leotron
第2楼2006/08/22
3.FMN
FMN (Flavin MonoNucleotide) is a prosthetic group of some flavoproteins. It is similar in structure to FAD (Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide), but lacking the adenine nucleotide.
When free in solution, FMN (like FAD) can accept 2 e- + 2 H+ to yield FMNH2. When bound at the active site of some enzymes, FMN can accept 1 e-, converting it to the half-reduced semiquinone radical. The semiquinone can accept a second e- to yield FMNH2
Role of FMN: Since it can accept/donate either 1 or 2 e-, FMN has an important role in mediating electron transfer between carriers that transfer 2 e- (e.g., NADH) and carriers that can only accept 1 e- (e.g., Fe+++). 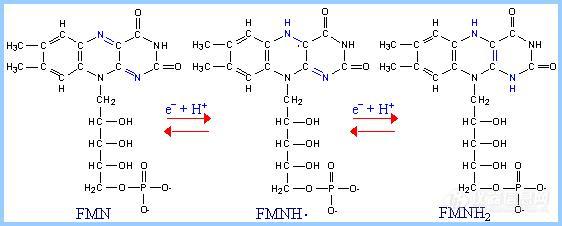
leotron
第3楼2006/08/22
4.FAD/FADH2
FAD (Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide) also functions as an electron acceptor. The portion of FAD that undergoes reduction/oxidation is the dimethylisoalloxazine ring, derived from the vitamin riboflavin.FAD is a prosthetic group, that usually remains tightly bound at the active site of an enzyme.
FAD normally accepts 2 e- and 2 H+ in going to its reduced state:
FAD + 2 e- + 2 H+ <-> FADH2 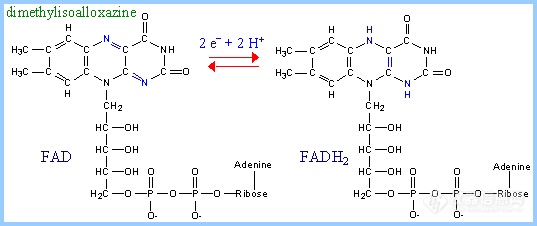
leotron
第4楼2006/08/22
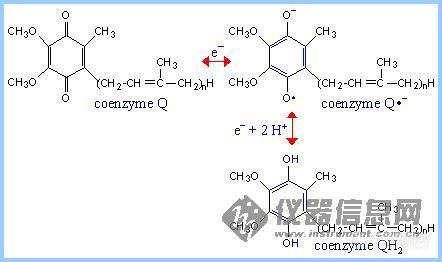
5.Coenzyme Q
Coenzyme Q (also called CoQ, Q or ubiquinone) is very hydrophobic. It dissolves in the hydrocarbon core of a membrane. The structure of CoQ includes a long isoprenoid tail, with multiple units having a carbon skeleton comparable to that of the compound isoprene. Most often the number of isoprene units (n) is 10. The isoprenoid tail of Q10 is longer than the width of a lipid bilayer, but may be folded to yield a more compact structure.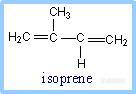
leotron
第5楼2006/08/22
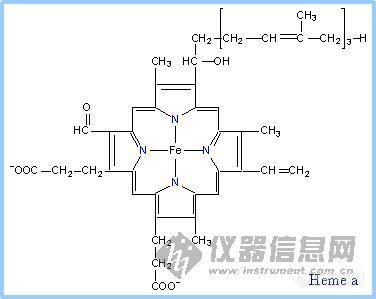
6.Heme
Heme is a prosthetic group of cytochromes. Heme contains an iron atom embedded in a porphyrin ring system, shown at right & below. The Fe is bonded to 4 N atoms of the porphyrin ring.
Hemes in the three classes of cytochrome (a, b, c) differ slightly in substituents on the porphyrin ring system .A common feature is two propionate side-chains.
Only heme c is covalently linked to the protein via thioether bonds to cysteine residues, as shown at right.
Heme a is unique in having a long farnesyl side-chain that includes three isoprenoid units.
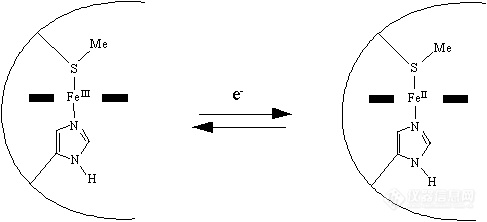
The heme iron atom can undergo a 1 e- transition between ferric and ferrous states:
Fe+++ + e- <-> Fe++ 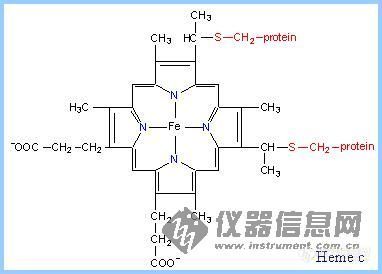

leotron
第6楼2006/08/22
7.Cytochromes
Cytochromes are proteins with heme prosthetic groups. They absorb light at characteristic wavelengths. Changes in light absorbance upon oxidation or reduction of the heme iron provide a basis for monitoring the redox state of the heme.
Some cytochromes are part of large integral membrane complexes, each consisting of several polypeptides and including multiple electron carriers.
Cytochrome c is instead a small, water-soluble protein, with a single heme group.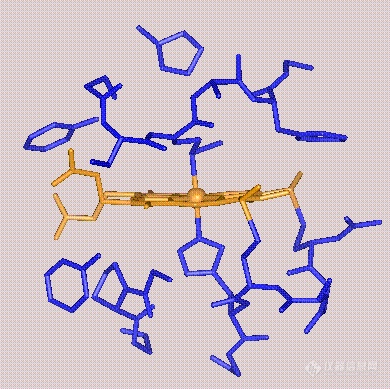
leotron
第7楼2006/08/22
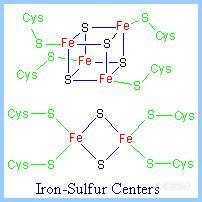
8.Iron-sulfur centers (Fe-S)
Iron-sulfur centers (Fe-S) are prosthetic groups containing 1 - 4 iron atoms, complexed to a combination of elemental sulfur and cysteine sulfur atoms. Electron transfer proteins may contain multiple iron-sulfur centers.
4-Fe centers have a tetrahedral structure, with Fe and S atoms alternating as vertices of a cube.
Iron-sulfur centers transfer only one electron even if they contain two or more iron atoms, because of the close proximity of the iron atoms.