方案详情文
智能文字提取功能测试中
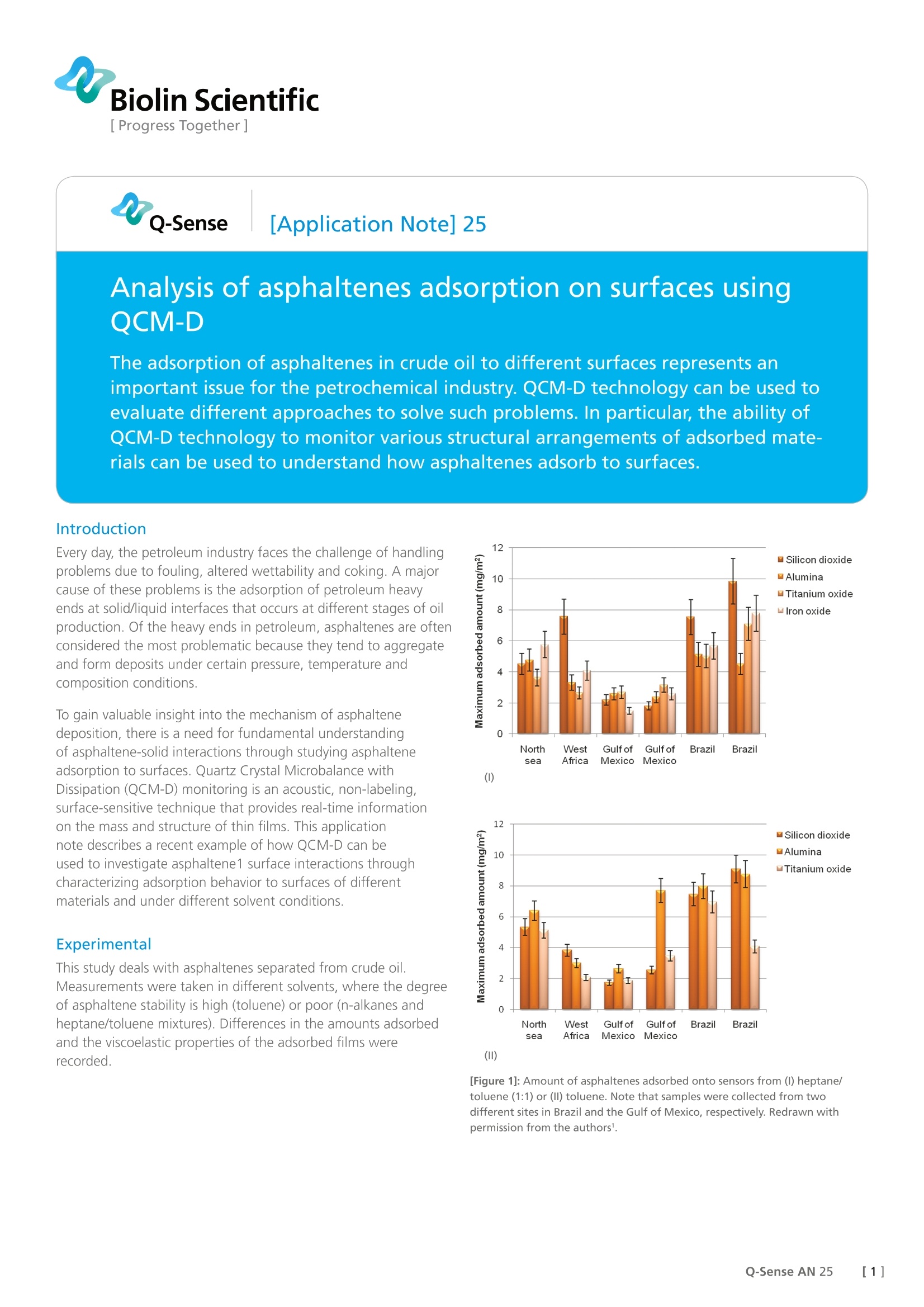
Biolin Scientific[ Progress Together] [Application Note] 25 Analysis of asphaltenes adsorption on surfaces usingQCM-D The adsorption of asphaltenes in crude oil to different surfaces represents animportant issue for the petrochemical industry. QCM-D technology can be used toevaluate different approaches to solve such problems. In particular, the ability of QCM-D technology to monitor various structural arrangements of adsorbed mate- rials can be used to understand how asphaltenes adsorb to surfaces. Every day, the petroleum industry faces the challenge of handlingproblems due to fouling, altered wettability and coking. A majorcause of these problems is the adsorption of petroleum heavyends at solid/liquid interfaces that occurs at different stages of oilproduction. Of the heavy ends in petroleum, asphaltenes are oftenconsidered the most problematic because they tend to aggregateand form deposits under certain pressure, temperature andcomposition conditions. To gain valuable insight into the mechanism of asphaltenedeposition, there is a need for fundamental understandingof asphaltene-solid interactions through studying asphalteneadsorption to surfaces. Quartz Crystal Microbalance withDissipation (QCM-D) monitoring is an acoustic, non-labeling,surface-sensitive technique that provides real-time informationon the mass and structure of thin films. This applicationnote describes a recent example of how QCM-D can beused to investigate asphaltene1 surface interactions throughcharacterizing adsorption behavior to surfaces of differentmaterials and under different solvent conditions. This study deals with asphaltenes separated from crude oil.Measurements were taken in different solvents, where the degreeof asphaltene stability is high (toluene) or poor (n-alkanes andheptane/toluene mixtures). Differences in the amounts adsorbedand the viscoelastic properties of the adsorbed films wererecorded. (1) () [Figure 1]: Amount of asphaltenes adsorbed onto sensors from (I) heptane/toluene (1:1) or (II) toluene. Note that samples were collected from twodifferent sites in Brazil and the Gulf of Mexico, respectively. Redrawn withpermission from the authors1. Results and discussion The adsorption of purified asphaltenes in heptane/toluene andtoluene onto four different hydrophilic surfaces (SiO,, alumina(Al,O), TiO, and FeO) was found to depend mainly on the originof the crude oils as well as on the solvent conditions. The maximum amounts adsorbed onto the different surfacesare shown in Figure 1. Note that samples with asphaltenesfrom oils from the same region of the world behaved similarly;in general, samples from Brazil displayed high adsorption to allsurfaces, whereas samples from the Gulf of Mexico displayedlow adsorption to all surfaces. It was also noted that most of theasphaltenes had the lowest adsorption to the TiO surface. In addition, the adsorbed layers of asphaltenes of differentorigins resulted in different dissipation shifts (not shown). Thisshift indicates that the adsorbed materials vary structurally. Forexample, asphaltene from Brazil yielded significantly higherdissipation shifts than asphaltene from the Gulf of Mexico,which could be explained by differences in solubilization states.Asphaltene from Brazil was beyond the flocculation point; theauthors suggested the structural model shown in Figure 2. Conclusions QCM-D enables real-time characterization of asphalteneadsorption onto different surfaces. The adsorbed amounts andcharacteristics of adsorption depend on the solubility state of theasphaltene as well as its origin. Furthermore, surface adsorptionvaries to a small extent between different hydrophilic sensorcoatings. Acknowledgements Prof. Johan Sjoblom and Dr. Dorota Dudasova, Department ofChemical Engineering, Norwegian University of Science andTechnology (NTNU), Trondheim are acknowledged for valuableinput during the preparation of this application note. ( R eferences: ) [1] Dudasova,D, Silset, A, and Sjoblom, J. Quartz Crystal Microbalance Moni-toring of Asphaltene Adsorption/Deposition, Journal of Dispersion Scienceand Technology 29, 139-146 (2008). []Q-Sense AN
关闭-
1/2
-
2/2

产品配置单
瑞典百欧林科技有限公司为您提供《沥青质中表面吸附检测方案 》,该方案主要用于沥青中表面吸附检测,参考标准《暂无》,《沥青质中表面吸附检测方案 》用到的仪器有QSense卓越版四通道石英晶体微天平、QSense Explorer扩展版石英晶体微天平、QSense全自动八通道石英晶体微天平。
我要纠错
相关方案





 咨询
咨询







