方案详情文
智能文字提取功能测试中
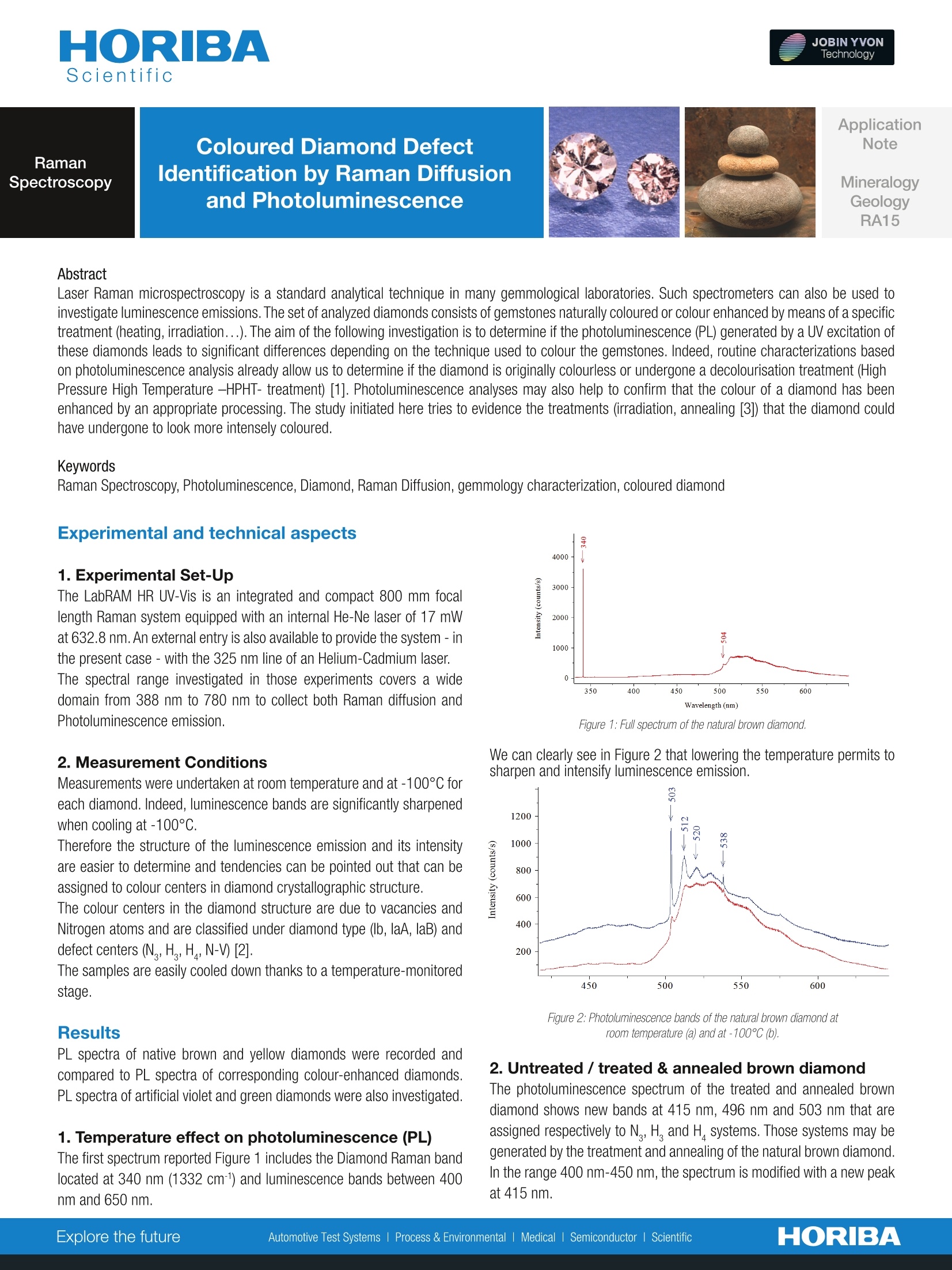
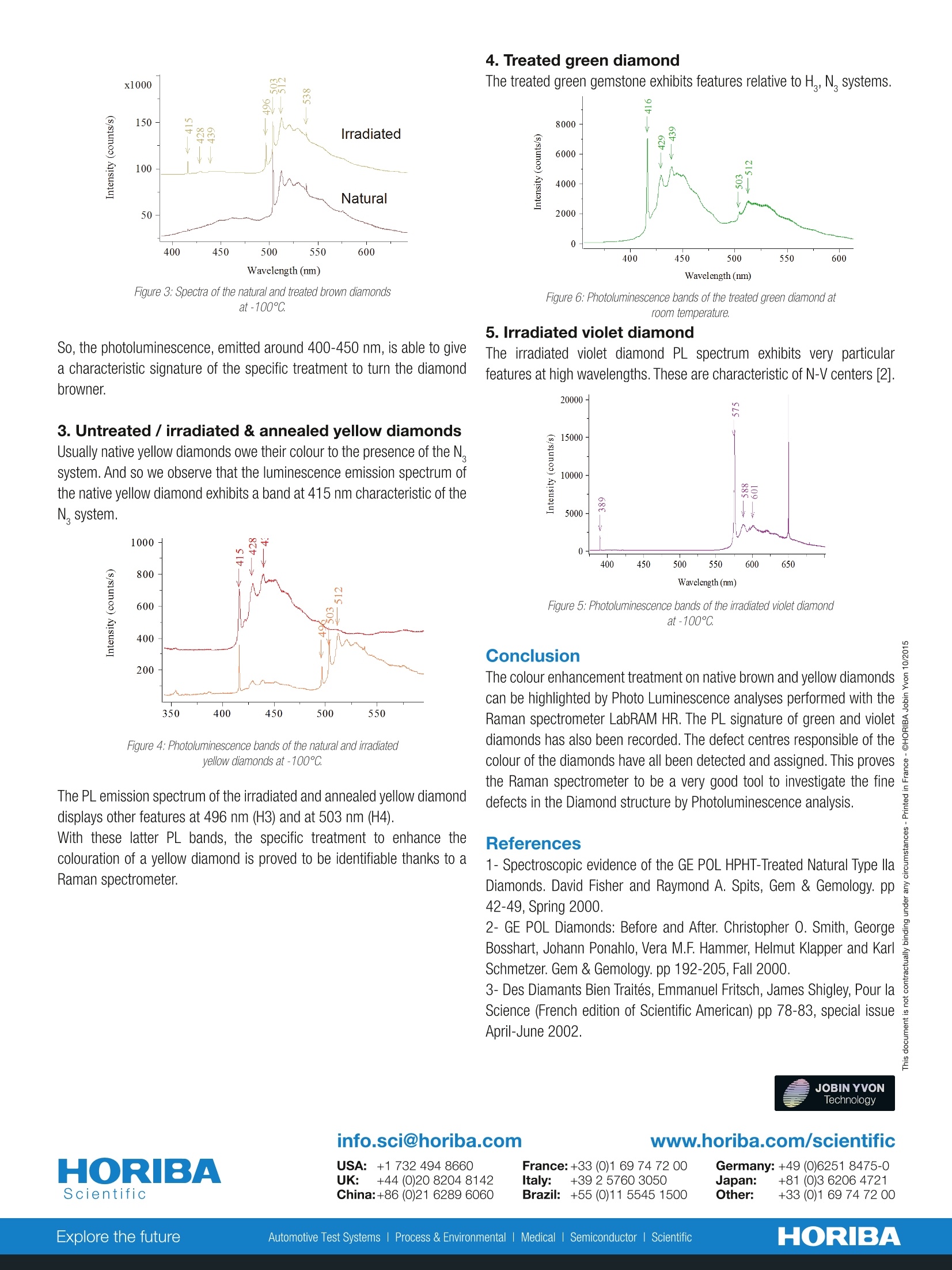
Application RamanSpectroscopy Coloured Diamond DefectIdentification by Raman Diffusionand Photoluminescence NoteMineralogyGeologyRA15 Abstract Laser Raman microspectroscopy is a standard analytical technique in many gemmological laboratories. Such spectrometers can ialso be unvestigatsed toe luminescence emissions. The set of analyzed diamonds consists of gemstones naturally coloured or colour enhanced by means of a specifictreatment (heating, irradiation...). The aim of the following investigation is to determine if the photoluminescence (PL) generated by a UV excitation ofthese diamonds leads to significant differences depending on the technique used to colour the gemstones. Indeed, routine characterizations basedon photoluminescence analysis already allow us to determine if the diamond is originally colourless or undergone a decolourisation treatment (HighPressure High Temperature -HPHT- treatment) [1]. Photoluminescence analyses may also help to confirm that the colour of a diamond has beenenhanced by an appropriate processing. The study initiated here tries to evidence the treatments (irradiation, annealing [3]) that the diamond couldhave undergone to look more intensely coloured. Keywords Raman Spectroscopy, Photoluminescence, Diamond, Raman Diffusion, gemmology characterization, coloured diamond Experimental and technical aspects 1. Experimental Set-Up The LabRAM HR UV-Vis is an integrated and compact 800 mm focallength Raman system equipped with an internal He-Ne laser of 17 mWat 632.8 nm. An external entry is also available to provide the system-inthe present case - with the 325 nm line of an Helium-Cadmium laser..The spectral range investigated in those experiments covers a widedomain from 388 nm to 780 nm to collect both Raman diffusion andPhotoluminescence emission. 2. Measurement Conditions Measurements were undertaken at room temperature and at -100℃ foreach diamond. Indeed, luminescence bands are significantly sharpenedwhen cooling at -100°℃. Therefore the structure of the luminescence emission and its intensityare easier to determine and tendencies can be pointed out that can beassigned to colour centers in diamond crystallographic structure. The colour centers in the diamond structure are due to vacancies andNitrogen atoms and are classified under diamond type (lb, laA, laB)anddefect centers (N,H,H,N-V)[2]. The samples are easily cooled down thanks to a temperature-monitoredstage. Results PL spectra of native brown and yellow diamonds were recorded andcompared to PL spectra of corresponding colour-enhanced diamondsPL spectra of artificial violet and green diamonds were also investigated. 1. Temperature effect on photoluminescence (PL) The first spectrum reported Figure 1 includes the Diamond Raman bandlocated at 340 nm (1332 cm) and luminescence bands between 400nm and 650 nm. Figure 1: Full spectrum of the natural brown diamond. We can clearly see in Figure 2 that lowering the temperature permits tosharpen and intensify luminescence emission. Figure 2: Photoluminescence bands of the natural brown diamond atroom temperature (a) and at-100℃ (b). 2. Untreated/treated & annealed brown diamond The photoluminescence spectrum of the treated and annealed browndiamond shows new bands at 415 nm, 496 nm and 503 nm that areassigned respectively to N, H, and H systems. Those systems may begenerated by the treatment and annealing of the natural brown diamond.In the range 400 nm-450 nm, the spectrum is modified with a new peakat 415nm. Figure3: Spectra of the natural and treated brown diamondsat-100℃ So, the photoluminescence, emitted around 400-450 nm, is able to givea characteristic signature of the specific treatment to turn the diamondbrowner. 3. Untreated /irradiated & annealed yellow diamonds Usually native yellow diamonds owe their colour to the presence of the N,system. And so we observe that the luminescence emission spectrum ofthe native yellow diamond exhibits a band at 415 nm characteristic of theN, system. Figure 4: Photoluminescence bands of the natural and irradiatedyellow diamonds at-100℃ The PL emission spectrum of the irradiated and annealed yellow diamonddisplays other features at 496 nm (H3) and at 503 nm (H4). With these latter PL bands, the specific treatment to enhance thecolouration of a yellow diamond is proved to be identifiable thanks to aRaman spectrometer. 4. Treated green diamond The treated green gemstone exhibits features relative to H,N, systems. Figure 6: Photoluminescence bands of the treated green diamond atroom temperature. 5. Irradiated violet diamond The irradiated violet diamond PL spectrum exhibits very particularfeatures at high wavelengths. These are characteristic of N-V centers [2]. Figure 5: Photoluminescence bands of the irradiated violet diamondat-100℃ Conclusion The colour enhancement treatment on native brown and yellow diamondscan be highlighted by Photo Luminescence analyses performed with theRaman spectrometer LabRAM HR. The PL signature of green and violetdiamonds has also been recorded. The defect centres responsible of thecolour of the diamonds have all been detected and assigned. This provesthe Raman spectrometer to be a very good tool to investigate the finedefects in the Diamond structure by Photoluminescence analysis. References 1-Spectroscopic evidence of the GE POL HPHT-Treated Natural Type llaDiamonds. David Fisher and Raymond A. Spits, Gem & Gemology. pp42-49, Spring 2000. 2- GE POL Diamonds: Before and After. Christopher 0. Smith, GeorgeBosshart, Johann Ponahlo, Vera M.F. Hammer, Helmut Klapper and KarlSchmetzer. Gem & Gemology. pp 192-205, Fall 2000. 3- Des Diamants Bien Traites, Emmanuel Fritsch, James Shigley, Pour laScience (French edition of Scientific American) pp 78-83, special issueApril-June 2002. ococO工O'cocEcdccccooco info.sci@horiba.com USA: +1732 494 8660 ·UK: +44 (0)20 82048142 www.horiba.com/scientific China:+86 (0)2162896060 France:+33 (0)1 69 74 72 00Germany: +49 (0)6251 8475-0Italy: +39257603050Japan: +81 (0)3 6206 4721Brazil: +55 (0)11 5545 1500Other: +33(0)1 69 74 72 00 HORIBAExplore the futureAutomotive Test SystemslProcess & EnvironmentaledicalSemiconductor Scientific 显微激光拉曼光谱仪是许多宝石实验室的标准分析仪器,它同时也是一台很好的光致发光分析系统。光致发光光谱可以用于表征钻石是否是天然的还是经过了脱色处理(高压高温HPHT-处理)或颜色增强处理(加热、辐射)。
关闭-
1/2
-
2/2
产品配置单
HORIBA(中国)为您提供《彩钻中天然还是人工处理检测方案(激光拉曼光谱)》,该方案主要用于文教办公品中天然还是人工处理检测,参考标准《暂无》,《彩钻中天然还是人工处理检测方案(激光拉曼光谱)》用到的仪器有HORIBA LabRAM Odyssey 高速高分辨显微共焦拉曼光谱仪。
我要纠错
推荐专场
相关方案






 咨询
咨询




