


第1楼2005/12/30
麻省理工学院课件----Physical Methods in Inorganic Chemistry, Spring 2005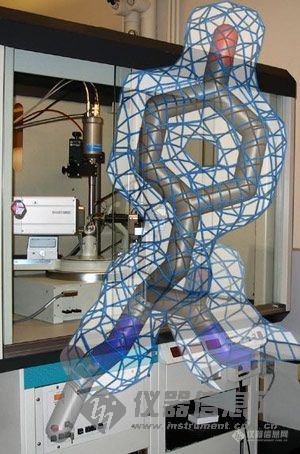
Physical Methods in Inorganic Chemistry, Spring 2005
Molecular model of the amino acid tyrosine with experimental electron density in front of an X-ray diffractometer at MIT. The tyrosine is part of the crystal structure of phosphoglycerate mutase from M. tuberculosis. See P. Mueller et al. (2005). Acta Cryst. D61, 309-315. (Figure and photograph by Dr. Peter Mueller. Used with permission.)
课程特点Highlights of this Course
This course features a selection of downloadable 讲义.
课程简介Course Description
This course covers the following topics: X-ray diffraction: symmetry, space groups, geometry of diffraction, structure factors, phase problem, direct methods, Patterson methods, electron density maps, structure refinement, how to grow good crystals, powder methods, limits of X-ray diffraction methods, and structure data bases.
Staff
Instructor:
Dr. Peter Mueller
Course Meeting Times
Lectures:
Eighteen sessions for 7 weeks
1 hour / session
Level
Graduate
Feedback
Send feedback about OCW or this course.
Introduction (PDF)
地址:下载
Overview, Textbooks, History of Crystallography
2 Symmetry in 2D (PDF)
地址:下载
Definition of Symmetry, Introduction of Symmetry Operators
Compatibility of Symmetry Operators with Translation
Combining Symmetry Operations and Determination of Plane Groups
3 Symmetry in 3D (PDF - 1.0 MB)
地址:下载
Extension of the Plane Groups Concept to the Third Dimension: Space Groups
Introduction of Screw Axes and Glide Planes
Point Groups v/s Space Groups
The Unit Cell and Crystallographic Conventions
4 X-rays and Matter (PDF)
地址:下载
X-ray Generation
Diffraction Experiment with Optical Grids and Laser Pointers
Convolution Theorem and Fourier Transformation
Introduction of Bragg's Law and Miller Indices
5 Geometry of Diffraction (PDF)
地址:下载
Reciprocal Space v/s Real Space
Ewald Construction as a Geometric Interpretation of Bragg's Law
6 Structure Factors
Real Atoms are no Point Atoms (Atomic Form Factors) and Show Thermal Motion (Atomic Displacement Factors)
Having More than One Atom per Unit Cell Leads to Structure Factors
Fourier Transformation Gives Rise to Electron Density; Crystallographic Resolution
7 Structure Factors II (PDF - 1.8 MB)
地址:下载
Complex Numbers, Euler's Equation and the Argand Plane
Introduction of the Phase Problem
8 Symmetry in Reciprocal Space (PDF)
地址:下载
Introduction of Friedel's Law and Laue Groups
Space Group Determination: |E2-1| Statistics, Systematic Absences, Crystallographic Directions for Triclinic, Monoclinic, Orthorhombic and Tetragonal Systems
Introduction of the Patterson Function and Harker Sections, as well as Direct Methods for Structure Solution
9 Structure Refinement (PDF)
地址:下载
Different Types of Electron Density Maps (Fo, Fc, Fo-Fc, etc.)
Introduction of Anisotropic Displacement Parameters
Minimization Functions: The Least-squares Approach and Different R-factors
Crystallographic Parameters, Constraints and Restraints
10 Structure Refinement II
Problems and Pitfalls: Wrong Space Group, Atom Type Assignment (All Electrons are Blue), Disorder, Twinning
What are Artifacts (Libration, C-C Triple Bonds, Fourier Truncation Ripples, etc.)?
Finding the Hydrogen Atoms, "Riding Model"
11 Anomalous Scattering (PDF)
地址: 下载
Absorption of X-ray Photons Leads to Loss of Symmetry in Orbital Geometry, Which Results in a Violation of Fridel's Law
12 Practical Aspects and Related Methods
Growing Crystals and Keeping Them Alive (Never Remove the Mother Liquor!)
Mounting Crystals onto the Diffractometer
Short Introduction of Powder Diffraction, Neutron Diffraction and EXAFS
Crystallographic Data Bases (ICSD, CSD, PDB, Reciprocal Net)
13 Quick Recap
Symmetry, Bragg's Law, Miller Indices, Real Space v/s Reciprocal Space, Ewald Construction, Structure Factors, Electron Density, Symmetry in Reciprocal Space, Laue Groups v/s Point Groups v/s Space Groups, Space Group Determination, Patterson Function, Structure Refinement, Parameters / Constraints / Restraints, Anisotropic Displacement Parameters, Libration, Hydrogen Atoms
14 Exam
You have 50 minutes to answer all questions. You can use pens, a calculator, ruler and compass, as well as a letter sized piece of paper with anything written on it. No books or other material is allowed.