方案详情文
智能文字提取功能测试中
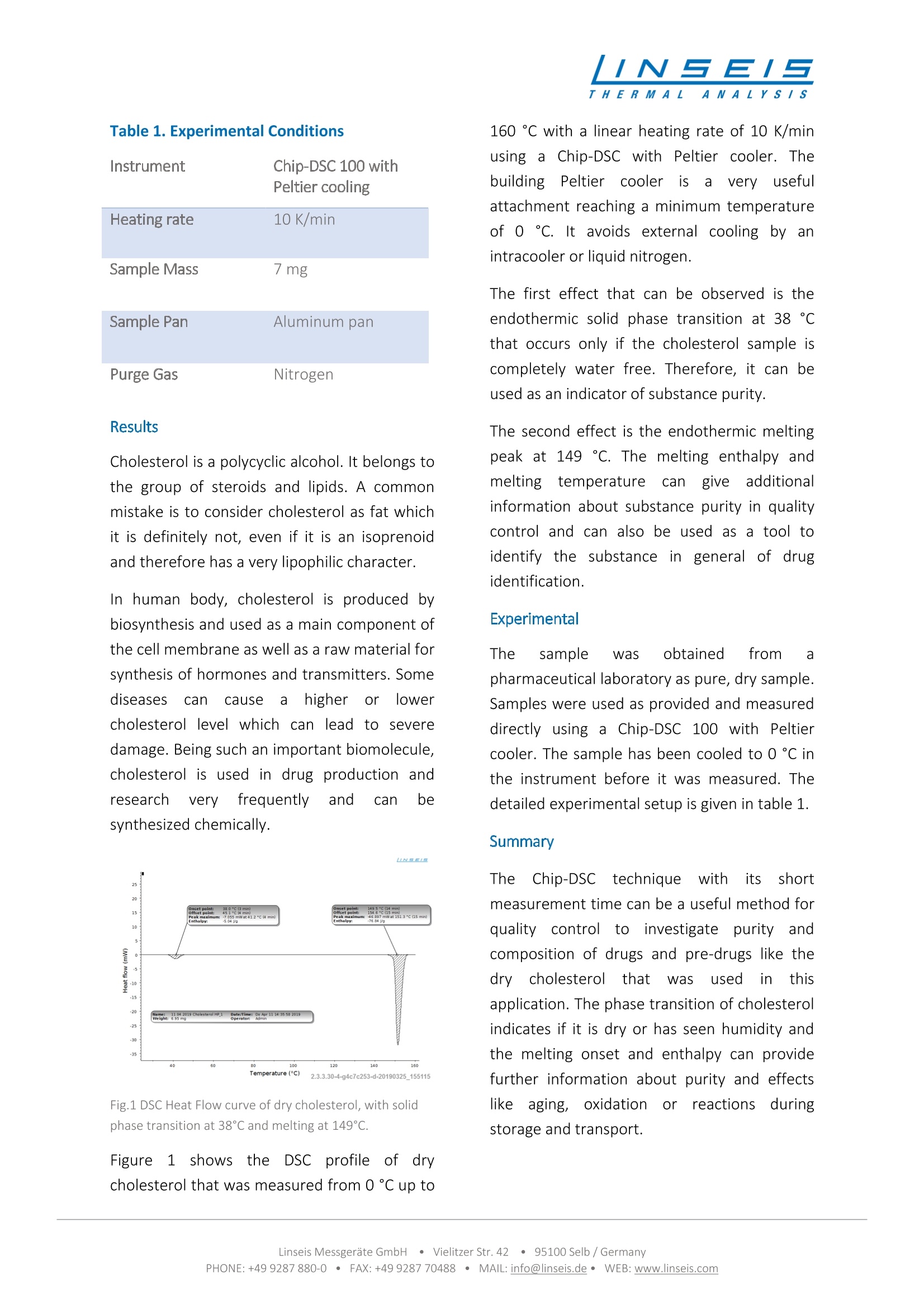
/INSEISTHERMAL A NALYS/S2019-05-06Application note No.11-003 /INSEISTHERMA L ANALYS/S Differential Scanning CalorimeterThermal analysis of Cholesterol Introduction The pharmaceutical industries develop tons of drugs and naturalproducts as therapeutics for various diseases. All these productsundergo a very strict quality control program and usually arecharacterized very well before they are used in any kind oftherapy. Among the characterization methods, there are also acouple of calorimetric experiments that can be very useful forquality control, solubility prediction or analysis of composition. Methods Using a DSC for analyzing pharmaceutical products is a more or less common technique. In thisapplication, the new Chip-DSC was used for measurements of dry cholesterol powder to checkmelting and phase transition behavior. This test is useful to control the substance purity before it isused for the preparation of tablets. The DSC signal in general is generated by heating a sample containing pan and an empty referencepan with the same heat source and subtracting the heat flow signals of the two pans from eachother, resulting in endothermic or exothermic peaks if the sample shows thermal effects. The Chip-DSC sensors integrates all essential parts of DSC in a small chip. The chip-arrangementcomprises the heater and temperature sensor in a chemically inert ceramic arrangement withmetallic heater and temperature sensor. Therefore, the Chip-DSC allows very fast heating andcooling rates combined with high resolution and accuracy as well as reproducibility. The result of a DSC measurement can be used as a fingerprint model for substance identification inquality control but can also be used to determine enthalpies of effects like phase transitions. Table 1. Experimental Conditions Peltier cooling Heating rate 10 K/min Sample Mass 7 mg Sample Pan Aluminum pan Purge Gas Nitrogen Results Cholesterol is a polycyclic alcohol. It belongs tothe group of steroids and lipids. A commonmistake is to consider cholesterol as fat whichit is definitely not, even if it is an isoprenoidand therefore has a very lipophilic character. In human body, cholesterol is produced bybiosynthesis and used as a main component ofthe cell membrane as well as a raw material forsynthesis of hormones and transmitters. Somediseases Can cause a higherr or lowercholesterol level which can lead to severedamage. Being such an important biomolecule,cholesterol is used in drug production andresearch verVyfrequently and can besynthesized chemically. Fig.1 DSC Heat Flow curve of dry cholesterol, with solidphase transition at 38℃ and melting at 149℃. Figure11 showsthee cDSC profile of drycholesterol that was measured from 0℃ up to 160℃ with a linear heating rate of 10 K/minusing a Chip-DSC with FPeltier cooler. Thebuilding Peltier cooleris a veryyUusefulattachment reaching a minimum temperatureof 0 C. It avoids external cooling by/canintracooler or liquid nitrogen. The first effect that can be observed is theendothermic solid phase transition at 38 ℃that occurs only if the cholesterol sample iscompletely water free. Therefore, it can beused as an indicator of substance purity. The second effect is the endothermic meltingpeak at 149 ℃. The melting enthalpy andmeltingtemperature can give additionalinformation about substance purity in qualitycontrol and can also be used as a tool toidentify the substance inlgenerall of drugidentification. Experimental The sample was obtained from apharmaceutical laboratory as pure, dry sampleSamples were used as provided and measureddirectly using a Chip-DSC 100 with Peltiercooler. The sample has been cooled to 0 C inthe instrument before it was measured. Thedetailed experimental setup is given in table 1. Summary TheetChip-DSC ttechniquewith its shortmeasurement time can be a useful method forquality controlto investigate purityandcomposition of drugs and pre-drugs like thedryy cCholesterol that was used in thisapplication. The phase transition of cholesterolindicates if it is dry or has seen humidity andthe melting onset and enthalpy can providefurther information about purity and effectslikee aaging, oxidationn Cor reactionssduringstorage and transport. Linseis Messgerate GmbH · Vielitzer Str. Selb/GermanyPHONE: + FAX: +MAIL: info@linseis.de·WEB: www.linseis.com 在制药行业中,所有产品都经过严格的质量控制,其中量热分析,对质量控制、溶解度预测或分析非常有用。 方法:在此应用中,采用Chip DSC测量干胆固醇粉末的熔化和相变行为,用于片剂制备前可用于控制物质纯度。测试条件:仪器: Chip-DSC 100(with Peltier cooling) 加热速率: 10 K/min样品质量: 7 mg样品盘: 铝吹扫气: 氮气所有样品都是从当地的食品供应商处获取。按规定使用样品,直接用带淬冷器的Chip-DSC进行测量,测试前所有样品均用液氮冷却至-60°C。测试结果:胆固醇是一种多环醇,属于甾类和脂类。在人体内,胆固醇通过生物合成产生,作为细胞膜的主要成分,也是合成激素和递质的原料。有些疾病会导致胆固醇水平升高或降低,从而导致严重的损害。在药物生产和研究中胆固醇应用非常广泛,并可用化学方法合成。上图为使用CHIP DSC 100得到的干胆固醇粉末DSC曲线,以10K/min的加热速率从0℃加热至160℃(使用帕尔贴冷却装置,达到0℃)如图,首先是38°C时的吸热固相转变,只有当胆固醇样品完全无水时才会发生。因此,可以作为样品纯度的指标。第二个反应是149°C时的吸热熔化峰,熔化焓和熔化温度可提供有关质量控制中物质纯度的附加信息,也可作为一般药物鉴定中鉴别物质的工具。样品是从制药实验室获得的纯干样品。按照规定使用样品,使用带珀尔帖冷却器的CHIP DSC 100直接测量。样品预先在仪器中冷却至0°C。具体可见【测试条件】。 总结:芯片差示扫描量热法(DSC)测量时间短,是一种有效的质量控制方法,用于研究该应用中使用的药物和前药(如干胆固醇)的纯度及成分。胆固醇的相变可表征湿度,而熔点及熔化焓进一步表征纯度及诸如储存和运输期间的老化、氧化或反应带来的影响。
关闭-
1/2

-
2/2
产品配置单
德国林赛斯热分析为您提供《干胆固醇粉末中样品纯度检测方案(差示扫描量热)》,该方案主要用于中药制剂中含量测定检测,参考标准《暂无》,《干胆固醇粉末中样品纯度检测方案(差示扫描量热)》用到的仪器有德国LINSESI 差示扫描量热仪Chip-DSC-10。
我要纠错
推荐专场
差示扫描量热仪(DSC/DTA)
更多相关方案






 咨询
咨询


