
方案摘要
方案下载| 应用领域 | 医疗/卫生 |
| 检测样本 | 其他 |
| 检测项目 | |
| 参考标准 | / |
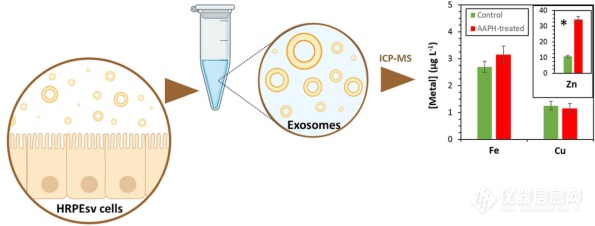
使用ICP-MS测定氧化应激条件下人视网膜色素上皮体外模型分泌的细胞外囊泡中的内源性微量元素
使用电感耦合等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS)测定体外人视网膜色素上皮细胞(HRPEsv 细胞系)模型分泌的外泌体(<200 nm 细胞外囊泡)中的内源性Fe、Cu和Zn。将经2,2'-偶氮二(2-甲基丙脒)二盐酸盐 (AAPH) 诱导氧化应激 (OS) 条件处理的细胞的结果与未处理(对照)细胞进行比较,以评估两组之间金属成分可能存在的差异。为进行ICP-MS分析,研究测试了三种样品导入系统:一种微型雾化器和两种单细胞雾化系统(作为总消耗装置),发现其中一种单细胞系统(以批量模式运行)最适合本项测试。本研究分别基于差速离心法和聚合物试剂沉淀法,研究了从细胞培养基中分离外泌体的两种方案。透射电子显微镜测量结果显示,与差速离心法相比,沉淀法纯化的外泌体尺寸更小、更均匀(差速离心法:20-180 nm,沉淀法纯化:15-50 nm),颗粒浓度更高。不过,与差速离心法相比,聚合物沉淀法会显著升高Fe, Cu和Zn的本底。考虑到HRPEsv细胞系外泌体中被评估的内源元素浓度较低,放弃了基于聚合物的沉淀方法。在比较对照组和经OS处理的HRPEsv细胞样本中的金属含量时,Fe和Cu的结果在统计学上较为相近。然而,在OS条件下,Zn含量上升(对照组11 μg L-1 ,OS处理组:34 μg L-1),这表明OS诱导的分泌活动会消耗Zn,这是RPE细胞抗氧化能力的基础。
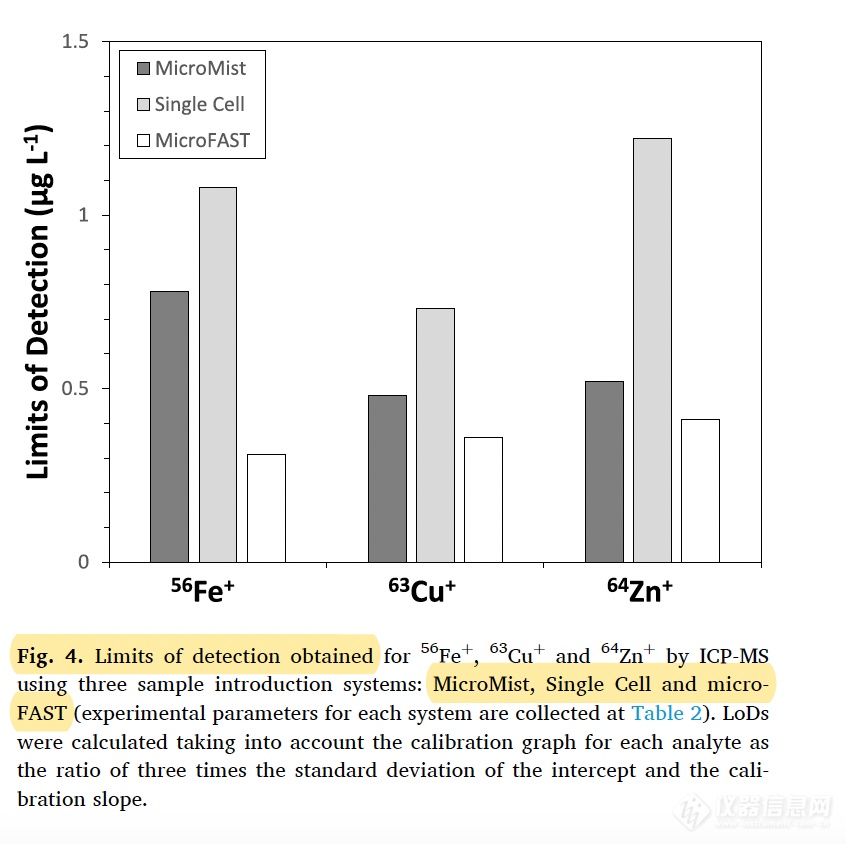
图4. 使用 MicroMist、Single Cell和microFAST三种进样系统时ICP-MS的56Fe+、63Cu+和64Zn+的检出限(实验参数见表2)。LoDs的计算考虑了每种分析物的校准图,即截距和校准斜率的三倍标准偏差之比。
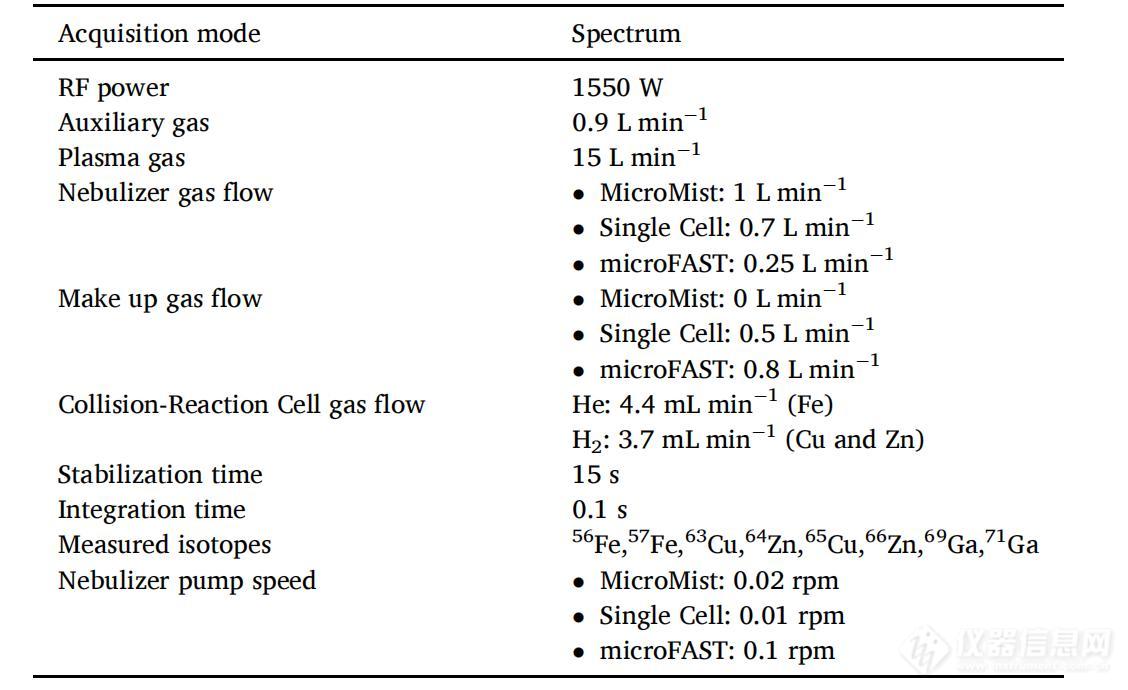
表2. 使用不同的进样系统(MicroMist DC雾化器、Glass Expansion公司的单细胞系统和 Elemental Scientific公司的microFAST单细胞系统)分析来自HRPEsv细胞培养基的外泌体中痕量元素的ICP-MS操作条件。
The determination of endogenous Fe, Cu and Zn in exosomes (<200 nm extracellular vesicles) secreted by an in vitro model of the human retinal pigment epithelium (HRPEsv cell line) was carried out by inductively coupled plasma - mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). Results for cells treated with 2,2′-azobis (2-methylpropionamidine) dihydrochloride (AAPH) inducing oxidative stress (OS) conditions were compared with non-treated (control) cells in order to evaluate possible differences in the metal composition between both groups. Three sample introduction systems were tested for ICP-MS analysis: a micronebulizer and two single cell nebulization systems (as total consumption set-ups), being found one of the single cell systems (operating in bulk mode) as the most suitable. Two protocols for the isolation of exosomes from cell culture media were investigated based on differential centrifugation and precipitation with a polymer-based reagent. Transmission electron microscopy measurements showed smaller and more homogeneous sizes (15–50 nm versus 20–180 nm size range) together with a higher particle concentration for exosomes purified by precipitation compared to differential centrifugation. However, it was observed that the contribution of polymer-based protocol to the Fe, Cu and Zn blank was significant as compared to the differential centrifugation protocol. Therefore, considering the low concentrations of the evaluated endogenous elements in exosomes from the HRPEsv cell line, the polymer-based precipitation method was discarded. When comparing metal levels in samples from control versus OS-treated HRPEsv cells, results for Fe and Cu were statistically similar. However, upregulation of Zn was found during OS conditions (11 versus 34 μg L−1 in control and OS-treatment, respectively), showing Zn depletion through secretory activity induced by OS, underlying the antioxidant ability of RPE cells.

MPx深海多金属结核成像
多功能集成色谱-电感耦合等离子体质谱(ICP-MS)法 快速测定饮用水中砷形态
适用于单个流体包裹体 LA-ICP-MS 分析的多元素流体包裹体标样合成及飞秒激光分析方法的建立
相关产品
上海凯来GenesisGEO新型飞秒激光剥蚀系统
ESLumen LIBS: LIBS & LA-ICP-MS 同步进行
ESLfemto 飞秒激光剥蚀系统
ESLimageGEO 激光剥蚀系统(地质成像)
ESL193HE 高能量准分子激光剥蚀系统
Artifact 双样品仓激光剥蚀系统(文博考古)
Vitesse飞行时间等离子体质谱仪(TOF-ICP-MS)
LaserTRAX 高通量全自动激光剥蚀系统
ESLimageBIO266 激光剥蚀系统(生物成像)
ESL213 灵活的激光剥蚀系统
MIR 102 激光熔融加热系统
MicroMill2 高精度微区取样仪
Iolite v4 多功能数据处理软件
prepFAST SE 超纯化学品自动加标系统(半导体应用)
prepFAST SF 超纯化学品全自动在线稀释系统 (半导体应用)

关注

拨打电话

留言咨询