

haypiny
第1楼2007/03/27
Background on Oxygen Demand Testing
Oxygen demand is an important parameter for determining the amount of organic pollution in water. The test has its widest application in measuring waste loadings of treatment plants and in evaluating the efficiency of treatment processes. Other applications include testing lake and stream water samples for organic pollution. Oxygen demand testing does not determine the concen-tration of a specific substance; rather, it measures the effect of a combination of substances and conditions. Because oxygen demand is not a pollutant, it poses no direct threat to fish or other life. It can, however, pose an indirect threat to living organisms by reducing the level of dissolved oxygen. There are three widely-used methods of measuring oxygen demand. Two measure oxygen demand directly: Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) and Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD). A third method—Total Organic Carbon (TOC)—measures oxygen demand indirectly.
需氧量测试相关背景
需氧量是测量水中有机物的含量的一个重要的参数。这一测试在测量处理厂的废物排放以及评价处理过程的效率上有它最广泛的应用。其它应用包括测定湖泊及河水样的有机污染。需氧量测试并不取决于某种特定物质的浓度。而是测量一种物质和相应条件下的综合的影响。因为需氧量本身并非一种污染,它没有对鱼及其它生命造成直接威胁。如能,只是通过减少溶解氧水平对有机生命造成间接威胁。有三种广泛用到的测需氧量的方法,两种直接法:生化需氧量(BOD)和化学需氧量(COD)
第三种方法-总有机碳(TOC)-间接测定需氧量
haypiny
第2楼2007/03/27
BOD Test
Of the three test methods that determine oxygen demand (BOD, COD and TOC), the BOD test most closely models aerobic waste treatment and the aquatic ecosystem. In this test, microorganisms consume organic compounds for food while consuming oxygen at the same time. The standard BOD test measures the amount of oxygen consumed in a sample over a five-day period. Due to the length of time required to complete the test, results provide historical data only and do not facilitate rapid water quality assessment or optimal process control. The test is limited in some applications such as industrial wastewaters, which often contain heavy metal ions, cyanides, and other substances toxic to microorganisms. When microorganisms become poisoned by toxicsubstances, they are unable to oxidize waste, in which case the BOD test becomes an ineffective measure of organic pollution.
BOD 测试
从测需氧量的三种方法(BOD, COD和TOC)来看, BOD测试是最接近废物处理和水生态系统的耗氧模式的。这一测试中微生物消耗有机物作食物同时耗氧。标准的测量需氧量测一个样要花费5天的时间,由于完成测试需要时间的长度结果只提供一个历史性的数据且不方便快速评定水质或优化处理控制。这一测定方法在一些对诸如工业排放废水的检测上的应用是受到限制的。它们当中通常含重金属离子,氰化物,以及其它一些对微生有机生物有毒害的物质。而微生有机物被毒物质毒害,它们不能氧化废水,这种情形下BOD的测定以检定有机污染变得无效。
haypiny
第3楼2007/03/27
TOC Test
The Total Organic Carbon (TOC) test uses heat, ultraviolet light, and a strong chemical oxidant (or a combination of these three) to oxidize organic compounds to CO2 and H2O. Oxygen demand is measured indirectly by determining the amount of CO2 produced using infrared spectroscopy, conductivity, or coulometry (an electrochemical technique). The test can take several minutes to several hours to complete, and information obtained from TOC analysis is less useful than information obtained from BOD and COD analysis. Also, the TOC test does not differentiate between compounds with the same number of carbon atoms in different stages of oxidation and will thus produce different oxygen demand results. Because BOD and COD tests directly measure the amount of oxygen required to stabilize a waste sample, results reflect the original oxidation state of the chemical pollutants. This is demonstrated using the following example, where two compounds with the same number of carbon atoms in different oxidation states are oxidized to CO2 and H2O.
Oxalic Acid: C2H2O4 + 1/2 O2——> 2 CO2 + H2O
Ethanol: C2 H6O + 3 O2——> 2 CO2 + 3 H2O
While TOC results are identical for both compounds, the oxygen demand of ethanol is six times greater than oxalic acid, and will thus have a much greater effect on the dissolved oxygen content of a receiving water.
TOC 检测
总有机碳(TOC)检测用加热,紫外光,和强化学氧化剂(或这三种措施的混合)去氧化有机化合物转成二氧化碳和水,通过用红外光度法,电导法,或比色法(一种电化学技术)检测生成二氧化碳的量间接地测定需氧量。完成测定需几分到几小时,并且从TOC分析获得的信息不如从BOD和COD分析检测到的数据有用,且TOC不能区分含不同氧化态又数目相同的碳原子的化合物而依此产生不同的需氧量结果,因为BOD和COD直接测定稳定氧化一个废水样所需要的氧量,结果反映化学污物的初始氧化状态。这是可用如下的一个例子来说明的,这里两种化合物含有处于不同氧化态相同数目的碳原子被氧化成CO2 和H2O。
草酸:
C2H2O4 + 1/2 O2—> 2 CO2 + H2O
乙醇:
C2 H6O + 3 O2—> 2 CO2 + 3 H2O
两种化合物的TOC没有区别,而乙醇的耗氧是草酸耗氧的六倍,这对水样的溶氧量是有很大影响的。
haypiny
第4楼2007/03/27
Test COD
The Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) test uses a strong chemical oxidant in an acid solution and heat to oxidize organic carbon to CO2 and H2O. By definition, chemical oxygen demand is “a measure of the oxygen equivalent of the organic matter content of a sample that is susceptible to oxidation by a strong chemical oxidant.”* Oxygen demand is determined by measuring the amount of oxidant consumed using titrimetric or photometric methods. The test is not adversely affected by toxic substances, and test data is available in 1-1/2 to 3 hours, providing faster water quality assessment and process control.COD test results can also be used to estimate the BOD results on a given sample. An empirical relationship exists between BOD, COD and TOC. However, the specific relationship must be established for each sample. Once correlation has been established, the test is useful for monitoring and control. Table 1 compares the attributes of BOD, COD and TOC tests. Table 1:
Parameter COD BOD TOC
Oxidant Used K2Cr2O7 Oxidation by microorganisms • O2
Mn2 (SO4)3 • K2 S2O8
• Heat
• Combination of the above with various catalysts
Most Rapid and frequent monitoring
Modeling treatment plant
Measures amount of total
Suitable Use of treatment plant efficiency process and the effects of organic carbon in samples and water quality organic compounds on the dissolved oxygen content of
receiving waters
Test Completion 1-1/2 to 3 hours 5 days (for standard BOD test) Several minutes to hours Time
Accuracy and 5 - 10% relative standard 15% relative standard 5 - 10% relative standard
Precision deviation; may be higher when deviation; not considered deviation; may be higher when samples contain suspended highly accurate samples contain suspended solids; sample homogenization solids; sample homogenization
can be important can be important
Advantages • Correlates with BOD • Most closely models the • Correlates with BOD on
on waste with constant natural environment when waste with constantcomposition.
used with the proper “seed” composition, but not as
• Toxic materials do not closely as COD
affect oxidant. • Short analysis time
• Changes in the COD value between influent and
effluent may parallel BOD content and supplement BOD results
• Short analysis time
COD检测
化学需氧量(COD)检测用一强氧化剂在酸液中加热条件下将有机碳氧化成CO2和H2O。严格定义,化学需氧量就是“用一种强氧化剂去测定含有易氧化有机物的样品所等价的氧的检测方法。”通过用滴定或比色方法测量氧化剂的消耗以测定需氧量。毒物质对这一测定没有不利影响,1.5到3小时可以得到测定数据。提供稍快的水质评定结果和处理控制。COD测定结果也用于估计给定水样的BOD 结果。BOD,COD和TOC之间存在一个经验关系。但是这一特定关系须对每一样品建立。关系一旦确立,测定对监控是有用的。表1比较了BOD,COD和TOC测定的特征.
参数 COD BOD TOC
所用氧化剂:重铬酸钾;
微生物氧化;
氧气,硫酸锰,过硫酸钾,加热,上面的混合加不同催化剂。
最快速和有效的监视;
模拟处理工厂;
测定总量。
适用处理厂的有效处理和分析有机碳对水质的影响以及有机化合物对收集水样含氧的影响。
1.5到3小时完成;5天(标准BOD测试);几分钟至几小时。
准确5-10%的相对标准偏差;15%; 5-10%。
精密偏差;可能高的偏差;可不计偏差;可能高当样品中悬浮物高精密当样含悬浮固体;
样品均化固体;样品的均化很重要;很重要。
优点 与BOD相关;最靠近实际模式; 与BOD相关当废水所处的自然环境及组成成分恒定时。
同样标样也要有同样的组成。
有毒物不如COD那样影响氧化
分析周期短
流入口和流出口COD值的变化可能与BOD平行也可能只是BOD的一部分。
用时短。
haypiny
第5楼2007/03/27
Disadvantages • Interference from chloride •
Toxic materials kill • Requires expensive
ions microorganisms equipment• Some organic compounds • Microorganisms do not • Some organic compoundsare not oxidized completely oxidize all materials present are not oxidized completely
in waste • Measures Total Organic
• Inaccuracies when used Carbon and not oxygen
with improper “seed” demand
• Lengthy test period
不足处 受氯离子干扰;
有毒物杀死微生物;需贵重离子微生物装配一些有机化合物,微生物不氧化;废样中一些有机化合物没有完全氧化所有存在的物质没完全氧化;测量总的有机物
当用不正确的“种子”时结果会不精确。
分析时间长
haypiny
第6楼2007/03/27
Oxidants Used for COD Testing
Analysts have attempted to use many different oxidants
in the COD test procedure. Hach laboratories have
experimented with permanganate (in both acidic and
basic solutions), cerate, persulfate, periodate, iodate,
bromate, perbromate, hypochlorite, perchlorate, ferrate,
bismuthate, hydrogen peroxide, ozone, oxygen,
hydroxyl radical, vanadate, ultraviolet light, bomb
colorimetry, combinations of several oxidants and
electrochemical techniques. These approaches have not
been suitable due to difficulties in reagent preparation,
reagent stability, photosensitivity, low oxidation
potential, poor oxidation efficiency, expense, and user
protocols that proved too complex.
Several oxidants, however, have proven to overcome
most of these difficulties. The most widely used oxidant
is potassium dichromate and more recently manganese
III sulfate. Table 2 summarizes the attributes of oxidants
not widely used for COD testing.
COD测试用到的氧化剂
在测试COD手续上分析工作者们已试用了多种不同的氧化剂。哈希实验室就试验过高锰酸盐(酸性及碱性溶液中),铈盐,过硫酸盐,过碘酸盐,碘酸盐,高铁酸盐,溴酸盐,过溴酸盐,过氧化氢,臭氧,氧,羟基,钒酸盐,紫外光,氧化弹,比色计,数种氧化剂与电化学技术的结合,这些方法已不适用,由于试剂难于制备,试剂稳定性,光敏感,低氧化电位,低氧化率,昂贵,用户证实太复杂方面的问题。然而,几种氧化剂,已证明克服了这些难点。最广泛用到的就是重铬酸钾及最近用到的硫酸锰,表2列举了这些没有广泛用于COD测试的氧化剂的特点。
haypiny
第7楼2007/03/27
II. DICHROMATE CHEMICAL、
OXYGEN DEMAND
Dichromate has been used to oxidize organic matter for
more than 70 years. It has been preferred over other
oxidants because of its superior oxidizing ability on a
large variety of samples, and for its ease of use. The test
measures the oxygen equivalent of the amount of organic
matter oxidized by potassium dichromate in a 50%
sulfuric acid solution. Generally, a silver compound is
added as a catalyst to promote the oxidation of certain
classes of organic compounds. A mercuric compound
may be added to reduce the interference from oxidation
of chloride ions.
There are two digestion methods used in the COD test:
the older Macro Digestion Method, and the Micro Digestion Method. The Macro Digestion Method requiresa considerable amount of space, equipment and volume
of reagents for each test. Each set-up includes a flask, a glass condenser with hose, a hot plate, a laboratory stand,and clamps. Sample volumes are also relatively large.Because of these inconveniences, the macro method hasbeen virtually replaced by the micro method. The MicroDigestion Method minimizes reagent consumption and
reduces the required space and equipment to one reactor block that will digest up to 25 samples at one
time. Each test set-up is a self-contained disposable vial,
which is inserted into a block heater. Reagent and
sample volumes are considerably smaller, which
decreases reagent cost and waste volume.
The two-hour digestion time can be reduced if caution is
observed. Many types of waste are digested completely
in 30 minutes or less at 150 °C, the normal operating
temperature. The time of complete digestion can be
recognized through experience, or by using a colorimetric
reading with the micro method discussed later. In this
approach, many consecutive readings are taken on a
single sample, allowing a final determination of when
the reaction is complete.
After the oxidation step is completed, the amount of dichromate consumed is determined titrimetrically or colorimetrically. Either the amount of reduced chromium (trivalent) or the amount of unreacted dichromate(hexavalent) can be measured. Endproducts of the reaction are carbon dioxide, water, and various states of the chromium ion.
II 重铬酸盐化学需氧量
重铬酸盐用于氧化有机物质已超过70年。它被证明对多种样品它是优于其它氧化剂的因为其本身的强氧化性能,且还因为它易于使用。这种方法一般是测定在50%的硫酸中用重铬酸钾氧化有机物所等价的氧量。通常用到一种银盐作催化剂以加速对不同形式的有机物的氧化。一种汞盐也被加入以减少氯离子的干扰。
COD测定用到两种消解方法:老的大型消解法,以及微量消解法。大量消解法需要一个大的空间,设备和大量试剂以完成每一次的测定,每一套包括一个烧瓶,一玻璃带软管的冷凝管,一电热板,一铁架台,一铁夹。取样量也相对地大。因为有这一些不方便因素,大量消解的方法实质上已被微量法取代。微量消解法减少了试剂的消耗,而且减少了所需空间和设备,一个反应器块能一次消解25个样品,每次检测包括一单独任意使用的小瓶子,它被插入到加热块,试剂和取样量都相当少,这减少了试剂费用及污水排放量。两小时的消解时间仔细考察后是可减少的。许多样在不到150 °C 的情况下不到30分钟就能完全消解,这是一个通常操作温度,完全消解样品的时间是能通过实验验证的,或用比色计用下述方法验证。这一方法中单个样连续读数被记录直到检测到反应已到终点。氧化步骤完成后,消耗的重铬酸盐的量由滴定或比色测出。还原生成的三价铬的量或未反应的重铬酸钾的量能被测出。最终产物是二氧化碳和水,及处于不同价态的铬离子
haypiny
第8楼2007/03/27
5r7 aOxidant Advantages Disadvantages
KMnO4 • Stable for several months, MnO2 must be excluded • Relatively slow-acting and is not quantitative• Is used in acidic, neutral and basic media • Results may depend upon sample size• Manganese is a non-hazardous metal • Does not oxidize volatile acids or amino acids• Incomplete oxidation of many organic compounds• Unstable in solution: Forms MnO2 precipitate which catalyzes reagent decomposition. Ce(SO4)2 • More complete oxidation of organic compounds • Incomplete oxidation of many organic compounds than KMnO4 • Poor reproducibility• More stable than KMnO4 • Photometric measurement at 320nm where incompletely oxidized organic compounds interfere• Relatively expensive K2S2O8 • Oxidizes many organic
nitrogen-containing • Requires elaborate equipment
compounds more completely than other oxidants • More labor intensive
• Widely used with TOC instrumentation • Relatively unstable
KIO3 • Strong oxidant • Difficult to use
• Questionable accuracy
O2 • Oxygen consumption measured directly • Elaborate equipment required
The oxidants described in Table 2 have a number of limitations which are eliminated when K2Cr2O7 are used as an oxidant.
6
The micro method has several advantages over the macro
method, including the capture of volatile organics, small
sample size, elimination of cumbersome equipment,
and a reduction in the volume of expensive and hazardous
reagents.
5氧化剂优缺点
高锰酸钾:稳定数月,但须除去二氧化锰。反应慢不定量,被用于酸性,中性及碱性介质中;结果依赖于样品的种类操作中无有害金属,不能氧化挥发性酸或氨基酸;不能完全地氧化许多种有机化合物;在溶液中不稳定:形成二氧化锰沉淀能催化试剂的分解。硫酸铈:比较完全地氧化有机物;不能象高锰酸钾完全氧化许多有机物;重现性差;比高锰酸钾稳定;320nm分光检测没完全氧化的有机物存在干扰;相对昂贵。过硫酸钾:氧化许多含有氮元素的有机物;需要精密设备;化合物较其它氧化剂更完全地被氧化;较大的劳动强度。
广泛地用于TOC的仪器测量中;相对不稳定
碘酸钾:强氧化剂;难于使用;精度可疑,
氧气:直接测量消耗的氧;需精心制作的相关设备;表2中所列氧化剂的种种局限在用重铬酸钾作为氧化剂后被消除了,
6
微量法相对大量法有诸多优点包括获取挥发性的有机物,小的取样量,无需笨重的设备,且减少了贵重及有害试剂的使用。
haypiny
第9楼2007/03/27
Dichromate COD Chemistry
When organic matter is oxidized by dichromate in sulfuric
acid, most of the carbon is converted to CO2. Hydrogen
present is converted to H2O. The reaction is illustrated
using the primary standard, potassium acid phthalate
(KHP), as an example:
2 KC8H5O4 + 10 K2Cr2O7 + 41 H2SO4——>
16 CO2 + 46 H2 O + 10 Cr2 (SO4)3 + 11 K2 SO4
Dichromate ions (Cr2O72-) form orange-colored solutions.When dichromate is reduced to chromic ion
(Cr3+), the solution becomes green. Intermediate valence states may also occur. The standard reduction potential, E° (25 °C vs.Normal Hydrogen Electrode, pH = 0) is about 1.36 volts.The actual potential will vary with temperature, pH, and the ratio of dichromate to chromic ion concentrations according to the following equation: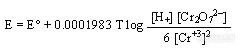
Precision and Accuracy
A number of samples have been tested using Hach’s High
Range, Low Range, and Ultra Low Range Dichromate
COD vials. Results are given in Table 3 below.
重铬酸钾化学
当有机物在硫酸中被重铬酸盐氧化时,绝大多数的碳转化为二氧化碳。而当中的氢被转化为水。反应可以用邻苯二甲酸氢钾这一基准物质作为一个例子来说明:
2 KC8H5O4 + 10 K2Cr2O7 +41H2SO4—>
16 CO2 + 46 H2 O + 10 Cr2 (SO4)3 + 11 K2 SO4
重铬酸根离子(Cr2O72-)形成橙色溶液,当重铬酸根被还原成三价铬(Cr3+),溶液变绿,中间价态的铬也可能生成。标准还原电位,E0(25度,普通氢电极为参比,pH=0)大约为1.36伏。实际电位随温度,pH及重铬酸根离子转成三价铬的浓度而变化。可由下式表达:

精密度与准确度
大量的样品都用哈希的高范,
低范围,及超低范围重铬酸钾小瓶测试过.结果见下表3.
haypiny
第10楼2007/03/27
Pros and Cons of Dichromate
Pros
O Dichromate accomplishes a complete oxidation when
used with a catalyst and a two-hour digestion period.
O Dichromate is stable at room temperature when protected from exposure to light.
Cons
O Some organic compounds are only partially oxidized.
O Some organic compounds, such as pyridine, are not oxidized.
O There can be interference from inorganic pollutants,mainly chloride ions.
O Reaction temperature is limited by thermal decomposition of the oxidant.
O Dichromate is classified as a carcinogen.
Improving the Dichromate COD Test
Through careful research, many of the disadvantages to the COD test have been overcome or reduced in significance.
Incomplete oxidation of aliphatic hydrocarbons,organic acids or alcohols have been improved by using silver ion as a catalyst. Some compounds are not oxidized even with the catalyst. Disposal considerations play an increasingly important role in chemical testing. Although the micro method minimizes the volume of waste generated, the dichromate COD does contain hexavalent chromium, which must be treated as hazardous wastes and mercury.
重铬酸盐法正反面
正面O用重铬酸盐法能达到完全氧化在用一种催化剂且两个小时的时间时。
O室温且避光时重铬酸盐是稳定的。
反面
O一些有机物只部分地被氧化
O有些有机物,如嘧啶,不被氧化。
O会被主要是氯离子一类的无机污染物干扰。
O反应温度因氧化剂的热分解而受到限制。
O重铬酸盐为致癌类物质。
重铬酸盐法测COD的改进
通过仔细地研究,COD测试中的许多不足被克服或有了相当意义上的减少。对于脂肪族碳氢化合物的不完全氧化,在用银离子作催化剂有机酸和乙醇已有相当的改善。废液处理在化学测试中的重要性有所增加,尽管微量方法减少产生废液的量,但是重铬酸盐法测COD还是含有六价铬,它必须像对有害废液和汞一样进行处理。