硫醇硫测定仪怎么去的电位突变范围?
以前做锌分析时终点是突变为亮黄色,最近做样看不到突变,慢慢变亮黄无法判断终点分析方法是这样的,依次加3酸溶样冒白烟,加水至50ML,加氯化铵5g左 右,滴加氨水至铁沉淀完全并过量,加热过滤后调节PH,加抗坏血酸、硫脲、氟化钾,有时也加碘化钾,加二甲酚橙,乙酸乙酸钠缓冲溶液20ML,滴定
基因定点突变,顾名思义,就是把目的基因上的一个碱基有目的的替换为另一个碱基。体外定点突变时目前分子生物学领域中一种快速有效地手段。产生定点突变操作及所需仪器简单,随着技术的发展,方法也越来越快捷简便。定点突变除了可以生成点突变,多点突变外,还可以人为产生碱基删除和添加等。体外基因定点突变是实验室中优化改造基因,研究基因功能的常用方法之一。通过改造基因序列,可以对相应氨基酸序列进行改变,进而影响蛋白质的结构和功能,探讨突变氨基酸位点在蛋白结构和功能中所起的作用。在我多年的实验中,体外基因定点突变是其中一项重要的内容。在这里,我与大家分享一下我的实验方法和心得体会。多年来,我所采用的基因定点突变的方法主要有三种,这可能也包括了目前所有的定点突变的方法。基因定点突变使用的主要仪器就是PCR扩增仪(biometra),而这是每一个分子生物学实验室的必需品,也就是大家吃饭的家伙。下面从繁到简对我所采用的突变方法进行一下简单描述。http://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2012/12/201212032022_409068_1306303_3.jpg我所使用过的定点突变方法简单的说就是三步,两步和一步PCR法。三步PCR法是我早期在实验室使用的定点突变方法。利用三步PCR法构建一个点突变,需要4条PCR引物:L1,L2,R1和R2。L1和R1是目的基因5‘和3‘端的引物,分别包含起始和终止密码子。突变点设计在引物L2和R2的正中间位置,L2和R2是完全互补的两条PCR引物,长度一般在28-40 bp之间,推荐长度31-35 bp,这样可以保证突变的两边有效搭在一起。http://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2012/12/201212032026_409072_1306303_3.jpg三轮PCR均采用常规PCR反应条件,第一轮分别以L1和R2,L2和R1扩增获得目的片段L和R。第二轮PCR,不需要引物,仅加入模板L和R各100 nmol,进行约20 轮的PCR反应,获得产物m1。第三轮PCR以m1为模板,L1和R1为引物进行PCR扩增。最终得到目的产物m。得到的PCR产物进行克隆转化得到进一步扩增,便获得了突变的目的基因。在随后的实验中,我将三步PCR法简化为两步法PCR。两步法PCR和三步法PCR一样,需要引物四条,引物设计也与三步法相同,只是在第一轮PCR获得产物L和R之后不再单独进行第二轮PCR,而直接在PCR体系中加入等mol的产物L和R
近日测样品,发现Rh内标回收率有突变现象,从100%突变到50%,一会儿又是160%,其他元素也都跟着变,通过内标校正计算后数据倒也可以。进样系统正常,换了雾化器,咨询工程师说是矩管前的银屏蔽圈下面的触点接触不好,换了个新的屏蔽圈,下面的也用砂纸擦了,均无大的改善!求解?大家遇到如此问题吗?
8 kb)的原理我上面已经说了,只是补充了一些我认为的注意事项。如果你更有钱的话,那么你可以叫其它公司帮你做定点突变服务,大约是改一个点1000元左右。
对细菌突变,杂交重组、转化、转导、溶源性转换的研究属()范畴研究。 A、形式遗传学 B、分子遗传学 C、生理遗传学 D、生化遗传学
http://www.bioon.com/biology/UploadFiles/201208/2012080216013081.jpg癌症研究人员可以测定肿瘤细胞基因组的序列,扫描其异常的基因活性,剖析其突变的蛋白质和研究它们在实验室培养皿中的生长,但研究者一直无法跟踪细胞形成肿瘤的过程。现在三个独立研究小组在小鼠体内做到了这一点。他们的研究结果支持这样的观点:一小部分细胞驱动肿瘤的生长,而想要治愈癌症可能需要将这些所谓肿瘤干细胞清除。目前还无法确认,这些从脑瘤,肠癌和皮肤癌研究的结论是否适用于其他类型肿瘤,但是得克萨斯大学西南医学中心的路易斯·帕拉达认为,如果它们适用于其他肿瘤,"将深刻地改变目前的化疗疗效评价和临床疗法的制定标准"。 不仅是看某种疗法是否缩小肿瘤,研究人员将更关注是否杀死了正确的细胞。帕拉达和他的同事们想检测是否特异性标识健康成人神经干细胞的一个遗传标记,也可标识神经母细胞瘤中的癌症干细胞。他们发现,所有神经母细胞瘤样本中至少有几个标记细胞 - 大概是干细胞。未标记细胞可被标准化疗杀死,但肿瘤可迅速恢复。进一步的实验表明,未标记细胞起源于标记的细胞祖先。当研究者把化疗与抑制标记细胞的遗传手段相结合进行治疗时,帕拉达说,肿瘤显著缩小到"残留遗迹"的水平。在另一项研究中,荷兰乌得勒支Hubrecht研究所的干细胞生物学家们把注意力瞄着了肠道。利用药物驱动的荧光素标志物表达系统,他们在小鼠体内证实,多种不同类型的肿瘤细胞,其实是来源于同一干细胞的。而且,这些干细胞是肿瘤发展的驱动力。对皮肤癌的研究,Blanpain和他的小组标记单个肿瘤细胞,而不是特异地标记干细胞。他们发现,细胞表现出两种不同的分工模式:它们要么在慢慢耗尽前分裂出少数细胞,或者产生许多细胞。这再次证实,一类独特的细胞亚群是肿瘤生长的驱动力。研究者说,下一步的研究计划将是,搞清楚这些实验所跟踪的细胞如何与通过多年移植实验所确定的,假定的癌症干细胞相联系的。研究人员已经紧锣密鼓地在寻找杀死这些细胞的方法;现在他们有更多的工具来测试这样的策略是否会奏效。
我想请问一下有没有做“致突变”相关的仪器设备
MSDS中物质如何判断是致癌,致基因突变物质?如果有SVHC中物质,如何判断符合性?
中国科技网讯 DNA序列中最轻微的变异也会影响深远,无论对研究还是医学应用,可靠识别这些序列都非常重要。据物理学家组织网近日报道,美国华盛顿大学和莱斯大学研究人员合作,开发出一种荧光DNA探测分子,能检查出一段目标DNA链中单个碱基的变化。而这些微小突变可能是造成某些疾病的根源,或耐抗生素细菌的原因。这一成果有助于诊断和治疗像癌症、肺结核这样的疾病。相关论文发表于7月28日的《自然·化学》杂志网站上。 不同的DNA序列为不同生物设定了独特的基因标记。现代基因组学研究表明,仅一个碱基对的变化都足以引发严重的生物后果,可能决定了一种疾病能否被治愈,也解释了疾病的突发或某些疾病对常规抗生素治疗无效的原因。论文领导作者、华盛顿大学电力工程和计算机科学与工程副教授乔治·塞利格说,比如造成肺结核的细菌有很强的耐药性,这种能力通常来自其基因序列中的少量突变。现在,人们已能预先查出这种突变。 “我们真正改进了以往的方法。”塞利格说,“新方法不需要任何复杂的反应或添加酶,就只用DNA。这意味着无论温度及其他环境变量怎样变化,该方法都是稳定的,所以很适合用于低资源设置中的诊断。” 这种探测分子经过专门设计,采用了新的编程机制,能与一个可疑的DNA序列结合,对其双螺旋链生成互补的DNA序列。把含有两种序列的分子在盐水试管中混合,如果两条链的碱基对都是完好的,它们自然地匹配在了一起,探测分子会发出荧光;如果不发光,则意味着上面有碱基对发生了突变。与以往技术不同的是,探测分子会检查目标DNA双螺旋的两条链是否发生了突变,而不是一条,这使检验更加全面具体。 此外,探测分子由许多寡核苷酸构成,克服了合成上的局限,可以探测更长的DNA序列中更详细的变异信息,达到200个碱基对,而现有探测突变的方法只能检查20个。 目前,研究人员与华盛顿大学商业化中心一起对该技术提出了专利申请,他们希望把这种技术和诊断试纸结合用于疾病测试。(常丽君) 《科技日报》(2013-8-7 二版)
我是做水质化验的,现在领导安排要做一份关于水质突变的应急预案,请问各位有没有什么资料可以参考?或者教教我应该怎么写?谢谢

中国在癌症的许多临床实践中都紧跟在西方国家之后,然而,近年来随着靶向治疗l方面的一些发现,中国在某些肿瘤类型的治疗领域可能处于领先地位。靶向治疗是一种相对较新的癌症治疗方式,定位于肿瘤发生的特定分子靶点。这类药物与传统的化疗不同,传统化疗是特异性地杀伤快速分裂的细胞,包括非癌症性的正常细胞;而靶向治疗仅仅攻击肿瘤内部激活的特异性信号通路,而不会波及肿瘤周围的正常组织细胞。因此,靶向治疗相对于传统的肿瘤治疗毒副作用更小而疗效更强。肺癌为全球癌症死亡的首要原因,而非小细胞肺癌近乎占肺癌死亡率的85%。在2003年,美国FDA批准吉非替尼,一种针对非小细胞肺癌的靶向治疗药物。这类药物通过抑制癌细胞表面的表皮生长因子受体而发挥作用。这类受体在调节重要的细胞过程中发挥了关键作用,包括肿瘤增殖,而这类受体在非小细胞肺癌患者体内通常是高表达。然而,吉非替尼在美国的初步试验,提示它与传统化疗在疗效上没有差异。随后,在2007年,研究者报道:中国肺癌患者与白种人肺癌患者相比,前者体内引起表皮生长因子受体过表达的基因突变率显著偏高。“正因为如此,中国对靶向治疗甚感兴趣,”中国广东省肺癌研究所所长吴一龙教授是2007年那项研究的主要作者,他说道:“在欧洲和美国,吉非替尼的使用并未超越化疗,而中国病人与美国及欧洲病人的差异使得这类药物在中国的使用更为有效”。2011年早些时候,吴教授带领的中国胸部肿瘤研究小组公布了在EGFR突变的中国肺癌患者群体中厄洛替尼的试验结果,厄洛替尼靶向治疗机制与吉非替尼类似,试验结果令人备受鼓舞。 “参加靶向治疗患者的存活率是接受化疗患者的三倍”吴教授说。厄洛替尼虽比化疗好,但只为因基因突变致使表皮生长因子受体过度表达的患者提供略多于一年的无进展生存期(即初步治疗后病情无恶化的时间)。吴教授现正与美国和中国研究人员合作以更好地了解耐药的发生机制和解决方法。吴教授提到“首先我们必须对耐药机制有更好的理解,这样我们才能开发出更好的靶向治疗药物来延长患者的生命”。 http://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2012/01/201201070917_344460_2019107_3.jpg
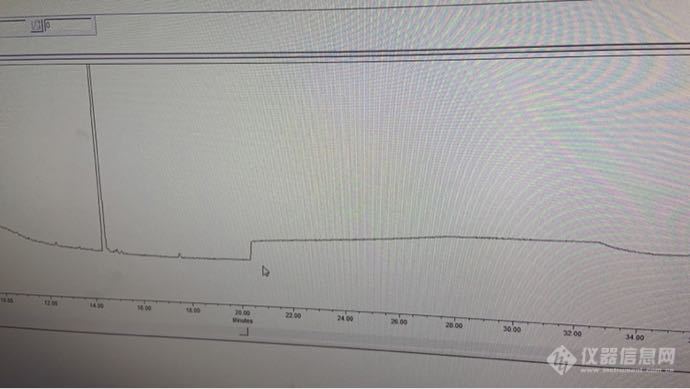
各位大佬,请问这种垂直上升的信号突变是什么原因造成的条件:安捷伦1260,dad检测器,同一个方法,一个序列中只可能有一针出现也可能一针都没有,我在不同的序列中寻找发现每次出现这种垂直的保留时间都不同,并且不止一台液相有这种情况,,并且压力也正常[img=,690,388]https://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2020/06/202006101637044347_7090_4134806_3.png[/img]
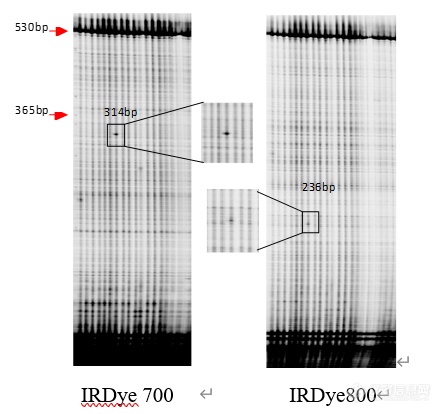
[align=center][b][font=黑体][font=黑体]基于[/font][font=黑体]TILLING技术的基因突变分析[/font][/font][/b][/align][align=center][/align][font=黑体]小麦是我国主要的粮食作物,其栽培面积和总产量仅次于水稻,随着生活水平的日益提高,人们对小麦品质的要求也越来越高,因此,品质改良已成为小麦育种工作的重要目标之一[/font][sup][font='Times New Roman'][[/font][/sup][sup][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]1[/font][/font][/sup][sup][font='Times New Roman']][/font][/sup][font=黑体]。[/font][font=黑体][font=黑体]小麦是异源[/font][font=Times New Roman]6[/font][font=黑体]倍体植物,基因组庞大,突变机制较为复杂[/font][/font][font=黑体][font=黑体],反向遗传学技术,例如[/font][font=Times New Roman]T-DNA[/font][font=黑体]插入、转座子标签,已经越来越多的应用于研究中。然而,这些方法大多数,应用于基因组较小的模式植物,小麦的多倍性及转化体获得的难度,制约了这些方法的更好使用,而[/font][font=Times New Roman]TILLING[/font][font=黑体]技术不受物种倍性影响,[/font][/font][font=黑体]推动了基因功能研究和品质改良的发展[/font][font=黑体]。[/font][b][font=黑体][font=宋体]1 [/font][font=黑体]材料与方法[/font][/font][/b][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]1.1 [/font][/font][font=黑体]植物[/font][font=黑体]材料[/font][font=黑体]春小麦([/font][i][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]Triticum aestivum[/font][/font][/i][font=黑体] [font=Times New Roman]L.[/font][font=黑体])品种龙辐麦[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']17[font=黑体]经航天诱变[/font][/font][font=黑体]选育而成。[/font][font=黑体][font=黑体]共获得[/font][font=Times New Roman]1122[/font][font=黑体]个[/font][/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]EMS[/font][font=黑体]诱变的龙辐麦[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']17[/font][font=黑体] [font=Times New Roman]M[/font][/font][sub][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]2[/font][/font][/sub][font=黑体]代单粒传[/font][font=黑体]植株,苗期单株编号,采集[/font][font=黑体][font=黑体]叶片,迅速冷冻干燥,用于[/font][font=Times New Roman]DNA[/font][font=黑体]提取。[/font][/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]1.2 [/font][font=黑体]基因组[/font][font=Times New Roman]DNA[/font][font=黑体]提取及[/font][font=Times New Roman]DNA[/font][font=黑体]池构建[/font][/font][font=黑体][font=黑体]将干燥后的叶片按编号置于装有珠子的[/font][font=Times New Roman]1.5ml[/font][font=黑体]离心管中,利用组织研磨器[/font][font=Times New Roman]Vibration Mill Type MM301[/font][font=黑体]([/font][font=Times New Roman]Retsch GmbH Co, Germany[/font][font=黑体])将叶片磨成粉末状;加[/font][font=Times New Roman]600[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']μl[/font][font=黑体] [font=Times New Roman]DNA[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman'] Extraction buffer[/font][font='Times New Roman'] [/font][font='Times New Roman'][[/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]0.1[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman'] mol/ L[/font][font=黑体] [/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]Tris[/font][font=黑体];[/font][font=Times New Roman]0.[/font][/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]1[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman'] mol/ L[/font][font=黑体] [font=Times New Roman]KCl[/font][font=黑体];[/font][font=Times New Roman]0.5M EDTA pH 8.0[/font][font=黑体];[/font][font=Times New Roman]1[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman'] mol/ L[/font][font=黑体] [font=Times New Roman]PVP 40[/font][font=黑体];[/font][font=Times New Roman]1.5[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman'] mol/ L[/font][font='Times New Roman'] Na[/font][sub][font='Times New Roman']2[/font][/sub][font='Times New Roman']S[/font][sub][font='Times New Roman']2[/font][/sub][font='Times New Roman']O[/font][sub][font='Times New Roman']6[/font][/sub][font='Times New Roman']][/font][font=黑体][font=黑体],充分混匀;保温振动[/font][font=Times New Roman]1 h[/font][font=黑体];加[/font][font=Times New Roman]200μl 5 mol/[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']L KAc[/font][font=黑体][font=黑体],混匀并离心;取约[/font][font=Times New Roman]300 μl[/font][font=黑体]上清液加至[/font][font=Times New Roman]165 μl[/font][font=黑体]预冷的异丙醇中,沉淀[/font][font=Times New Roman]DNA[/font][font=黑体];用[/font][font=Times New Roman]70 %[/font][font=黑体]乙醇洗[/font][font=Times New Roman]DNA[/font][font=黑体],干燥后,溶于[/font][font=Times New Roman]TER[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman'][[/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]Tris 10mmol/L[/font][font=黑体],[/font][font=Times New Roman]EDTA 1 mmol/L[/font][font=黑体],[/font][font=Times New Roman]RNA[/font][font=黑体]酶[/font][font=Times New Roman]0.05mg/ml[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']][/font][font=黑体][font=黑体],[/font][font=Times New Roman]-20 [/font][font=黑体]℃保存备用。[/font][/font][font=黑体][font=黑体]利用[/font][font=Times New Roman]1.0%[/font][font=黑体]的琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测[/font][font=Times New Roman]DNA[/font][font=黑体]样品,并将其稀释至[/font][font=Times New Roman]40 ng/[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']μ[/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]l[/font][font=黑体],随机两两等量混匀,构建两倍的[/font][font=Times New Roman]DNA[/font][font=黑体]池,用于后续[/font][font=Times New Roman]TILLING[/font][font=黑体]筛选。[/font][/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]1.3 [/font][font=黑体]特异性引物设计及筛选[/font][/font][font=黑体][font=黑体]根据[/font][font=Times New Roman]NCBI[/font][font=黑体]提供的目标基因序列信息,在线设计引物,并用[/font][font=Times New Roman]1%[/font][font=黑体]琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测[/font][font=Times New Roman][url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/jp][color=#3333ff]PCR[/color][/url][/font][font=黑体]产物,选择[/font][font=Times New Roman][url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/jp][color=#3333ff]PCR[/color][/url][/font][font=黑体]产物条带单一,大小在[/font][font=Times New Roman]700-1500[/font][font=黑体]左右的[/font][font=Times New Roman]4[/font][font=黑体]对引物(表[/font][font=Times New Roman]1[/font][font=黑体]),其中[/font][/font][font=黑体]除[/font][i][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]Pinb[/font][/font][/i][font=黑体][font=黑体]引自[/font][font=Times New Roman]Wang[/font][font=黑体]等[/font][/font][sup][font='Times New Roman'][[/font][/sup][sup][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]2[/font][/font][/sup][sup][font='Times New Roman']][/font][/sup][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman](2008)[/font][font=黑体]。[/font][/font][align=center][font=黑体][font=黑体]表[/font][font=Times New Roman]1 [/font][font=黑体]用于[/font][font=Times New Roman]TILLING[/font][font=黑体]检测的基因及其荧光标记引物序列[/font][/font][/align][align=center][font='Times New Roman']Table1 [/font][font=黑体] [font=Times New Roman]Genes and their [/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']IRDye labled primer sequence[/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]s [/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']used[/font][font=黑体] [font=Times New Roman]in TILLING[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman'] [/font][/align][table][tr][td=1,2][align=center][b][font=黑体]基因[/font][/b][/align][align=center][b][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]Gene[/font][/font][/b][/align][/td][td=2,1][align=center][b][font=黑体][font=黑体]引物序列[/font] [font=Times New Roman]Primer sequence (5[/font][font=黑体]′–[/font][font=Times New Roman]3[/font][font=黑体]′[/font][font=Times New Roman])[/font][/font][/b][/align][/td][td=1,2][align=center][b][font=黑体]长度[/font][/b][/align][align=center][b][font='Times New Roman']Length[/font][font=黑体][font='Times New Roman'] [/font][font=Times New Roman](bp)[/font][/font][/b][/align][/td][/tr][tr][td][align=center][b][font=黑体][font=黑体]正向[/font] [font=Times New Roman]Forward[/font][/font][/b][/align][/td][td][align=center][b][font=黑体][font=黑体]反向[/font] [font=Times New Roman]Reverse [/font][/font][/b][/align][/td][/tr][tr][td][align=center][i][font='Times New Roman']P[/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]in[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']b[/font][/i][/align][/td][td][align=center][font='Times New Roman']CCAACGAAACTAATGAGAAATAAAAAGGTG[/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font='Times New Roman']AAGTTGTTGGATGGACGAATAAGGTT[/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font='Times New Roman']1334[/font][font=黑体][font='Times New Roman'] [/font][/font][/align][/td][/tr][tr][td][align=center][i][font='Times New Roman']W[/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]a[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']x[/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]y[/font][/font][/i][/align][/td][td][align=center][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]ACCCGCATGGTGTTTGATAATTTCAGTG[/font][/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]AGAATGCCACCTAGCCATGAAATGAGT[/font][/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font='Times New Roman']790[/font][font=黑体][font='Times New Roman'] [/font][/font][/align][/td][/tr][/table][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]1.4 TILLING[/font][font=黑体]检测[/font][/font][font=黑体]参照潘娜[/font][sup][font='Times New Roman'][[/font][/sup][sup][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]3[/font][/font][/sup][sup][font='Times New Roman']][/font][/sup][font=黑体][font=黑体]([/font][font=Times New Roman]2011[/font][font=黑体])建立的小麦[/font][font=Times New Roman]TILLING[/font][font=黑体]技术检测平台,对目的基因进行检测。采用[/font][/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]Touchdown [/font][/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman][url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/jp][color=#3333ff]PCR[/color][/url][/font][font=黑体]程序,[/font][/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]10μl [/font][/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman][url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/jp][color=#3333ff]PCR[/color][/url][/font][/font][font=黑体]体系含[/font][font='Times New Roman']10 ×Buffer[/font][font=黑体] [font=Times New Roman]0.5μl[/font][font=黑体];[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']Mg[/font][sup][font='Times New Roman']2+[/font][/sup][sup][font=黑体] [/font][/sup][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]0.6[/font][/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]μl[/font][/font][font=黑体];[/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]dNTP [/font][/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]0.8[/font][/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]μl[/font][/font][font=黑体];[/font][font=黑体]引物各[/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]0.4[/font][/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]μl[/font][font=黑体];[/font][/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]Ex Taq HS DNA[/font][font=黑体]聚合酶[/font][font=Times New Roman]0.05[/font][/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]μl[/font][font=黑体],[/font][/font][font=黑体][font=黑体]在[/font][font=Times New Roman]Bio-Rad c1000[/font][font=黑体]仪上扩增。扩增后加[/font][font=Times New Roman]20[/font][/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]μl[/font][/font][font=黑体] [font=Times New Roman]0.1M CEL[/font][font=黑体]Ⅰ酶,[/font][font=Times New Roman]45[/font][font=黑体]℃酶切[/font][font=Times New Roman]15 min[/font][font=黑体],利用[/font][font=Times New Roman]Sephadex G50[/font][font=黑体]([/font][font=Times New Roman]GE Healthcare [/font][font=黑体]公司)纯化板纯化酶切产物,并[/font][font=Times New Roman]90[/font][font=黑体]℃浓缩[/font][font=Times New Roman]35-45 min[/font][font=黑体]。利用[/font][font=Times New Roman]6[/font][font=黑体]%变性聚丙烯酰胺凝胶,在[/font][font=Times New Roman]LI-COR 4300[/font][font=黑体]仪器中电泳检测酶切产物[/font][/font][font=黑体]并[/font][font=黑体][font=黑体]采用[/font][font=Times New Roman]Gelbuddy[/font][font=黑体]软件对电泳图像分析处理,标记突变位点。[/font][/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]1.5 [/font][font=黑体]基因点突变分析[/font][/font][font=黑体][font=黑体]检测到突变后对[/font][font=Times New Roman][url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/jp][color=#3333ff]PCR[/color][/url][/font][font=黑体]产物进行测序验证,利用[/font][font=Times New Roman]Invitrogen[/font][font=黑体]软件、[/font][font=Times New Roman]NCBI[/font][font=黑体]等对序列进行比对、翻译等分析,确定突变位置与类型。[/font][/font][font=黑体][font=黑体]点突变密度[/font][font=Times New Roman](%)=[/font][font=黑体]突变碱基数[/font][font=Times New Roman]/[/font][font=黑体]检测总碱基数×[/font][font=Times New Roman]100%[/font][font=黑体]。[/font][/font][b][font=黑体][font=宋体]2 [/font][font=黑体]结果与分析[/font][/font][/b][font=黑体]本实验对[/font][font=黑体]小麦籽粒硬度基因[/font][i][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]pinb[/font][/font][/i][font=黑体][font=黑体]进行了[/font][font=Times New Roman]1122[/font][font=黑体]个单株的[/font][font=Times New Roman]TILLING[/font][font=黑体]检测。[/font][/font][font=黑体]基因的突变密度分别为[/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]1/374.18 kb[/font][/font][font=黑体]。[/font][i][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]Pinb[/font][/font][/i][font=黑体][font=黑体]基因共获得[/font][font=Times New Roman]7[/font][font=黑体]个突变株系的[/font][font=Times New Roman]4[/font][font=黑体]个不同的突变位点[/font][font=Times New Roman]([/font][font=黑体]图[/font][font=Times New Roman]1)[/font][font=黑体],有[/font][font=Times New Roman]6[/font][font=黑体]个突变单株的碱基突变位点均位于外显子区域,突变株编号及突变位点分别是[/font][font=Times New Roman]LF996[/font][font=黑体]第[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']51[/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]2bp[/font][font=黑体]位的[/font][font=Times New Roman]C-T[/font][font=黑体]碱基转换,[/font][font=Times New Roman]LF[/font][/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]892[/font][font=黑体]、[/font][font=Times New Roman]LF997[/font][font=黑体]、[/font][font=Times New Roman]LF919[/font][font=黑体]第[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']7[/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]26bp[/font][font=黑体]位的[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']G[/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]-[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']A[/font][font=黑体][font=黑体]碱基转换,及[/font][font=Times New Roman]LF791[/font][font=黑体]、[/font][font=Times New Roman]LF1114[/font][font=黑体]第[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']750[/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]bp[/font][font=黑体]位的[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']G[/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]-[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']A[/font][font=黑体][font=黑体]碱基转换,[/font][font=Times New Roman]LF996 [/font][/font][i][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]pinb[/font][/font][/i][font=黑体][font=黑体]基因第[/font][font=Times New Roman]37[/font][font=黑体]为氨基酸[/font][font=Times New Roman]S[/font][font=黑体]变为氨基酸[/font][font=Times New Roman]F[/font][font=黑体],[/font][font=Times New Roman]LF[/font][/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]892[/font][font=黑体]、[/font][font=Times New Roman]LF997[/font][font=黑体]、[/font][font=Times New Roman]LF919[/font][/font][i][font=黑体] [font=Times New Roman]pinb[/font][/font][/i][font=黑体][font=黑体]基因第[/font][font=Times New Roman]110[/font][font=黑体]为氨基酸[/font][font=Times New Roman]G[/font][font=黑体]变为氨基酸[/font][font=Times New Roman]S[/font][font=黑体],[/font][font=Times New Roman]LF791[/font][font=黑体]、[/font][font=Times New Roman]LF1114[/font][font=黑体]第[/font][font=Times New Roman]116[/font][font=黑体]位氨基酸[/font][font=Times New Roman]W[/font][font=黑体]被终止,内含子区域突变是[/font][font=Times New Roman]LF890[/font][font=黑体]突变株第[/font][font=Times New Roman]350bp[/font][font=黑体]碱基[/font][font=Times New Roman]G[/font][font=黑体]转换为碱基[/font][font=Times New Roman]A[/font][font=黑体]。见表[/font][font=Times New Roman]1[/font][/font][align=center][img=,442,414]https://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2022/12/202212160839201707_5062_3237657_3.png!w442x414.jpg[/img][/align][align=center][font=黑体] [/font][/align][align=center][font=黑体][font=黑体]图[/font][font=Times New Roman]1 [/font][/font][i][font='Times New Roman']W[/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]a[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']x[/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]y[/font][/font][/i][font=黑体]基因电泳图[/font][/align][align=center][font='Times New Roman']Fig[/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]1 [/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']E[/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]lectrophorogram of [/font][/font][i][font='Times New Roman']W[/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]a[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']x[/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]y gene[/font][/font][/i][/align][align=center][i][font=黑体] [/font][/i][/align][font='Times New Roman'][/font][align=center][font=黑体][font=黑体]表[/font][font=Times New Roman]1[/font][/font][font=黑体] [font=黑体]基因点突变信息[/font][/font][/align][align=center][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]Table1 Point[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman'] mutations[/font][font=黑体] [font=Times New Roman]of[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman'] quality[/font][i][font=黑体] [/font][/i][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]gene[/font][/font][/align][table][tr][td][align=center][b][font='Times New Roman'][font=黑体]基因名称[/font][/font][/b][/align][align=center][b][font='Times New Roman']Gene[/font][font=黑体][font='Times New Roman'] [/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']name[/font][/b][/align][/td][td][align=center][b][font='Times New Roman'][font=黑体]登录号[/font][/font][/b][/align][align=center][b][font='Times New Roman']Accession[/font][font=黑体][font='Times New Roman'] [/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']No.[/font][/b][/align][/td][td][align=center][b][font='Times New Roman'][font=黑体]基因大小[/font][/font][/b][/align][align=center][b][font='Times New Roman']Gene size[/font][font=黑体][font='Times New Roman'] [/font][/font][font='Times New Roman'](bp)[/font][/b][/align][/td][td][align=center][b][font='Times New Roman'][url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/jp][color=#3333ff]PCR[/color][/url][font=黑体]扩增长度[/font][/font][/b][/align][align=center][b][font='Times New Roman'][url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/jp][color=#3333ff]PCR[/color][/url] size (bp)[/font][/b][/align][/td][td][align=center][b][font='Times New Roman'][font=黑体]等位变异[/font][/font][/b][/align][align=center][b][font='Times New Roman']Mutant[/font][font=黑体][font='Times New Roman'] [/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']allele[/font][/b][/align][/td][td][align=center][b][font='Times New Roman'][font=黑体]氨基酸突变[/font][/font][/b][/align][align=center][b][font='Times New Roman']amino acid[/font][font=黑体][font='Times New Roman'] [/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']mutation[/font][/b][/align][/td][td][align=center][b][font='Times New Roman'][font=黑体]突变[/font][/font][font=黑体]株编号[/font][/b][/align][align=center][b][font=Calibri]Number[/font][font=黑体][font='Times New Roman'] [/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']of mutation[/font][/b][/align][/td][td][align=center][b][font='Times New Roman'][font=黑体]总突变频率[/font][/font][/b][/align][align=center][b][font='Times New Roman']Total[/font][/b][font=Calibri][color=#434343] [/color][/font][b][font='Times New Roman']mutation density[/font][font=黑体][font='Times New Roman'] [/font][/font][font='Times New Roman'](kb)[/font][/b][/align][/td][/tr][tr][td][align=center][i][font='Times New Roman']pinb[/font][/i][/align][/td][td][align=center][font='Times New Roman']AJ302100.1[/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font='Times New Roman']870[/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font='Times New Roman']1334[/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]C[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']51[/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]2T[/font][/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]S37F[/font][/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]996[/font][/font][/align][/td][td=1,4][align=center][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]1/374.18 [/font][/font][/align][/td][/tr][tr][td][align=center][font='Times New Roman'] [/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font='Times New Roman'] [/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font='Times New Roman'] [/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font='Times New Roman'] [/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font='Times New Roman']G7[/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]26[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']A [/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]G110S [/font][/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]892[/font][font=黑体]、[/font][font=Times New Roman]919[/font][font=黑体]、[/font][font=Times New Roman]997[/font][/font][/align][/td][/tr][tr][td][align=center][font='Times New Roman'] [/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font='Times New Roman'] [/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font='Times New Roman'] [/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font='Times New Roman'] [/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font='Times New Roman']G750A[/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]W116-[/font][/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]791[/font][font=黑体]、[/font][font=Times New Roman]1114[/font][/font][/align][/td][/tr][tr][td][align=center][font='Times New Roman'] [/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font='Times New Roman'] [/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font='Times New Roman'] [/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font='Times New Roman'] [/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font='Times New Roman']G350A[/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font='Times New Roman'][font=黑体]未改变[/font][/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]890[/font][/font][/align][/td][/tr][/table][font='Times New Roman'][/font][b][b][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]3[/font][/font][font=黑体] [font=黑体]讨论[/font][/font][/b][/b][font=黑体]籽粒硬度是小麦重要的品质性状,对食品加工及磨粉质量都有重要影响。[/font][i][font='Times New Roman']P[/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]inb[/font][/font][/i][font=黑体]是调控籽粒硬度的主效基因之一,与[/font][i][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]pina[/font][/font][/i][font=黑体]基因共同作用决定小麦胚乳质地[/font][sup][font='Times New Roman'][[/font][/sup][sup][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]4-5[/font][/font][/sup][sup][font='Times New Roman']][/font][/sup][font=黑体]。[/font][font=黑体]本实验[/font][i][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]Pinb[/font][/font][/i][font=黑体]基因的突变密度是[/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]1/374.18 [/font][/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]kb[/font][font=黑体],低于[/font][/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]Feiz[/font][font=黑体]等[/font][/font][sup][font='Times New Roman'][[/font][/sup][sup][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]6[/font][/font][/sup][sup][font='Times New Roman']][/font][/sup][font=黑体]在普通软质小麦突变体库得到的[/font][i][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]pinb[/font][/font][/i][font=黑体]基因[/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]1/12 kb[/font][font=黑体]的[/font][/font][font=黑体]突变密度,但高于[/font][font=黑体]潘娜[/font][sup][font='Times New Roman'][[/font][/sup][sup][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]3[/font][/font][/sup][sup][font='Times New Roman']][/font][/sup][font=黑体][font=黑体]利用空间诱变新麦[/font][font=Times New Roman]18[/font][font=黑体]突变体库群体得到的该基因[/font][/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]1/3073 kb[/font][font=黑体]的[/font][/font][font=黑体]突变密度。[/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]Morris[/font][font=黑体]等[/font][/font][sup][font='Times New Roman'][[/font][/sup][sup][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]5, 7[/font][/font][/sup][sup][font='Times New Roman']][/font][/sup][font=黑体]获得的硬红春小麦[/font][i][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]pinb[/font][/font][/i][font=黑体]基因突变体[/font][font=黑体],分别发生在[/font][i][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]pinb[/font][/font][/i][font=黑体][font=黑体]基因第[/font][font=Times New Roman]39[/font][font=黑体]位和第[/font][font=Times New Roman]44[/font][font=黑体]位的色氨基酸[/font][font=Times New Roman]T[/font][font=黑体]及第[/font][font=Times New Roman]56[/font][font=黑体]位半胱氨酸[/font][font=Times New Roman]C[/font][font=黑体],均突变为终止密码子。[/font][/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]Wang[/font][font=黑体]等[/font][/font][sup][font='Times New Roman'][[/font][/sup][sup][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]13[/font][/font][/sup][sup][font='Times New Roman']][/font][/sup][font=黑体]获得[/font][i][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]Pinb[/font][/font][/i][font=黑体][font=黑体]基因,[/font][font=Times New Roman]382bp[/font][font=黑体]处[/font][font=Times New Roman]C [/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']–[/font][font=黑体] [font=Times New Roman]T[/font][font=黑体]碱基转换和[/font][font=Times New Roman]257bp[/font][font=黑体]处[/font][font=Times New Roman]G [/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']–[/font][font=黑体] [font=Times New Roman]A[/font][font=黑体]碱基转换。[/font][/font][font=黑体]在潘娜[/font][sup][font='Times New Roman'][[/font][/sup][sup][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]3[/font][/font][/sup][sup][font='Times New Roman']][/font][/sup][font=黑体]创制[/font][font=黑体][font=黑体]的[/font][font=Times New Roman]TILLING[/font][font=黑体]群体中,[/font][/font][i][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]pinb[/font][/font][/i][font=黑体][font=黑体]基因组[/font][font=Times New Roman]736 bp[/font][font=黑体]的[/font][font=Times New Roman]A[/font][font=黑体]碱基缺失,引起移码突变,而本实验突变株[/font][font=Times New Roman]LF[/font][/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]791[/font][font=黑体]、[/font][font=Times New Roman]LF1114[/font][font=黑体],[/font][font=Times New Roman]LF996[/font][font=黑体],[/font][font=Times New Roman]LF[/font][/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]892[/font][font=黑体]、[/font][font=Times New Roman]LF997[/font][font=黑体]、[/font][font=Times New Roman]LF919[/font][font=黑体]的基因突变依次为[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']750[/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]bp[/font][font=黑体]位的[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']G[/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]-[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']A[/font][font=黑体]碱基转换,[/font][font='Times New Roman']51[/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]2bp[/font][font=黑体]位的[/font][font=Times New Roman]C-T[/font][font=黑体]碱基转换,[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']7[/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]26bp[/font][font=黑体]位的[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']G[/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]-[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']A[/font][font=黑体]碱基转换,[/font][font=黑体]均导致错义突变。[/font][font=黑体]王亮等[/font][sup][font='Times New Roman'][[/font][/sup][sup][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]8[/font][/font][/sup][sup][font='Times New Roman']][/font][/sup][font=黑体][font=黑体]和[/font][font=Times New Roman]Chen[/font][font=黑体]等[/font][/font][sup][font='Times New Roman'][[/font][/sup][sup][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]9[/font][/font][/sup][sup][font='Times New Roman']][/font][/sup][font=黑体][font=黑体]的研究中几乎所有[/font][font=Times New Roman]Puroindoline[/font][font=黑体]变异类型的籽粒硬度值都显著高于野生型,而[/font][/font][font=黑体][font=黑体]本实验,对突变株进行表型分析,籽粒硬度测定显示[/font][font=Times New Roman]LF996[/font][font=黑体]、 [/font][font=Times New Roman]LF[/font][/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]892[/font][font=黑体]、[/font][/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]LF1114[/font][font=黑体]突变株的[/font][/font][font=黑体]籽粒硬度均[/font][font=黑体]极显著低于野生型。此外,[/font][font=黑体]突变体自交系研究发现[/font][font=黑体],突变[/font][font=黑体]对小麦出粉率、面包体积、面粉灰分等品质性状均有影响,[/font][font=黑体][font=黑体]不同[/font][font=Times New Roman]Puroindoline[/font][font=黑体]变异类型之间在磨粉、面包等加工品质上也存在较差别[/font][/font][sup][font='Times New Roman'][[/font][/sup][sup][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]9-10[/font][/font][/sup][sup][font='Times New Roman']][/font][/sup][font=黑体]。基于以上的研究发现,可利用本实验获得的突变株,进行后代品质研究,为品质改良奠定基础。[/font][b][b][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]4 [/font][/font][font=黑体][font=黑体]结[/font] [font=黑体]论[/font][/font][/b][/b][font=黑体]本研究所获得的基因点突变及表型突变株为植物基因功能研究及小麦品质改良提供了新材料。[/font][font=黑体] [/font][font=黑体] [/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]References[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman'][[/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]1[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']][/font][font=黑体] [/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]Liu L([/font][font=黑体]刘丽[/font][font=Times New Roman]), Yang J-H([/font][font=黑体]杨金华[/font][font=Times New Roman]), Hu Y-X([/font][font=黑体]胡银星[/font][font=Times New Roman]), Cheng G([/font][font=黑体]程耿[/font][font=Times New Roman]).[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman'] Research Progress in Effects of Glutenin Subunits on[/font][font=黑体] [/font][font='Times New Roman']Wheat Processing Quality[/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman].[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman'] [/font][font=黑体] [/font][i][font='Times New Roman']Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology[/font][/i][font=黑体] [font=Times New Roman]([/font][font=黑体]中国农业科技导报[/font][font=Times New Roman]), 2012, 14(1): 33-42 [/font][/font][font='Times New Roman'](in Chinese with English abstract)[/font][font='Times New Roman'][[/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]2[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']][/font][font=黑体] [/font][font='Times New Roman']Wang J, Sun J Z, Liu D C, Yang W L, Wang D W, Tong Y P, Zhang A M. Analysis of [/font][i][font='Times New Roman']Pina[/font][/i][font='Times New Roman'] and [/font][i][font='Times New Roman']Pinb[/font][/i][font=黑体] [/font][font='Times New Roman']alleles in the microcore collections of chinese wheat germplasm by Ecotilling and identification of[/font][font=黑体] [/font][font='Times New Roman']a novel [/font][i][font='Times New Roman']Pinb[/font][/i][font='Times New Roman'] allele[/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]. [/font][/font][font='Times New Roman'] [/font][i][font='Times New Roman']Journal of Cereal Science[/font][/i][font=黑体] [/font][font='Times New Roman']2008, 48(3): 836-[/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]842[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman'][[/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]3[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']][/font][font=黑体][font=黑体]潘娜[/font][font=Times New Roman]. [/font][font=黑体]空间环境诱发小麦突变体的[/font][font=Times New Roman]TILLING[/font][font=黑体]分析[/font][font=Times New Roman], [/font][font=黑体]中国农业科学院[/font][font=Times New Roman], 2011.[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman'][[/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]4[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']][/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]CaPPaerlliR[/font][font=黑体],[/font][font=Times New Roman]Bo[/font][font=黑体]币[/font][font=Times New Roman]elloqGirouxMJ[/font][font=黑体],[/font][font=Times New Roman]AmoorsoMGPuorindolineA[/font][font=黑体]一[/font][font=Times New Roman]geneexPerssion15involved[/font][/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]inassociationofPuroindolinetostacrh.TheoerctialandAPPliedGenetics[/font][font=黑体],[/font][font=Times New Roman]2003[/font][font=黑体],[/font][font=Times New Roman]107:1463[/font][font=黑体]一[/font][font=Times New Roman]1468[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman'][[/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]5[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']][/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]Chen F. Molecular Characterization of Puroindoline Alleles in Chinese and CIMMYT Common Wheats and Their [/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']Eeffct[/font][font=黑体] [/font][font='Times New Roman']on[/font][font=黑体] [/font][font='Times New Roman']Porcessing[/font][font=黑体] [/font][font='Times New Roman']Quaiity[/font][font='Times New Roman'][[/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]6[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']]Feiz L, Martin J M, Giroux M J. Creation and functional analysis of new Puroindoline alleles[/font][font=黑体] [/font][font='Times New Roman']in Triticum aestivum.[/font][i][font='Times New Roman']Theoretical and Applied Genetics[/font][/i][font='Times New Roman'],2009, 118:247-257[/font][font='Times New Roman'][[/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]7[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']][/font][font=黑体] [font=Times New Roman]Morris C F[/font][font=黑体],[/font][font=Times New Roman]Lillemo M[/font][font=黑体],[/font][font=Times New Roman]Simeone M C[/font][font=黑体],[/font][font=Times New Roman]Giorux M J[/font][font=黑体],[/font][font=Times New Roman]Bbab S L[/font][font=黑体],[/font][font=Times New Roman]Kimberiee K K.Pervalence of [/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']Puorindoline[/font][font=黑体] [/font][font='Times New Roman']garin[/font][font=黑体] [/font][font='Times New Roman']hdarness[/font][font=黑体] [/font][font='Times New Roman']genotypes[/font][font=黑体] [/font][font='Times New Roman']among[/font][font=黑体] [/font][font='Times New Roman']historieally[/font][font=黑体] [/font][font='Times New Roman']significant[/font][font=黑体] [/font][font='Times New Roman']North[/font][font=黑体] [/font][font='Times New Roman']American[/font][font=黑体] [/font][font='Times New Roman']s[/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]p[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']ring[/font][font=黑体] [/font][font='Times New Roman']and[/font][font=黑体] [/font][font='Times New Roman']winter[/font][font=黑体] [font=Times New Roman]wheats. [/font][/font][i][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]Crop Scienee[/font][/font][/i][font=黑体][font=黑体],[/font][font=Times New Roman]2001,41:218-228[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman'][[/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]8[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']][/font][font=黑体] [font=Times New Roman]C[/font][/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]hen F[/font][font=黑体],[/font][font=Times New Roman]He z H[/font][font=黑体],[/font][font=Times New Roman]Xia x C[/font][font=黑体],[/font][font=Times New Roman]el a1[/font][font=黑体].[/font][font=Times New Roman]Molecular and biochemical charac[/font][font=黑体]—[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']terization of P“roindoline a and b alleles in Chinese landraces and[/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]historical eultivars[J][/font][font=黑体].[/font][font=Times New Roman]Theoretical and Applied Genetics. 2006[/font][font=黑体],[/font][font=Times New Roman]112[/font][font=黑体]:[/font][font=Times New Roman]400[/font][font=黑体]—[/font][font=Times New Roman]409[/font][font=黑体].[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman'][[/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]9[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']][/font][font=黑体] [font=黑体]王亮,穆培源,桑伟,等.新疆小麦品种籽粒硬度及[/font][font=Times New Roman]Puroindoline[/font][font=黑体]基因等位变异的分子检测[/font][font=Times New Roman][J][/font][font=黑体].麦类作物学报。[/font][font=Times New Roman]2010[/font][font=黑体],[/font][font=Times New Roman]30(1)[/font][font=黑体]:[/font][font=Times New Roman]17-22[/font][font=黑体].[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman'][[/font][font=黑体][font=Times New Roman]10[/font][/font][font='Times New Roman']][/font][font=黑体] [font=黑体]赵新,王步军.不同硬度小麦品质差异的分析[/font][font=Times New Roman][J][/font][font=黑体].麦类作物学报,[/font][font=Times New Roman]2009[/font][font=黑体],[/font][font=Times New Roman]29(2)[/font][font=黑体]:[/font][font=Times New Roman]246[/font][font=黑体]—[/font][font=Times New Roman]251[/font][font=黑体]。[/font][/font]
英国变异毒株杀入广东!粤港澳大湾区是一体,11个城市600万平方公里,七千万人口,是中国对开放的前沿阵地,与英美来往密切,大湾区的朋友们一定要警惕!这个变异毒株,重点不在毒,在“变”!感染性极强,遑论大人,过去不易感的儿童都会超大概率中招!?根据广东疾控中心通报,英国留学生12月4日入境广州,检测是阴性,隔离14后检测为阴阳性!这个变异病毒潜伏期这么长,感染性这么强,相当狡猾,这就是我说的,新冠病毒是特洛伊木马攻城,载人载物由欧美向中国大陆进击!?1月2日,广东省疾控中心在一名英国输入新冠肺炎确认病例的咽拭子样本中发现了B.1.1.7突变株,与近期英国报道的变异病毒基因序列高度相似。英国变异病毒最大的特点即其S蛋白与人类ACE2受体结合亲和力提高了100倍,传播速度比之前的毒株高达70%,已成为伦敦地区的主要毒株,英国回国的留学生,一定不要只隔离14天就出去逛,还得要居家再多隔离七天,再检查无问题后再玩,切切。保护好自己,也是保护家人,保护所在社区!
大家好最近在做DNA点突变的研究,由于基因很大,有七十几个外显子,如果一一扩增测序的话成本和时间上都不划算.所以在考虑能否用质谱的方法,或者其他什么分析的方法先进行下初筛。和标样比较,如果看到了某个峰有异常的话,再专门扩增这个外显子去测序外显子一般200-300bp。想请教大家,不知道用质谱的方法可不可以?另外,国内有哪里用质谱进行DNA序列的研究的吗?我知道用MALDI-TOF-TOF这个进行SNP的研究,但是对于我们这个200-300bp来说量程上就太小了。期待大家的回答~~~~
食品安全国家标准 细菌回复突变试验
求《计量技术》2016年第11期:《居民用户智能电能表电能数据突变的产生和预防》一文,谢谢!
香港发现的德尔塔毒株或有全新基因突变,不排除动物传人可能性.

走基线时,基线反向突变,有很多毛刺,是什么原因造成的?是进样器衬管脏了,还是检测器脏了,两个都要清洗吗?还有其他的原因吗?http://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2011/03/201103161838_283283_1621482_3.jpg
长期以来,手术、放疗、化疗三大疗法一直主宰着肿瘤治疗的统治地位。一方面,由于三大疗法本身技术的发展和完善,使得肿瘤治疗较过去有了可喜的进步,手术联合放化疗在很大程度上提高了肿瘤的治疗效果。另一方面是过度治疗事与愿违,对于晚期病人而言,其复发和转移的比例一直居高不下,治疗效果仍然不理想,五年生存率普遍较低。 六步自然疗法抗肿瘤新突破 21世纪,随着分子生物学和微生态学以及免疫学的发展,一种全新的抗肿瘤方法“六步综合疗法”应运而生,所谓“六步综合疗法”是将中药治疗、营养、体能锻炼等多种方法科学地运用到患者的综合治疗中,调整病人心理状态,提高免疫功能,以期达到提高生存率、延长生存期,改善生存质量,使肿瘤患者能最大限度地回归社会,像健康人一样生活和工作。 发酵中药为六步自然疗法第一步 发酵中药是国内首例通过仿生学手法和微生物发酵工艺研制而成的中药微生态制剂,圆了无痛苦消瘤的千年梦想。众所周知,中药在肿瘤的综合治疗中发挥着重要的作用。传统的中药生产工艺落后,不能在临床上起到作用。发酵中药它创造性地采用了人体仿生学手法,在体外模拟健康人的消化系统,中药成分经过生物转化,使大分子物质变成小分子物质,从而被人体吸收和利用,使药效提高4至28倍。 国际自然抗癌学会副会长史宗山教授认为:中药中的有效成份是其中的次生代谢物,是在随中药进入人体后,经过人体细胞代谢产生的物质而发挥治病作用。这些有效成分通过对致癌基因的抑制、抑癌基因的激活和生长调控基因的修复,来实现多靶点作用。发酵中药正是通过高科技生物转化后的有效成分,在细胞分子水平上调节了这些对肿瘤有影响的机制而发挥抗肿瘤、抗复发、抗转移功能。 发酵中药五大革命性突破 发酵中药抗肿瘤成功实现五大突破:1)首次把中药抗肿瘤活性成分从大分子转变成小分子,有效成分可迅速穿透毛细血管壁直达肿瘤病灶;2)首次激活传统中药未被开发的抗肿瘤活性物质-CSD因子,诱导肿瘤细胞分化凋亡;3)首次实现中药多靶点靶向识别、抑杀肿瘤细胞,抑制肿瘤新生血管形成,防止复发转移。4)中药无毒化,通过益生菌对中药有效成分的多次仿生分解及转化,彻底去除中药有毒成分,并大幅提高中药药效及吸收效果。5)口感良好,真正改变了中药良药苦口世界形象。
迄今为止,虽然在人类中只发生孤立的H5N1禽流感病毒(H5N1 bird flu virus)感染病例,但是这种感染并没有发生广泛的传播,这是因为该病毒不能够在人鼻子中有效地复制。在一项新的研究中,来自英国肯特大学和伦敦帝国理工学院的研究人员发现H5N1禽流感病毒发生较小的基因突变就能够在哺乳动物鼻子中更容易复制。相关研究结果于2013年3月13日在线发表在Journal of General Virology期刊上,论文标题为“Mutations in hemagglutinin that affect receptor binding and pH stability increase replication of a PR8 influenza virus with H5 HA in the upper respiratory tract of ferrets and may contribute to transmissibility”。这一发现支持了2012年发表的一项争议性研究的结论:只需几次基因突变就能够让禽流感在雪貂(常被用作人类流感病毒感染的研究模型)之间传播。
对结构独特、活性显著的天然产物进行生物合成研究是从基因簇、生物合成途径及酶催化反应角度理解自然界“全合成”的生物-化学过程。中国科学院上海有机化学研究所生命有机化学国家重点实验室唐功利课题组多年来致力于复杂抗肿瘤天然产物的生物合成研究,经过几年的努力,该课题组最近在两个课题上均取得突破。 抗生素谷田霉素(Yatakemycin,YTM)可以抑制致病真菌,且对肿瘤细胞表现出极强的毒性(比抗肿瘤药物丝裂霉素的活性高约1000倍);该家族化合物属于DNA烷基化试剂,典型的结构特征是吡咯吲哚环上的环丙烷结构。为了阐明其独特的生物合成机制,课题组利用全基因组扫描技术定位其生物合成基因簇,通过基因敲除结合生物信息学分析确定了基因簇边界。在对突变株的发酵检测中成功分离鉴定了中间体YTM-T的结构,并结合体外生化实验揭示了一类同源于粪卟啉原III-氧化酶(Coproporphyrinogen III oxidase)的甲基化酶以自由基机理催化YTM-T发生C-甲基化(J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134, 8831-8840),这是此类蛋白催化自由基甲基化反应的首例报道。这一阶段性结果为下一步阐明YTM结构中最重要的环丙烷部分生物合成途径奠定了基础。 萘啶霉素(Naphthyridinomycin,NDM)、奎诺卡星(Quinocarcin,QNC)及Ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743)均属于四氢异喹啉生物碱家族化合物,它们都具有显著的抗肿瘤活性,其中ET-743已发展为第一例海洋天然产物来源的抗肿瘤新药。这三种化合物都具有一个独特的二碳单元结构,其生物合成来源问题一直没有得到解决。为了揭示这一谜团,唐功利课题组在克隆了NDM和QNC生物合成基因簇的基础上,通过前体喂养标记、体内相关基因敲除-回补以及体外酶催化反应等多种实验手段相结合的方式,阐明了二碳单元的独特生源合成机制:NapB/D及QncN/L在催化功能上均属于丙酮酸脱氢酶及转酮醇酶的复合体,它们负责催化二碳单元由酮糖转移至酰基承载蛋白(ACP)上,而后经过非核糖体蛋白合成(NRPS)途经进入到最终的化合物中。这一结果发表在《美国国家科学院院刊》(Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2012, 109, 8540-8545)上。这种将基础代谢中的酮糖直接转化为次级代谢所需要的二碳单元在非核糖体肽合成途经中是首次报道,该研究结果也有助于揭示海洋药物ET-743独特的二碳单元生物合成来源,为非核糖体聚肽类天然产物的组合生物合成带来新的前体单元。 上述研究工作得到国家自然科学基金委、科技部和中国科学院的资助。http://www.cas.cn/ky/kyjz/201207/W020120704343205531340.pngYTM合成机制http://www.cas.cn/ky/kyjz/201207/W020120704343205536236.gif四氢异喹啉生物碱化合物的独特生源合成机制
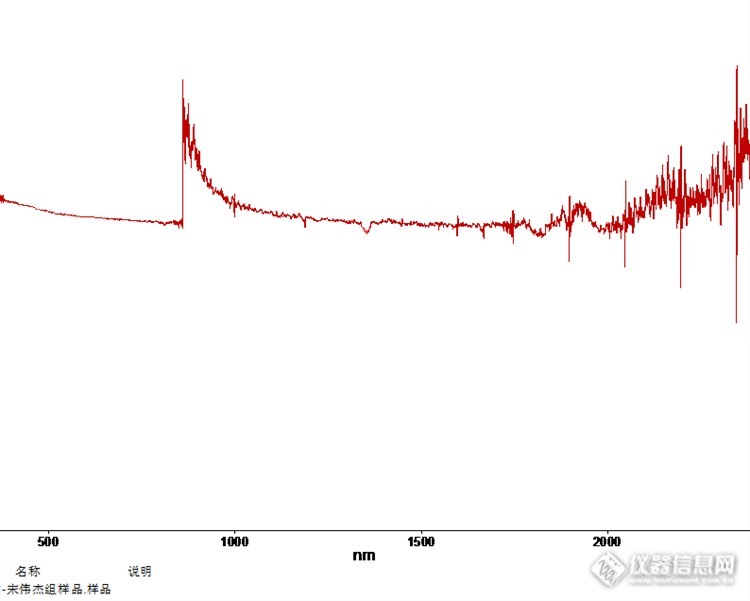
单位有台Lambda950型紫外,测反射率在860nm处切换检测器时有3%左右的突变,不知道是什么原因,请高手指点?另外有哪个单位也有Lambda950的紫外吗?想联系交流一下http://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2015/08/201508211811_562100_3024213_3.png
食品安全国家标准 体外哺乳类细胞HGPRT基因突变试验
广东:首次发现新冠病毒巴西突变株,28名密切接触者已隔离
食品安全国家标准 体外哺乳类细胞TK基因突变试验
可选择性杀伤HIV感染细胞,为HIV药物生产提供新思路 经过多年的科技攻关,近日,香港中文大学教授邵鹏柱学科组与中科院昆明动物研究所研究员郑永唐学科组合作,从玉米中获得了一种能够选择性地杀伤艾滋病病毒(HIV)感染细胞的蛋白酶突变体。该研究成果为研发特异性靶向HIV感染细胞的新型抗HIV药物提供了新思路和新策略。 据悉,HIV存在潜藏机制可以长期潜伏在细胞中而逃逸宿主免疫系统的攻击,目前已上市的抗HIV药物均不能选择性地杀伤感染细胞而根除病毒。郑永唐认为,新的研究思路对开发新型抗HIV药物显得非常重要,研究具有选择性地杀伤HIV感染细胞而保护正常细胞不受伤害的抗艾滋病药物是极有前景的方向。 核糖体失活蛋白(RIPs)具有RNA N-糖苷酶活性,可以阻遏延长因子EF-1或EF-2与核糖体的结合,抑制蛋白质的生物合成。因此,RIPs具有很高的细胞毒性,常常被开发成为免疫毒素、抗病毒或抗肿瘤药物。RIP分为3类:I型、II型和III型。其中,III型RIP以玉米RIP为代表,先合成无活性的含有一段25氨基酸的内部失活结构域的前体蛋白,前体蛋白被切除该结构域后才成为有活性的核糖体失活蛋白。 在香港研究资助局、科技部“973”项目、国家重大科技专项、中科院等项目的资助下,邵鹏柱、郑永唐等对玉米RIP的内部失活结构域进行一系列的结构修饰和改造,获得了对HIV-1蛋白酶特异识别并激活的玉米RIP突变体。细胞水平实验的研究表明,突变体对未感染细胞毒性低,但突变体进入HIV-1感染细胞后则可被细胞内的HIV-1蛋白酶识别并切割去除失活结构域转变成为活性蛋白,从而选择性地杀伤HIV-1感染细胞。同时,通过增加突变体进入细胞的效率,对HIV-1感染细胞的杀伤力更强。突变体也可以被HIV-1蛋白酶耐药株的蛋白酶识别并激活,因此突变体对HIV-1蛋白酶耐药株感染细胞也有很好的选择杀伤性。 该研究成果已在国际学术期刊《核酸研究》(Nucleic Acids Research)上发表。
[size=14px] [/size] [size=14px]葫芦素B ( cucurbitacin B,CuB ) 是瓜蒂等葫芦科清热解毒中药的主要药效成分, 是葫芦素家族中含量最丰富的成员,具有保肝、消炎和抗肿瘤等广泛的药理活性。虽然已经有很多学者研究了CuB的不同抗癌机制,但大多数都是下游途径和疗效表型,CuB在多种肿瘤中的直接作用靶点至今尚未明确。[/size] [size=14px]今天为大家分享2篇关于葫芦素B在抗肿瘤应用中的高水平文章,分别发表在Acta Pharm Sin B(IF=14.5)和ACS Central Science(IF=18.2),思路经典,以供学习参考。[/size] [size=14px]文献1:葫芦素B抑制结膜黑色素瘤的直接靶点[/size] [size=14px]2022年5月23日,华东理工大学药学院李剑、上海九院眼科徐晓芳/贾仁兵团队合作在Acta Pharm Sin B(IF=14.5)上发表了题为“Cucurbitacin B-induced G2-M cell cycle arrest of conjunctival melanoma cells mediated by GRP78–FOXM1–KIF20A pathway”的文章,揭示了葫芦素B抑制结膜黑色素瘤直接靶点及相关机制。[/size] [size=14px] [/size] [size=14px]研究首先利用结膜黑色素瘤(Conjunctival melanoma,CM)细胞株筛选自建的上市老药库(含1400个化药和天然药),发现葫芦素B对NRAS和BRAF突变的CM细胞均表现出突出的抗增殖活性。接着作者利用细胞实验发现CuB抑制CM细胞增殖并导致G2/M细胞周期停滞,并通过RNA-Seq、q[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/jp][color=#3333ff]PCR[/color][/url]和Western blot发现CuB抑制CM细胞FOXM1/PLK1 -KIF20A通路。进一步作者采用ABPP识别CuB的直接靶蛋白,在9种候选蛋白中,GRP78已被报道为多种癌症的潜在生物标志物和治疗靶点,可抑制癌细胞的进展、增殖、侵袭和转移。作者通过Pulldown+WB、MST、TSA等验证了两者直接结合,并通过质谱鉴定发现CuB通过α-β-不饱和酮部分与GRP78的Lys326位点互作。最后Rescue实验发现GRP78敲低削弱CuB抑制细胞增殖的作用,而GRP78过表达强化CuB抑制细胞增殖的作用,表明葫芦素B通过GRP78发挥功能。总之,CuB通过结合GRP78抑制GRP78-FOXM1-KIF20A通路进而抑制CM细胞周期发挥功能。[/size] [size=14px] [/size] [size=14px]文献2:中药瓜蒂活性成分葫芦素B抗肿瘤作用分子靶点及作用机制[/size] [size=14px]2022年5月17日,北京大学药学院屠鹏飞/曾克武团队在ACS Cent Sci(IF=18.2)上发表了题为“Allosteric regulation of IGF2BP1 as a novel strategy for the activation of tumor immune microenvironment”的文章,揭示了葫芦素B发挥抗肿瘤作用的直接靶点及相关机制。[/size] [size=14px] [/size] [size=14px]研究首先通过体内外实验发现IGF2BP1(m6A reader protein)敲低能够募集肿瘤浸润性免疫细胞,阻断PD-L1表达,增强抗肿瘤免疫抑制HCC进展。进一步采用高通量筛选系统(基于IGF2BP1可识别并结合m6A探针,小分子抑制IGF2BP1与m6A探针结合,SPR检测结合能力)从先前建立的天然产物小分子库(889种)中筛选能够抑制IGF2BP1的小分子,发现6种候选化合物对m6A的抑制率达70%,进一步发现其中的葫芦素B对肝癌细胞增殖展现最佳抑制效果。随后SPR、ITC、CETSA、DARTS、Pulldown、分子对接证实IGF2BP1与葫芦素B的直接结合。机制上,葫芦素B通过共价修饰IGF2BP1的253位半胱氨酸,诱导IGF2BP1蛋白变构,抑制IGF2BP1对下游m6A的识别,并且影响多个肿瘤相关靶基因的表达,发挥诱导肿瘤细胞凋亡和改善肿瘤免疫微环境的作用。[/size] [size=14px]总结[/size] [size=14px]越来越多的中药活性成分被发现在多种疾病中发挥药理活性,发现其在不同疾病中的不同的直接作用靶点将有助于深入挖掘其作用机制。近年来筛选并验证中药活性成分的直接靶点的技术手段越来越多,且各具特色,这将极大的推动中药现代化研究进程。[/size]
20世纪30年代臭名昭著的劫匪约翰-狄林杰为了不让警方发现犯罪现场的指纹与他的指纹一样,不惜忍受巨大的痛苦,利用硫酸把指纹烧掉。但是对我们来说,没有指纹是一件非常可怕的事情,它会在边界控制和证明身份时造成很多麻烦。科学家目前已经确定可以导致一些人天生没有指纹的基因。http://www.bioon.com/biology/UploadFiles/201109/2011092211413775.jpg皮纹病患者天生没有指纹这种情况被称作皮纹病(adermatoglyphia)或者“入境延期病(Immigration Delay Disease)”,患有这种疾病的人天生手指肚上没有指纹。以色列特拉维夫大学的艾里-斯普雷彻教授获得的最新发现显示,一种基因突变造成这种与众不同的病变。一名瑞士女性试图穿越边境,进入美国,边境控制人员需要收集她的指纹。然而当这位女子告诉他们,她无法满足他们的要求,因为她根本没有指纹时,这些官员感到非常迷惑。这也促使医学界开始注意皮纹病。研究人员对这位女性以及她的另外9名没有指纹的家庭成员进行遗传分析。特拉维夫大学的科学家将存在这种情况的人的基因与没有这种情况的人的基因进行比对,确定基因变异到底发生在哪里。他们发现,SMARCAD1突变影响了指纹的形成。研究发现,没有指纹的人拥有的与皮肤发育有关的这种基因更少。现在科学家将能进一步研究这种基因是如何调控指纹的发展的。与DNA一样,每个人的指纹也是独一无二的,即使是同卵双胞胎也不例外,因此它们也成为破案和国际旅行管理等的重要鉴定工具。它们之所以会被当作确定身份的工具,是因为它们在受精24周后就会发育健全,而且整个一生都不会发生任何改变。目前全球仅有4个记录在案的家庭存在这种情况。斯普雷彻表示,不仅手指上长有带图案的皮肤,手掌、脚趾和足底也长着被称作皮纹的纹路。然而他说:“胚胎发育阶段导致指纹形成和拥有不同图案的因素目前大部分还不得而知。”除了缺少指纹外,这种情况还导致汗腺减少。指纹异常可能也是出现更严重的疾病的一种预警信号。该研究成果发表在《美国人类基因学期刊》上。2009年,一名中国女性通过整形手术改变她的指纹,想利用这种方法非法进入日本。东京警方表示,以前因签证过期被驱逐出日本的林荣(Lin Rong)花了1.5万美元在中国做了这项整形手术。警方认为,这种欺骗行为可能普遍存在,因为中国经纪人进行了大量指纹修改手术。这项手术涉及到摘除拇指和食指上的指纹,然后把它们嫁接到另一只手的手指上。