]N[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]4[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]O[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]6[/size][/font][size=16px],化学结构式见图[/size][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px],具有一个核糖醇侧链的异咯嗪的衍生物。橙黄色晶体,[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]280℃即熔化分解。在平常的湿度下稳定,而且不受空气中氧的影响。微溶于水,溶液呈现出强的黄绿色荧光。不溶于有机溶剂,在强酸溶液中稳定;在碱性条件下或者暴露于可见光或紫外线中时不稳定。食物中的核黄素很容易吸收,但单独服用,则只有15%的吸收率。核黄素在生物体储存量不多,多余的在尿液中排出,使尿液呈鲜黄色。核黄素在生物界分布极广,各种组织中均含有核黄素,广泛地分布在所有的叶菜,温血动物和鱼的肉中,但各种食物的含量相差很大,每[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]一[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]百[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]克[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]食物含量低的只有0.01mg,高的可[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]达[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]3.5mg,以肝脏含量最高,浅色蔬菜和薯类含量最低。[/size][/font][align=center][img]https://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2021/07/202107251438050080_5202_1608728_3.png[/img][/align][align=center][size=13px]图[/size][font='times new roman'][size=13px]1[/size][/font][size=13px]核黄素的化学结构[/size][/align][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]1[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6].[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]3[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]核黄素的光物理和光化学性质[/color][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]在生物学上,核黄素具有重要作用,如:向光性,趋光性和光治疗,其本身又是一类重要的光敏化剂[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px],研究表明这些重要的光生物学过程大多与核黄素的激发态有关。由于核黄素的吸收波段很宽(从紫外到可见光)且系间窜越的量子产额较高([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]Φ[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]ISC[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]=[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]67[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px])[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px],故无论在生物体内还是体外的组织和器官,只要能透过光,就能激发产生激发态,并与细胞内的[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]DNA[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]或其他组分发生反应,导致细胞死亡或加速衰老[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]3[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]。[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]研究发现,核黄素在[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]337nm[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]激光作用下,可产生激发三重态;而在[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]248nm[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]激光作用下,既可产生激发三重态,又可生成氧化性自由基,核黄素氧化性自由基比激发三重态具有更强的氧化性[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]4[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]。[/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]第二章核黄素的生理功能[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]2[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6].[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]1[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]核黄素与生长发育[/color][/size][/font][size=16px]核黄素为机体健康和正常生长所必需,其形成的辅酶是许多氧化酶系统不可缺少的组成部分,在生物氧化过程中参与氢的传递,促进碳水化合物,蛋白质,脂肪,核酸的代谢。其缺乏可产生一些重要的影响,其中最主要的是生长障碍。杨焕民等人以[/size][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][size=16px]日龄大鼠作实验时发现,低温下补充适量核黄素有利于生长激素和胰岛素的分泌,从而有利于生长;且通过增加肾上腺皮质束状带宽度及束状带和髓质细胞数,降低血清[/size][font='times new roman'][size=16px]T3[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]、[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]T4[/size][/font][size=16px]皮质醇水平,促进机体冷适应[/size][size=16px],[/size][font='arial'][size=16px]提高机体耐寒力。因此耐寒环境下适量补加核黄素有利于动物的生长[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]5[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]。人体研究也得出相应的结论[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]6[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px],[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]7[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]:孕期核黄素摄入量与新生儿出生体重呈正相关,强化核黄素的食品能有效地改善小学生营养状况和促进其生长发育。[/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]2[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6].[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]2[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]核黄素与铁代谢[/color][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]核黄素的缺乏将导致人和动物铁吸收、储存、利用降低,其机制可能通过影响体内[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]NAD[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]-[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]FMN[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]氧化还原酶而起作用,核黄素缺乏时引起人和动物生长停滞,因而铁缺乏的同时,核黄素的严重缺乏将抑制儿童和幼龄动物对铁的需求,从而掩盖肌体铁的缺乏。因此,无论治疗核黄素缺乏病还是缺铁性贫血,同时补充铁和核黄素都是有益的[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]8[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]。[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]国内外大量的动物实验表明,核黄素缺乏可能通过影响小肠中[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]NADH[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]-[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]FMN[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]氧化还原酶(即铁蛋白还原酶)活力而参与铁代谢[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][6][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px],即核黄素缺乏可能影响到体内铁的吸收,从而导致缺铁性贫血[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px](IDA)[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]发生率的增多。人群调查证实,核黄素缺乏者的平均血红蛋白量[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px](Hb)[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]与血清铁蛋白([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]SF[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px])浓度均低于正常者,且其贫血率及缺铁率高于核黄素营养状况正常者,全血谷胱甘肽还原酶活性系数与[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]Hb[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]、[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]SF[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]均呈负相关[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][9][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]。[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]在核黄素与铁同时缺乏的研究中,动物实验表明,核黄素缺乏对缺铁大鼠的铁状况不但不进一步协同加速恶化,相反起一定程度的缓解作用[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]8[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]。[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]其[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]原因可能是核黄素与铁同时缺乏时,核黄素缺乏因明显地抑制了大鼠的生长,使体重增长缓慢、血容量扩充不明显,使机体对铁的需求相对降低,即核黄素缺乏对铁状况有“节约效应”。而单纯缺铁时,体重增长抑制远不如核黄素和铁同时缺乏时明显,血容量仍大量扩充,机体对铁的需求大,饲料又缺铁,就易出现铁营养状况的恶化。因此,二者同时缺乏时,核黄素缺乏通过其对生长的抑制作用而掩盖铁状况的恶化。[/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]2[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6].[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]3[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]核黄素与癌[/color][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]大量的流行病学和动物实验资料表明,核黄素等微量营养素具有防癌和抗癌作用。据调查发现[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]:[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]伊朗[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]、[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]中国等地居民因核黄素缺乏或严重摄入不足导致慢性食道炎普遍存在或食管癌区域高发[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][10][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]。林英等研究也证实:补充核黄素组的食管癌前病人的食管上皮细胞增生转换的好转率和稳定率明显高于安慰剂组。可见核黄素可抑制食管上皮增生或促进其向正常转化[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]11[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]。除影响上皮组织完整性外,核黄素还有抗突变作用,经[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]Ames[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]试验检测,核黄素是黄曲霉毒素[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]B1[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]突变剂的很有效的拮抗物[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]12[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px] 周纯先[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]13[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]指出:小鼠腹腔注射核黄素[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0mg[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]/[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]kg[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]以上及饮水含核黄素[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]10mg[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]/[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]L[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]时,可显著降低[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]HgCl2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]致小鼠微核作用 随后李建端等以大鼠作实验时发现,在[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]RPMI1640[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]培养基中添加核黄素([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]26[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]~[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]130μmol[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]/[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]L[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px])可显著抑制甲基苄基亚硝胺([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]MBNA[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px])的致细胞突变作用[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]14[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]。[/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]2[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6].[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]4[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]核黄素与心血管疾病[/color][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]核黄素通过黄素辅酶参与机体的生物氧化还原反应,抑制脂质过氧化,减少自由基的生成,保护心血管系统免受氧化损伤。而核黄素缺乏会激发细胞凋亡,造成正常细胞损伤,削弱了机体的抗氧化能力。研究表明,氧化应激的过度和机体抗氧化能力的不足是心血管疾病和其他疾病的发病机制之一[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]15[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]。单细胞凝胶电泳实验显示,冠状动脉疾病患者与正常健康者对照比较[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]DNA[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]损伤程度显著升高,而且损伤程度与总抗氧化能力呈负相关。冠心病患者总抗氧化能力下降,[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]DNA[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]损伤增加,而且[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]DNA[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]损伤增加与年龄相关的抗氧化酶减少和修复能力的下降有关。核黄素作为抗氧化剂,可能有助于保护[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]DNA[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]免于受损。刘秀玲等[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][16][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]报道,适宜浓度的核黄素能降低过氧化氢诱导的[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]DNA[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]氧化损伤。殷慧群[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]等[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][17][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]研究证明,[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]通过核黄素干预后[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px],有助于保护冠状动脉血管内皮,维持内皮功能的完整性[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]。[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]综上所述,核黄素是机体必需微量营养素之一,具有广泛的生理功能,世界卫生组织([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]WTO[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px])将其列为评价人体生长发育和营养状况六大指标之一。但我国人均每日摄取入核黄素([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]VB2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px])不足[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]8[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]尤见于儿童、青少年、孕妇,。因此,正确引导儿童的食物消费,优化膳食模式,增加富含核黄素等一些微量营养素食物的摄入,如:动物内脏,奶类,蛋类,豆制品及蔬菜,并对缺乏者采用适宜的干预措施和核黄素药物治疗,仍是当前营养工作中的一个重要环节。[/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]第三章 核黄素的应用[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]3[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6].[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]1[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6] 核黄素与放射性黏膜炎[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6] [/color][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]肿瘤患者在放疗、化疗过程中容易出现口腔黏膜炎、肠黏膜炎、胃溃疡等,严重时可导致全身性感染,危及生命。对于中晚期鼻咽癌,同期放化疗已经成为标准的治疗模式。然而同期放化疗在杀伤肿瘤细胞的同时也造成对正常组织的损伤,尤其是黏膜炎加重,降低了部分患者的耐受性,增加了患者的痛苦。在实际临床工作中也可能因为耐受性的问题而调整治疗强度,中断、甚至停止治疗。因此在治疗期间防治黏膜炎已成为鼻咽癌同期放化疗过程中面临的主要问题之一。[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]核黄[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]素类药物对治疗黏膜炎和口腔溃疡有较好的疗效[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]18[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px],1[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]9[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]。蒋秀美等[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]20][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]报道,核黄素可用于预防造血干细胞移植后口腔黏膜炎,使黏膜炎损伤程度减轻,恢复时间比较快。[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]核黄素缺乏间接地削弱了机体的抗氧化功能,而补充核黄素则可能增加机体的抗氧化功能,从而可以很好地预防黏膜炎和口腔溃疡,提高了放疗、化疗患者的耐受力[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][21][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]。[/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]3.2 核黄素与秋季腹泻[/color][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]秋季腹泻是儿科最常见的疾病之一,估计我国[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]5[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]岁以下小儿中腹泻病平均 每年[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]5[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]次/人,而秋季腹泻占[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]87%[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px],[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]主要病原是轮状病毒。临床应用核黄素治疗小儿腹泻,增加了机体的抗氧化功能,使肠黏膜细胞得到快速修复,从而使其吸收和分泌功能恢复正常[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][21][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]。[/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]3.3 核黄素与烧伤[/color][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px] [/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px] [/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]核黄素是一种可用于中小面积烧伤创面的安全、有效的外用药。大面积烧伤的患者长时间大剂量应用抗生素[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px], 可诱发核黄素缺乏, 最终导致真菌感染加重, 辅以核黄素治疗有利于防止真菌感染[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]。其机制可能是核黄素参与了生物氧化作用和机体三大代谢过程[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px], 足量的核黄素使体内酸性物质减少, 不利于真菌生长, 从而使患者不易发生真菌感染[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][21][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]。[/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]3.4 [/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]核黄素与心血管疾病[/color][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=18px] [/size][/font][font='arial'][size=18px] [/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]核黄素类药物对患者心脏功能有一定的改善作用[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px], 核黄素通过黄素辅酶参与机体的生物氧化还原反应, 抑制脂质过氧化, 减少自由基的生成, 保护心血管系统免受氧化损伤。[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]而核黄素缺乏会激发细胞凋亡[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px], 造成正常细胞损伤, 削弱了机体的抗氧化能力[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][21][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]。[/size][/font][align=center][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]第四章核黄素的检测[/color][/size][/font][/align][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]4[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6].1.[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]高效液相色谱法[/color][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]4[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]原理[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]试样在稀盐酸环境中恒温水解,调[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]pH[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]至[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]6[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]~[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]6[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]5[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px],用木瓜蛋白酶和高峰淀粉酶酶解,定容过滤后,滤液经反相色谱柱分离,高效液相色谱荧光检测器检测,外标法定量。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]4[/size][/font][size=16px].[/size][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][size=16px].[/size][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2[/size][/font][size=16px]分析步骤[/size][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].试样制备[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]取样品约[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]500g[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px],用组织捣碎机充分打匀均质,分装入洁净棕色磨口瓶中,密封,并做好标记,避光存放备用。称取[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2g[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]~[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]10g[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px](精确至[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]01g[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px])均质后的试样(试样中维生素[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]B2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]的含量大于[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]5μg[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px])于[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]100mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]具塞锥形瓶中,加入[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]60mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]的[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1mol[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]/[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]L[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]盐酸溶液,充分摇匀,塞好瓶塞。将锥形瓶放入高压灭菌锅内,在[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]121[/size][/font][font='宋体'][size=16px]℃[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]下保持[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]30min[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px],冷却至室温后取出。用[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1mol[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]/[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]L[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]氢氧化钠溶液调[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]pH[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]至[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]6[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]~[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]6[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]5[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px],加入[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]混合酶溶液,摇匀后,置于[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]37[/size][/font][font='宋体'][size=16px]℃[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]培养箱或恒温水浴锅中过夜酶解。将酶解液转移至[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]100mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]容量瓶中,加水定容至刻度,用滤纸过滤或离心,取滤液或上清液,过[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]45μm[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]水相滤膜作为待测液。(注:操作过程应避免强光照射)[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]不加试样,按同一操作方法做空白试验。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].仪器条件[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px] [/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px] [/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]a[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px])色谱柱:[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]C18[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]柱,柱长[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]150mm[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px],内径[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]4[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]6mm[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px],填料粒径[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]5μm[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px],或相当者[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]b[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px])流动相:乙酸钠溶液([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]05mol[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]/[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]L[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px])-甲醇([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]65[/size][/font][font='宋体'][size=16px]∶[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]35[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]) [/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]c[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px])流速:[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]/[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]min[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px] [/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]d[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px])柱温:[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]30[/size][/font][font='宋体'][size=16px]℃[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px] [/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]e[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px])检测波长:激发波长[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]462nm[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px],发射波长[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]522nm[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px] [/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]f[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px])进样体积:[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]20μL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]3[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].标准曲线的制作[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px] [/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]将标准系列工作液分别注入高效液相色谱仪中,测定相应的峰面积,以标准工作液的浓度为横坐标,以峰面积为纵坐标,绘制标准曲线。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]4[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].试样溶液的测定[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px] [/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]将试样溶液注入高效液相色谱仪中,得到相应的峰面积,根据标准曲线得到待测液中维生素[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]B2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]的浓度。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]5[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].空白试验[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px] [/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]要求空白试验溶液色谱图中应不含待测组分峰或其他干扰峰。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]6[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]精密度[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px] [/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]在重复性条件下获得的两次独立测定结果的绝对差值不得超过算术平均值的[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]10[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]%。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]7[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].其他[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px] [/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]当取样量为[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]10[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]00g[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]时,方法检出限为[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]02mg[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]/[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]100g[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px],定量限为[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]05mg[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]/[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]100g[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]。[/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]4[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6].2[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]荧光分光光度法[/color][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]4[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]原理[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]维生素[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]B2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]在[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]440nm[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]~[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]500nm[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]波长光照射下发生黄绿色荧光。在稀溶液中其荧光强度与维生素[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]B2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]的浓度成正比。在波长[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]525nm[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]下测定其荧光强度。试液再加入连二亚硫酸钠,将维生素[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]B2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]还原为无荧光的物质,然后再测定试液中残余荧光杂质的荧光强度,两者之差即为试样中维生素[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]B2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]所产生的荧光强度。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]4[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]分析步骤[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].试样制备[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]试样的水解取样品约[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]500g[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px],用组织捣碎机充分打匀均质,分装入洁净棕色磨口瓶中,密封,并做好标记,避光存放备用。称取[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2g[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]~[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]10g[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px](精确至[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]01g[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px],约含[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]10μg[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]~[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]200μg[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]维生素[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]B2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px])均质后的试样于[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]100mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]具塞锥形瓶中,加入[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]60mL0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1mol[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]/[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]L[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]的盐酸溶液,充分摇匀,塞好瓶塞。将锥形瓶放入高压灭菌锅内,在[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]121[/size][/font][font='宋体'][size=16px]℃[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]下保持[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]30min[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px],冷却至室温后取出。用氢氧化钠溶液调[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]pH[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]至[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]6[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]~[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]6[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]5[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]试样的酶解加入[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]混合酶溶液,摇匀后,置于[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]37[/size][/font][font='宋体'][size=16px]℃[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]培养箱或恒温水浴锅中过夜酶解。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]3[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]过滤将上述酶解液转移至[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]100mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]容量瓶中,加水定容至刻度,用干滤纸过滤备用。此提取液在[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]4[/size][/font][font='宋体'][size=16px]℃[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]冰箱中可保存一周。注:操作过程应避免强光照射。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].氧化去杂质[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]视试样中核黄素的含量取一定体积的试样提取液(约含[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1μg[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]~[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]10μg[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]维生素[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]B2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px])及维生素[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]B2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]标准使用溶液分别置于[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]20mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]的带盖刻度试管中,加水至[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]15mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]。各管加[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]5mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]冰乙酸,混匀。加[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]5mL30g[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]/[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]L[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]高锰酸钾溶液,摇匀,放置[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2min[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px],使氧化去杂质。滴加[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]3[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]%过氧化氢溶液数滴,直至高锰酸钾的颜色褪去。剧烈振摇试管,使多余的氧气逸出。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]3[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].维生素[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]B2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]的吸附和洗脱[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]3[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]维生素[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]B2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]吸附柱硅镁吸附剂约[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1g[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]用湿法装入柱,占柱长[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]/[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]~[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]/[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]3[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px](约[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]5cm[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px])为宜(吸附柱下端用一小团脱脂棉垫上),勿使柱内产生气泡,调节流速约为[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]60[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]滴/[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]min[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]。(注:可使用等效商品柱)[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]3[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]过柱与洗脱将全部氧化后的样液及标准液通过吸附柱后,用约[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]20mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]热水淋洗样液中的杂质。然后用[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]5mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]洗脱液将试样中维生素[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]B2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]洗脱至[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]10mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]容量瓶中,再用[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]3mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]~[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]4mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]水洗吸附柱,洗出液合并至容量瓶中,并用水定容至刻度,混匀后待测定。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]4[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].标准曲线的制备[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]分别精确吸取维生素[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]B2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]标准使用液[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]3mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]、[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]6mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]、[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]9mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]、[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]25mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]、[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]5mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]、[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]5[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]、[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]10[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]、[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]20[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px](相当于[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]3μg[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]、[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]6μg[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]、[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]9μg[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]、[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]25μg[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]、[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]5μg[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]、[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]5[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0μg[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]、[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]10[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0μg[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]、[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]20[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0μg[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]维生素[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]B2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px])或取与试样含量相近的单点标准按[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]和[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]3[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]操作。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]5[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].试样溶液的测定[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]于激发光波长[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]440nm[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px],发射光波长[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]525nm[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px],测量试样管及标准管的荧光值。待试样管及标准管的荧光值测量后,在各管的剩余液(约[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]5mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]~[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]7mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px])中加[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1mL20[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]%连二亚硫酸钠溶液,立即混匀,在[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]20s[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]内测出各管的荧光值,作各自的空白值。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]6[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].精密度[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]在重复性条件下获得的两次独立测定结果的绝对差值不得超过算术平均值的[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]10[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]%。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]7[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].其他[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]当取样量为[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]10[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]00g[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]时,方法检出限[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]006mg[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]/[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]100g[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px],定量限:[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]02mg[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]/[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]100g[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]。[/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]4[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6].[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]3[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]微生物法[/color][/size][/font][size=16px]某一种微生物的生长繁殖必需某一种维生素,;例如干酪乳酸杆菌的生长需要核黄素,培养基中若缺乏这种维生素该细菌则不能生长。在一定条件下,该细菌生长情况,以及它的代谢物乳酸的浓度与培养基中该维生素含量成正比,因此可以用浑浊度的测定法来测试试样中核黄素的含量。[/size][size=16px]微生物法测定食物中核黄[/size][size=16px]素[/size][size=16px]是经典方[/size][size=16px]法,[/size][size=16px]特异性和灵敏度均高[/size][size=16px],[/size][size=16px]但方法费时[/size][size=16px],[/size][size=16px]周期较长[/size][size=16px],已从国家标准中删除。[/size][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]参考文献[/color][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px][1]Bensasson R V,Land E J,Truscott T G.Flash Photolysis and Pulse Radiolysis in Biologyand Medicine [J],Oxford:Pergamon Press,1993:140-147[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px][2]Ito K,Inous Yamamoto K,etal.8-Hydroxyguanosine formation at the5-GG3 sequences in double-stranded DNA by UV radiation with riboflavin[J].Journal Biological Chemistry.1993:268:13220-13227[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px][3]Frier C Fontecave M,Mouscadet J,et al. Flavin-oligonucleotide conjugates sequence specific photocleavage of DNA [J].Chemical Communication,1998:2457-2458[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]4[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]]陆长元,韩镇辉,蔡喜臣,陈雨玲,姚思德.核黄素(维生素[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]B2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px])的光物理和光化学性质[[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]J[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]].中国科学([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]B[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]辑化学),[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]2000[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]05[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]):[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]428[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]-[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]435[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px][5]Delane AA,Powers HJ.The influence of riboflavin deficiency on absorption and liver storage of iron in the growth rat[J].Br J Nutr,1986,8(1):41.[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px][6]Delane AA,Powers HJ.Efeccts of combined riboflavin and iron deficicncy on the hematological status and iron concert ration of the rat[J].JNutr,1986,116:1257.[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]7[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]]柳启沛,陈文根,张琪,翁聪颖,朱朝勇,邓春勤,朱元桢,张亚非,沈镇平,徐达道.铁、核黄素与贫血关系研究及其防治应用[[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]J[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]].医学研究通讯,[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]1994[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]10[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]):[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]29[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]-[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]30[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px].[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]8[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]]项昭保,戴传云,朱蠡庆.核黄素生理生化特征及其功能[[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]J[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]].食品研究与开发,[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]2004[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]06[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]):[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]90[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]-[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]92[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]+[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]95[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px].[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]9[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]][/size][/font][size=12px]陈文[/size][size=12px]根.核黄素缺乏对铁代谢的影响[/size][size=12px][[/size][font='times new roman'][size=12px]J[/size][/font][size=12px]]国外医学+卫生学分册[/size][size=12px],[/size][font='times new roman'][size=12px]1990[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]5[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]) [/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]283[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px][10][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px][back=#ffffff]Mu?ozN.,GrassiA.,QiongShen,etal.PRECURSORLESIONSOFOESOPHAGEALCANCERINHIGH-RISKPOPULATIONSINIRANANDCHINA[J].TheLancet,1982,319(8277):876-879.[/back][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px][back=#ffffff][11]林英,王旗,朱明君,陈萍萍.核黄素营养水平对食管上皮增生转化的影响[J].河南预防医学杂志,1995(04):192-193.[/back][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px][back=#ffffff][12]郭志成.维生素对突变的抑制作用[J].解放军预防医学杂志,1993(05):396-400.[/back][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px][back=#ffffff][13]周纯先,肖棣,王帮霞,王允滋.维生素B2拮抗HgCl2致小鼠微核作用的研究[J].癌变.畸变.突变,1995(04):220-221.[/back][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px][back=#ffffff][14]李建端,赵勤,李红娅,苗健,关链,陈本懋.核黄素等抗甲基苄基亚硝胺的致细胞突变作用[J].河南医科大学学报,1995(03):227-230.[/back][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]15[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]DemirhagR,YilmazR,KocyigitA.RelationshipbetweenDNAdamage,totalantioxidantcapacityandcoronaryarterydisease[J].MutatRes,2005,570(2):197-20[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]16]刘秀玲,王俐,姜春花,等.硫胺素和核黄素对H2O2诱导的DNA氧化损伤的影响[J[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]上海交通大学学报:医学版[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px],[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]2009[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px],[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]29(9):1049-1052.[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]17[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]殷慧群,陈冬云,周云泳[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]核黄素对心肌缺血再灌注损伤时一氧化氮及其合酶的影响[J[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px].皖南医学院学报[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px],[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]2005[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px],[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]24(3):179-181.[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]18[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]符起亚,邓芳成,张治汉.长效核黄素治疗复发性口腔溃疡患者疗效观察及对血清[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]IL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]-[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]水平的影响[[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]J[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]].海南医学院学报,[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]2009[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px],[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]15[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]10[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]):[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]1303[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]-[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]1304[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]19[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]史建国.核黄素磷酸钠防治放射性口腔咽炎的临床研究[[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]J[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]].中国肿瘤临床与康复,[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]2007[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px],[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]14[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]3[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]):[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]272[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]-[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]273[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]20[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]蒋秀美,芮雪芹,濮益琴,等.长效核黄素预防血液病造血干细胞移植后口腔黏膜炎[[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]J[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]].江苏医药,[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]2009[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px],[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]35[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]6[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]):[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]727[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]-[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]728[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px][21][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]李娜,杨建云,肖炳坤,黄荣清.核黄素临床应用研究进展[[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]J[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]].解放军医药杂志,[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]2012[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px],[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]24[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]04[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]):[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]52[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]-[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]54[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px].[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]22[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]] [/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]GB5009[/size][/font][size=12px].[/size][font='times new roman'][size=12px]85[/size][/font][size=12px]—[/size][font='times new roman'][size=12px]2016[/size][/font][size=12px]食品安全国家标准 食品中维生素[/size][font='times new roman'][size=12px]B2[/size][/font][size=12px]的测定[/size]
你好!我这学期在做姜黄素分光光度法测定食品中硼酸的相关论文。实验过程中碰到了该问题:不知道这个实验为何须在55摄氏度水浴箱中水浴蒸干。请有相关经验的大侠帮忙解答。同时有做过相关实验的朋友可以一起探讨。我的QQ是369583862(力)
[b][color=#444444]叶黄素酯有用量要求吗?[/color][/b]

10,抽取5个版友);中奖名单:mengzhaocheng(注册ID:mengzhaocheng)夏天的雪(注册ID:bingwang228)WUYUWUQIU(注册ID:wulin321)捌道巴拉巴巴巴(注册ID:v3082413)莫名其妙(注册ID:moyueqiu)http://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2017/02/201702271518_01_1610895_3.jpghttp://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2017/02/201702271518_02_1610895_3.jpg【注意事项】同样的答案,每人只能发一次PS:该贴浏览权限为“回贴仅作者和自己可见”,回复的版友仅能看到版主的题目及自己的回答内容,无法看到其他版友的回复内容。下午3点之后解除,即可看到正确答案、获奖情况及所有版友的回复内容。=======================================================================RP-HPLC法测定番石榴叶中桑黄素来苏糖苷和桑黄素阿拉伯糖苷的含量方法:HPLC基质:药品应用编号:102953固定相:Diamonsil C18(2)色谱柱/前处理小柱:Diamonsil 5μm C18(2), 250 x 4.6mm色谱条件:色谱柱:Diamonsil C18 250 mm× 4.6 mm, 5μm(Cat#:99603) 流动相: 甲醇-0.1% 磷酸溶液( 35: 65) 流速: 1.0 mL/min 柱温: 室温 进样量: 10 μL 检测器: UV 355 nm文章出处:中国实验方剂学杂志 2009, 15(6):21-23关键字:反相高效液相色谱, 番石榴叶, 桑黄素来苏糖苷, 桑黄素阿拉伯糖苷, Diamonsil C18, 钻石二代, 含量测定谱图:摘要:目的:建立番石榴叶中桑黄素来苏糖苷和桑黄素阿拉伯糖苷的含量测定方法。方法:用Diamonsil C18色谱柱(250mm×4.6mm,5μm),以甲醇-0.1%磷酸溶液(35∶65)为流动相,流速为1.0mL·min-1,检测波长为355nm。结果:桑黄素来苏糖苷在0.06132~0.14308μg范围内呈良好的线性关系(r=0.9999);桑黄素阿拉伯糖苷在0.05844~0.13636μg范围内呈良好的线性关系(r=1),平均回收率分别为98.6%和100.7%,RSD分别为1.0%和1.7%。结论:本方法对番石榴叶质量标准的制定具有很好的参考价值。http://www.dikma.com.cn/Public/Uploads/images/108-1.JPG
[align=center][b][font='times new roman'][size=18px]红花[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=18px]中[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=18px]羟基红花黄色素[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=18px]A[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=18px]和山奈[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=18px]酚[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=18px]测定[/size][/font][/b][/align][align=center][img]https://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2022/11/202211231824251465_793_1858223_3.jpeg[/img][/align][align=center][/align][font='times new roman']1 [/font][font='times new roman']材料与试剂[/font][font='times new roman']乙腈[/font][font='times new roman']、甲醇[/font][font='times new roman'](色谱级)、[/font][font='times new roman']甲醇、[/font][font='times new roman']盐酸、[/font][font='times new roman']磷酸[/font][font='times new roman'](分析纯)、[/font][font='times new roman']羟基红花黄色素[/font][font='times new roman']A[/font][font='times new roman']和山奈[/font][font='times new roman']酚[/font][font='times new roman'](购自中检院)、[/font][font='times new roman']红花[/font][font='times new roman']样品[/font][font='times new roman'](客户送检)[/font][font='times new roman']。[/font][font='times new roman']2 [/font][font='times new roman']色谱条件[/font][font='times new roman']LC-20AT[/font][font='times new roman'][url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/5p][color=#3333ff]液相色谱仪[/color][/url](日本岛津),色谱柱:[/font][font='times new roman']Zorbax[/font][font='times new roman'] [/font][font='times new roman']E[/font][font='times new roman']clipse[/font][font='times new roman'] XDB-[/font][font='times new roman'] [/font][font='times new roman']C18(250mm*4.6μm*5μm)[/font][font='times new roman'](安捷伦),[/font][font='times new roman'] [/font][font='times new roman']羟基红花黄色素[/font][font='times new roman']A[/font][font='times new roman']:[/font][font='times new roman']以甲醇[/font][font='times new roman']-[/font][font='times new roman']乙腈[/font][font='times new roman']-0.7%[/font][font='times new roman']磷酸溶液([/font][font='times new roman']26[/font][font='times new roman']:[/font][font='times new roman']2[/font][font='times new roman']:[/font][font='times new roman']72[/font][font='times new roman'])为流动相[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']柱温[/font][font='times new roman']3[/font][font='times new roman']5[/font][font='times new roman'] ℃[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']检测波长为[/font][font='times new roman']403nm[/font][font='times new roman'];[/font][font='times new roman']山奈[/font][font='times new roman']酚[/font][font='times new roman']:[/font][font='times new roman']以[/font][font='times new roman']甲醇[/font][font='times new roman']-[/font][font='times new roman']0.[/font][font='times new roman']4[/font][font='times new roman']%[/font][font='times new roman']磷酸水[/font][font='times new roman']梯度洗脱[/font][font='times new roman'];[/font][font='times new roman']柱温[/font][font='times new roman']3[/font][font='times new roman']5[/font][font='times new roman'] [/font][font='times new roman']℃[/font][font='times new roman']。[/font][font='times new roman']检测波长为[/font][font='times new roman']3[/font][font='times new roman']67[/font][font='times new roman']nm[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']3[/font][font='times new roman']溶液制备[/font][font='times new roman'](按照中国药典[/font][font='times new roman']2[/font][font='times new roman']020[/font][font='times new roman']年版一部[/font][font='times new roman']红花[/font][font='times new roman']项下测定)[/font][font='times new roman']3[/font][font='times new roman'].1[/font][font='times new roman']红花中羟基红花素[/font][font='times new roman']测定[/font][font='times new roman']对照品溶液的制备[/font][font='times new roman'] [/font][font='times new roman']取羟基红花黄色素[/font][font='times new roman']A[/font][font='times new roman']对照品适量,精密称定,加[/font][font='times new roman']25%[/font][font='times new roman']甲醇制成每[/font][font='times new roman']1m[/font][font='times new roman']L[/font][font='times new roman']含[/font][font='times new roman']0.1[/font][font='times new roman']4 [/font][font='times new roman']mg[/font][font='times new roman']的溶液,即得。[/font][font='times new roman'] [/font][align=center][font='times new roman'][img=,690,166]https://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2022/11/202211231826389211_7857_1858223_3.jpg!w690x166.jpg[/img] [/font][font='times new roman']羟基红花黄色素[/font][font='times new roman']A[/font][font='times new roman']对照品[/font][font='times new roman']色谱图[/font][/align][font='times new roman']样品[/font][font='times new roman']溶液的制备[/font][font='times new roman'] [/font][font='times new roman']取本品粉末(过三号筛)约[/font][font='times new roman']0.4g[/font][font='times new roman'],精密称定,[/font][font='times new roman']置具塞[/font][font='times new roman']锥形瓶中,精密加入[/font][font='times new roman']25%[/font][font='times new roman']甲醇[/font][font='times new roman']50m[/font][font='times new roman']L[/font][font='times new roman'],称定重量,超声处理(功率[/font][font='times new roman']300W[/font][font='times new roman'],频率[/font][font='times new roman']50kHz[/font][font='times new roman'])[/font][font='times new roman']40[/font][font='times new roman']分[/font][font='times new roman']钟,放冷,再称定重量,用[/font][font='times new roman']25%[/font][font='times new roman']甲醇[/font][font='times new roman']补足减失的[/font][font='times new roman']重量,摇匀,滤过,[/font][font='times new roman']取续滤液[/font][font='times new roman'],即得。 [/font][img]" style="max-width: 100% max-height: 100% [/img][align=center][img=,690,140]https://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2022/11/202211231827015873_9300_1858223_3.jpg!w690x140.jpg[/img][/align][align=center]红花药材中羟基红花素A测定色谱图[/align][font='times new roman']3.1[/font][font='times new roman']红花中[/font][font='times new roman']山奈[/font][font='times new roman']酚[/font][font='times new roman']测定[/font][font='times new roman']对照品溶液的制备[/font][font='times new roman'] [/font][font='times new roman']取山柰酚对照品适量,精密称定,加甲醇制成每[/font][font='times new roman']1ml[/font][font='times new roman']含[/font][font='times new roman']10 [/font][font='times new roman']μ[/font][font='times new roman']g[/font][font='times new roman']的溶液,即得。[/font][align=center][img=,690,131]https://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2022/11/202211231827143326_3128_1858223_3.jpg!w690x131.jpg[/img][/align][img]" style="max-width: 100% max-height: 100% [/img][align=center]山柰酚标品[/align][font='times new roman'] [/font][font='times new roman']样品[/font][font='times new roman']溶液的制备[/font][font='times new roman'] [/font][font='times new roman']取本品粉末(过三号筛)约[/font][font='times new roman']0.5g[/font][font='times new roman'],精密称定,[/font][font='times new roman']置具塞[/font][font='times new roman']锥形瓶中,精密加入甲醇[/font][font='times new roman']25m[/font][font='times new roman']L[/font][font='times new roman'],称定重量,加热回流[/font][font='times new roman']30[/font][font='times new roman']分钟,放冷,再称定重量,用甲醇[/font][font='times new roman']补足减失的[/font][font='times new roman']重量,摇匀,滤过,精密[/font][font='times new roman']量取续滤液[/font][font='times new roman']15m[/font][font='times new roman']L[/font][font='times new roman'],置平底烧瓶中,加盐酸溶液([/font][font='times new roman']15[/font][font='times new roman']→[/font][font='times new roman']37[/font][font='times new roman'])[/font][font='times new roman']5m[/font][font='times new roman']L[/font][font='times new roman'],摇匀,置水浴中加热水解[/font][font='times new roman']30[/font][font='times new roman']分钟,立即冷却,转移至[/font][font='times new roman']25m[/font][font='times new roman']L[/font][font='times new roman']量瓶中,用甲醇稀释至刻度,摇匀,滤过,[/font][font='times new roman']取续滤液[/font][font='times new roman'],即得[/font][align=center][img=,690,138]https://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2022/11/202211231827289628_6371_1858223_3.jpg!w690x138.jpg[/img][/align][img]" style="max-width: 100% max-height: 100% [/img][align=center]红花中山柰酚测定[/align][font='times new roman']结果:客户送检样品[/font][font='times new roman']红花[/font]中羟基红花素A含量为1.7%,山奈酚含量为0.065%[font='times new roman']。[/font][font='times new roman']注:[/font][font='times new roman']①[/font][font='times new roman']测定[/font][font='times new roman']红花药材中羟基红花素[/font][font='times new roman']A[/font][font='times new roman']时流动相为三相,如果[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/5p][color=#3333ff]液相色谱仪[/color][/url]为两通道建议混匀到一个流动相试剂瓶里进行测定。[/font][font='times new roman']②测定山奈酚时,需要用盐酸水解,加入盐酸后一定注意密塞,因为盐酸水浴容易挥发,影响水解效果。[/font]
求叶黄素的红外光谱,十分感谢!叶黄素资料:英文名称: Lutein 中文名称: 叶黄素 CAS号: 127-40-2 分子式: C40H56O2 分子量: 568.88 纯度: 98.00% 别名:α-Carotene-3,3'-diolβ, ε-carotene-3,3′-diolβ, ε-caroteneLutein [img]http://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2008/12/200812252139_126260_1781331_3.jpg[/img]