方案详情文
智能文字提取功能测试中
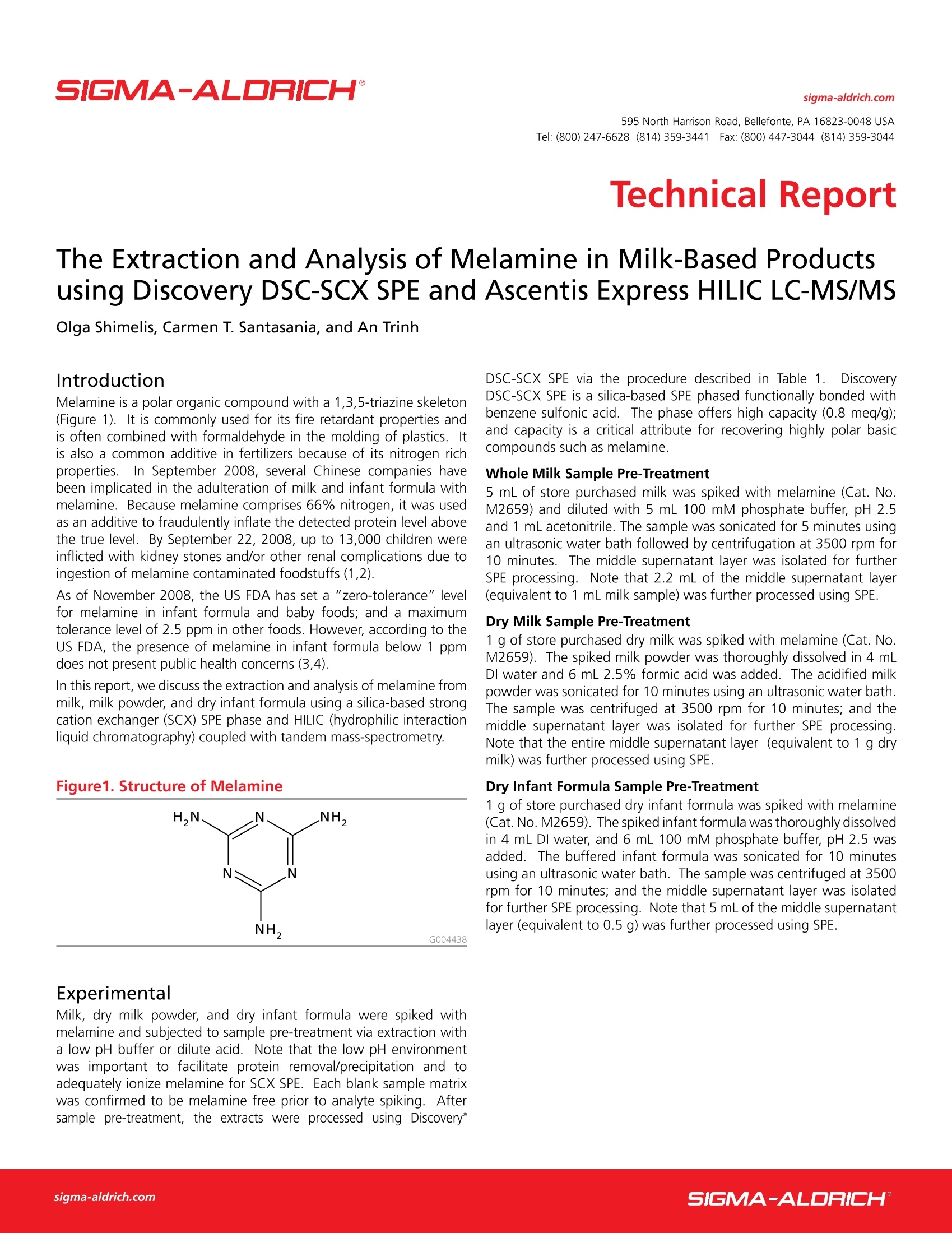
SIGMA-ALDRICHsigma-aldrich.comTel: (800) 247-6628 (814) 359-3441Fax: (800) 447-3044 (814) 359-3044 2 595 North Harrison Road, Bellefonte, PA 16823-0048 USA Technical Report The Extraction and Analysis of Melamine in Milk-Based Productsusing Discovery DSC-SCX SPE and Ascentis Express HILIC LC-MS/MS OIga Shimelis, Carmen T. Santasania, and An Trinh Introduction Melamine is a polar organic compound with a 1,3,5-triazine skeleton(Figure 1). It is commonly used for its fire retardant properties andis often combined with formaldehyde in the molding of plastics. Itis also a common additive in fertilizers because of its nitrogen richproperties. In September 2008, several Chinese companies havebeen implicated in the adulteration of milk and infant formula withmelamine. Because melamine comprises 66% nitrogen, it was usedas an additive to fraudulently inflate the detected protein level abovethe true level. By September 22, 2008, up to 13,000 children wereinflicted with kidney stones and/or other renal complications due toingestion of melamine contaminated foodstuffs(1,2). As of November 2008, the US FDA has set a "zero-tolerance" levelfor melamine in infant formula and baby foods; and a maximumtolerance level of 2.5 ppm in other foods. However, according to theUS FDA, the presence of melamine in infant formula below 1 ppmdoes not present public health concerns (3,4). In this report, we discuss the extraction and analysis of melamine frommilk, milk powder, and dry infant formula using a silica-based strongcation exchanger (SCX) SPE phase and HILIC (hydrophilic interactionliquid chromatography) coupled with tandem mass-spectrometry. G004438 Experimental Milk, dry milk powder, and dry infant formula were spiked withmelamine and subjected to sample pre-treatment via extraction witha low pH buffer or dilute acid. Note that the low pH environmentwas important to facilitate protein removal/precipitation and toadequately ionize melamine for SCX SPE. Each blank sample matrixwas confirmed to be melamine free prior to analyte spiking. Aftersample pre-treatment, the extracts were processed using Discovery° DSC-SCX SPE via the procedure described in Table 1. DiscoveryDSC-SCX SPE is a silica-based SPE phased functionally bonded withbenzene sulfonic acid. The phase offers high capacity (0.8 meq/g);and capacity is a critical attribute for recovering highly polar basiccompounds such as melamine. Whole Milk Sample Pre-Treatment 5 mL of store purchased milk was spiked with melamine (Cat. No.M2659) and diluted with 5 mL 100 mM phosphate buffer, pH 2.5and 1 mL acetonitrile. The sample was sonicated for 5 minutes usingan ultrasonic water bath followed by centrifugation at 3500 rpm for10 minutes. The middle supernatant layer was isolated for furtherSPE processing. Note that 2.2 mL of the middle supernatant layer(equivalent to 1 mL milk sample) was further processed using SPE. Dry Milk Sample Pre-Treatment 1 g of store purchased dry milk was spiked with melamine (Cat. No.M2659). The spiked milk powder was thoroughly dissolved in 4 mLDI water and 6 mL 2.5% formic acid was added. The acidified milkpowder was sonicated for 10 minutes using an ultrasonic water bath.The sample was centrifuged at 3500 rpm for 10 minutes; and themiddle supernatant layer was isolated for further SPE processing.Note that the entire middle supernatant layer (equivalent to 1 g drymilk) was further processed using SPE. Dry Infant Formula Sample Pre-Treatment 1 g of store purchased dry infant formula was spiked with melamine(Cat.No.M2659). The spiked infant formula was thoroughly dissolvedin 4 mL DI water, and 6 mL 100 mM phosphate buffer, pH2.5 wasadded. The buffered infant formula was sonicated for 10 minutesusing an ultrasonic water bath. The sample was centrifuged at 3500rpm for 10 minutes; and the middle supernatant layer was isolatedfor further SPE processing. Note that 5 mL of the middle supernatantlayer (equivalent to 0.5 g) was further processed using SPE. SPE Cartridge: Discovery DSC-SCX SPE, 500 mg/6 mL (Cat. No.52688-U) 1. Condition and equilibrate SPE cartridge with 3 mL methanolfollowed by 3 mL 0.1% formic acid. 2. Load sample (derived from sample pre-treatment). 3. Wash SPE cartridge with 3 mL 0.1% formic acid followed by 3mL methanol. 4.Elute melamine from SPE cartridge with 4 mL 5% ammoniadiluted in methanol. 5.**Evaporate SPE eluent to dryness with nitrogen at 5 psi and50°℃. Reconstitute in LC mobile phase A. **Note: For a quick evaluation, the SPE eluent can be directlyinjected as is. However, for accurate quantitation, evaporation andreconstitution is recommended. LC-MS/MS Analysis using HILIC Melamine (Figure 1) is a polar molecule with a pKa of 5.6 and aLog P value of -1.37 (5), making it a good candidate for AqueousNormal Phase (ANP) chromatography. In ANP chromatography, a polarhydrophilic analyte partitions between a relatively polar stationaryphase and a relatively non-polar mobile phase. ANP is commonlyreferred to as HILIC, but the term HILIC implies a mechanism thatis one of several mechanisms that may be operative under ANPconditions. This HILIC mechanism describes the process of preferential solvationof the polar stationary phase with the aqueous component of themobile phase and subsequent depletion of the mobile phase of water.This sets up a biphasic system where there is a semi-immobilized layerof water near the surface and an organic-rich mobile phase layer.A polar compound may then partition from the moving organic-richmobile phase into the stagnant aqueous solvent near the surface.Water then becomes the "strong" elution solvent, and analytesgenerally elute (assuming HILIC is the dominant mechanism) in orderof "decreasing"hydrophobicity (a lower log P, indicating a more polarmolecule, and consequently more retention). Detailed HILIC LC-MS/MS conditions are described in Table 2. Collision Cell Q1 Q3 Declustering Potential (DP) Entrance Potential (EP) Collision Energy (CE) Exit Potential (CXP) 127 85.0 4 4 127 68.0 4 4 curtain gas: 20 Results and Discussion Calibration Curve Whole milk samples were quantified against external calibrationstandards prepared in buffer. Dry milk powder and dry infant formulawere quantified against matrix match calibration standards. Toprepare matrix match standards, blank dry milk and infant formulawere pre-treated and subjected to SPE processing as described inTable 1. The resulting blank SPE eluent was spiked with melamine. Note that no signs of ion-suppression were evident for the extraction/analysis of whole milk and dry milk powder allowing for accuratequantitation against external standards diluted in buffer. However, upto 45-50% ion-suppression occurred for infant formula. Therefore,it is important to quantitate against matrix-match standards whenanalyzing melamine in infant formula. High Recoveries & Low Background Both milk and infant formula were spiked with melamine in triplicateat the levels of 10-2500 ng/mL and ng/g, respectively. Absoluterecovery was determined for each spike concentration (Table 3). Fordry milk powder, only one spike level was tested (1000 ng/g) and isnot included in Table 3. Recovery and reproducibility was high acrossall the sample matrices and spike levels tested. The average recoveryfor whole milk and infant formula were 89% and 82%, respectively.RSDs were less than 11% for all the spike levels tested. Recovery fordry milk powder was 81% at the 1000 ng/g spike level tested. Table 3. Average Absolute Recovery for Melamine inWhole Milk and Dry Infant Formula Sample Matrix **Whole milk spiked at the equivalent 10-2500 ng/mL level. Figure 2 depicts chromatograms of SPE extracts of blank infantmilk formula. The blank chromatograms were free of melamineand other interferences for the mass transitions monitored. Figure3 is a representative chromatogram of a whole milk sample spikedwith 100 ng/mL melamine and extracted using Discovery DSC-SCXSPE. HILIC chromatography of melamine provided good peak shapeand retention coupled with a short analytical run time of less than 4minutes. Figure 2. Chromatograms for SPE Extracts of BlankInfant Formula (127/85 and 127/68) Figure 3. Chromatogram of Whole Milk Spikedwith Melamine (100 ng/mL) and Extractedwith Discovery DSC-SCX SPE Low Limits of Quantitation Based on a signal-to-noise ratio of 10:1, the estimated lower limitof quantitation is 4 ng/g (ppb) for dry milk powder and 4 ng/mL forwhole milk. Note that background levels of melamine can be foundin plasticware,solvents, and reagents; and should be monitoredcarefully. For example, we have found up to 2-3 ng/g melamine whenprocessing 1 g of blank sample. In addition, the FDA has reported upto 40 ng/g of background melamine when analyzing infant formulausing a polymeric SPE phase (6) Melamine Analysis Coupled with Cyanuric Acid When melamine is present with cyanuric acid, supramolecularaggregates are formed that are not soluble in water and other solvents.Previous reports provided by the FDA have suggested that exposingthe samples to very high or low pH in conjunction with dilution is aneffective means for disrupting this complex, thereby aiding solubility(4,7,8). Whole milk samples were spiked with a mixture of melamine andcyanuric acid at the levels of 100 ng/mL and 1000 ng/mL prior tosample pre-treatment (described previously) and SPE cleanup (Table1). Because sample pre-treatment required dilution with a low pHbuffer, melamine was adequately dissolved prior to SPE processing;and melamine recovery was in the range of 99-102%. Conclusion In this report, we described an assay for the extraction and analysis ofmelamine in whole milk, dry milk powder, and infant formula. Becauseof melamine's basic and polar properties, a strong cation exchangeSPE phase was required for adequate recovery and selectivity duringsample preparation. When coupled with HILIC chromatography,excellent analyte retention was observed and MS response wasenhanced due to the high organic mobile phase inherent with thismode of chromatography. Using Discovery DSC-SCX SPE and AscentisExpress HILIC coupled with tandem mass-spectrometry, we were ableto achieve average recoveries in the range 80-90% and lower limitsof quantitation of 4 ng/g (ppb) for dry milk powder and 4 ng/mL forwhole milk Description Cat. No. Discovery DSC-SCX SPE, 500 mg/6 mL, pk. 30 52688-U Ascentis Express HILIC, 5 cmx 2.1 mm I.D.,2.7 um particles 53934-U Ascentis Express HILIC, 10 cm x2.1 mm I.D., 2.7 um particles 53939-U Melamine standard, 99% purity 52549 Cyanuric acid standard, 98% purity 16614 Melamine solution, 100 pg/mL in acetonitrile/water 44642-U References 1. Pickert, Kate.“Melamine". Time. Sep. 17, 2008. Accessed Dec. 15, 2008http://www.time.com/time/health/article/0,8599,1841757,00.html 2. Macartney, Jane."China baby milk scandal spreads as sick toll rises to13,000". Times Online. Sep.22, 2008. Accessed Dec. 15, 2008 http://www.timesonline.co.uk/tol/news/world/asia/article4800458.ece. 3. “FDA Sets Melamine Tolerance Levels". safetyissues.com. Nov. 24, 2008.Safetylssues. Accessed Dec. 15, 2008. http://www.safetyissues.com/site/consumers/fda_sets_melamine_tolerance_levels.html. 4."Melamine Contamination in China". US Food & Drug Adminstration.Updated Dec. 6, 2008. US Dept. of Health & Human Services. AccessedDec. 15,2008 http://www.fda.gov/oc/opacom/hottopics/melamine.html 5. ACD/ LogP DB, version 11.01, Advanced Chemistry Development, Inc.,Toronto, ON, Canada, www.acdlabs.com, 2007 6. Smoker, M., Krynitsky, A.J.,"Interim method for detemination ofmelamine and cyanuric acid in food using LC/MS-MS: Version 1.0". USFDA Laboratory Information Bulletin No. 4422, October 2008http://www.cfsan.fda.gov/~frf/lib4422.html 7. Litzau, J.J., Mercer, G.E., Mulligan, K.J., "GC-MS screen for the presenceof melamine, ammeline, ammelide and cyanuric acid". US FDALaboratory Information Bulletin No. 4423, October 2008 http://www.cfsan.fda.gov/~frf/lib4423.html 8. Turnipseed, S., Casey, C., Nochetto, C., Heller, D.N., "Determination ofmelamine and cyanuric acid residues in infant formula using LC-MS/MS".US FDA Laboratory Information Bulletin No. 4421, October 2008 http://www.cfsan.fda.gov/~frf/lib4421.html Trademarks Ascentis, Discovery - Sigma-Aldrich Biotechnology LP Accelerating Customers' Success through Innovation andLeadership in Life Science, High Technology and Service SIGMA-ALDRICHsigma-aldrich.com SIGMA-ALDRICH
关闭-
1/4
-
2/4

还剩2页未读,是否继续阅读?
继续免费阅读全文默克化工技术(上海)有限公司为您提供《SPE-HILIC方法分析乳制品中三聚氰胺和三聚氰酸》,该方案主要用于液体乳中非法添加检测,参考标准《暂无》,《SPE-HILIC方法分析乳制品中三聚氰胺和三聚氰酸》用到的仪器有三聚氰胺 标准品、三聚氰酸。
我要纠错
相关方案




 咨询
咨询




